Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
H 2 O
... The Warburg Effect • In oncology, the Warburg effect is that most cancer cells predominantly produce energy by a high rate of glycolysis followed by lactic acid fermentation in the cytosol, rather than by a comparatively low rate of glycolysis followed by oxidation of pyruvate in mitochondria like ...
... The Warburg Effect • In oncology, the Warburg effect is that most cancer cells predominantly produce energy by a high rate of glycolysis followed by lactic acid fermentation in the cytosol, rather than by a comparatively low rate of glycolysis followed by oxidation of pyruvate in mitochondria like ...
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Citric Acid Cycle
... Formation of Acetyl CoA Acetyl CoA is a metabolic intermediate that can be produced from amino acids, glucose (via pyruvate), and fatty acids ...
... Formation of Acetyl CoA Acetyl CoA is a metabolic intermediate that can be produced from amino acids, glucose (via pyruvate), and fatty acids ...
4)qualitative_tests_for_amino_acids
... -The reaction is also given by primary amines and ammonia but without the liberation of Co 2 -The amino acids proline and hydroxyproline also reacts but produce a yellow color. Method: 1 ml AA + 1 ml NH---- heat in boiling WB for 5min-----Purple color. ...
... -The reaction is also given by primary amines and ammonia but without the liberation of Co 2 -The amino acids proline and hydroxyproline also reacts but produce a yellow color. Method: 1 ml AA + 1 ml NH---- heat in boiling WB for 5min-----Purple color. ...
the PDF
... Enzymes Enzymes are proteins. They are important natural substances in the bodies of all living things. Enzymes are natural catalysts and without them, the biochemical reactions which happen in all living things would not take place. All enzymes are totally protein in their structure but some need a ...
... Enzymes Enzymes are proteins. They are important natural substances in the bodies of all living things. Enzymes are natural catalysts and without them, the biochemical reactions which happen in all living things would not take place. All enzymes are totally protein in their structure but some need a ...
Chapter 34 HEIN
... is termed glycolysis. • What glycolysis does for the cell can be summarized with the following net chemical equation: C6H12O6 + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2CH3CH(OH)COO- + 2 ATP + 150 kJ ...
... is termed glycolysis. • What glycolysis does for the cell can be summarized with the following net chemical equation: C6H12O6 + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2CH3CH(OH)COO- + 2 ATP + 150 kJ ...
KIEBER, ROBERT J., LINDA H. HYDRO, AND PAMELA J. SEATON
... synthetic product was also similar to the S13Cvalues of natural marine fulvic acids (Harvey and Boran 1985). The authors proposed a mechanism that involves free radical autooxidative cross-linking of unsaturated fatty acid chains of ...
... synthetic product was also similar to the S13Cvalues of natural marine fulvic acids (Harvey and Boran 1985). The authors proposed a mechanism that involves free radical autooxidative cross-linking of unsaturated fatty acid chains of ...
High Alcohol Fermentations: How to Manage Primary and
... Minimize the production of volatile acidity Minimize volatile sulfur off-aromas Balance % alcohol with phenolic maturity Complete the malo-lactic conversion in a timely manner • Minimize microbial deviations ...
... Minimize the production of volatile acidity Minimize volatile sulfur off-aromas Balance % alcohol with phenolic maturity Complete the malo-lactic conversion in a timely manner • Minimize microbial deviations ...
Citrate synthase
... Cycle. Citrate synthase is localized within eukaryotic cells in the mitochondrial matrix, but is encoded by nuclear DNA rather than mitochondrial. It is synthesized using cytoplasmic ribosomes, then transported into the mitochondrial matrix. Citrate synthase is commonly used as a quantitative enzyme ...
... Cycle. Citrate synthase is localized within eukaryotic cells in the mitochondrial matrix, but is encoded by nuclear DNA rather than mitochondrial. It is synthesized using cytoplasmic ribosomes, then transported into the mitochondrial matrix. Citrate synthase is commonly used as a quantitative enzyme ...
Lecture 4 - IISER Pune
... - amino acids and other complex molecules associated with life were present - 7–9% excess of four L-amino acids present - ElectromagneOc radiaOon emiIed in a corkscrew fashion from the poles of spinning neutron stars could lead to a bias of one mirror-image isomer over another when molecule ...
... - amino acids and other complex molecules associated with life were present - 7–9% excess of four L-amino acids present - ElectromagneOc radiaOon emiIed in a corkscrew fashion from the poles of spinning neutron stars could lead to a bias of one mirror-image isomer over another when molecule ...
Lecture 17/18 - Aerobic and Anaerobic Metabolism
... 7.) Explain how the concentrations of ATP, AMP, Acetyl CoA, and Citrate may all play into the regulation of PFK. 8.) What occurs at step 4? What occurs at step 5? What occurs at step 6? 9.) What specific type of phosphorylation occurs during glycolysis? Which steps does this reaction occur at? Expla ...
... 7.) Explain how the concentrations of ATP, AMP, Acetyl CoA, and Citrate may all play into the regulation of PFK. 8.) What occurs at step 4? What occurs at step 5? What occurs at step 6? 9.) What specific type of phosphorylation occurs during glycolysis? Which steps does this reaction occur at? Expla ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
Lecture 26
... Activated by AMP and ADP Inhibited by NADH and NADPH Competitively bind to the NAD+ binding site. Requires Mn2+ or Mg2+ cofactor. Mechanistically-oxidize to the b-keto acid. 2 forms of the enzyme Mitochondrial form is NAD+ dependant [ADP] E. coli, mitochondrial, cytoplasmic forms NADP+ ...
... Activated by AMP and ADP Inhibited by NADH and NADPH Competitively bind to the NAD+ binding site. Requires Mn2+ or Mg2+ cofactor. Mechanistically-oxidize to the b-keto acid. 2 forms of the enzyme Mitochondrial form is NAD+ dependant [ADP] E. coli, mitochondrial, cytoplasmic forms NADP+ ...
CHAPTER 19 LIPID METABOLISM Introduction: Fats are much more
... Note that reactions 4, 5 and 6 are the counterparts of beta oxidation. Reactions 1 3 involve the enzyme activities of the acyl carrier protein (ACP) and condensing enzyme (CE). The incoming malonyl CoA groups are transferred to ACP, which contains a phosphopanteine group identical to that of CoA (s ...
... Note that reactions 4, 5 and 6 are the counterparts of beta oxidation. Reactions 1 3 involve the enzyme activities of the acyl carrier protein (ACP) and condensing enzyme (CE). The incoming malonyl CoA groups are transferred to ACP, which contains a phosphopanteine group identical to that of CoA (s ...
II. Acids and Bases
... 11. In the example above, the acid (HX) becomes a base because it can now accept a positive hydrogen ion. 12. Conjugate acid: the species produced when a base accepts a hydrogen ion from an acid 13. Conjugate base: the species that results when an acid donates a hydrogen ion to a base 14. Amphoteric ...
... 11. In the example above, the acid (HX) becomes a base because it can now accept a positive hydrogen ion. 12. Conjugate acid: the species produced when a base accepts a hydrogen ion from an acid 13. Conjugate base: the species that results when an acid donates a hydrogen ion to a base 14. Amphoteric ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Phospholipids make up all cell membranes. – Polar phosphate “head” which is polar. – Nonpolar fatty acid “tails” which are nonpolar. – Hint: remember that water also had polar and nonpolar regions! Phospholipid ...
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Phospholipids make up all cell membranes. – Polar phosphate “head” which is polar. – Nonpolar fatty acid “tails” which are nonpolar. – Hint: remember that water also had polar and nonpolar regions! Phospholipid ...
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... Proteins and peptides are amino acid polymers in which the individual amino acid units, called residues, are linked together by amide bonds, or peptide bonds An amino group from one residue forms an amide bond with the carboxyl of a second residue ...
... Proteins and peptides are amino acid polymers in which the individual amino acid units, called residues, are linked together by amide bonds, or peptide bonds An amino group from one residue forms an amide bond with the carboxyl of a second residue ...
The Acid End-products of Glucose Metabolism of Oral
... in the presence of 2-oxoglutarate. It could be that the other strains were impermeable to 2oxoglutarate but the enzyme assays and the results of the experiment with radioactively labelled substrates suggest this is due to an incomplete tricarboxylic acid cycle. The probable pathway in haemophili is ...
... in the presence of 2-oxoglutarate. It could be that the other strains were impermeable to 2oxoglutarate but the enzyme assays and the results of the experiment with radioactively labelled substrates suggest this is due to an incomplete tricarboxylic acid cycle. The probable pathway in haemophili is ...
THE MOLECULES OF LIFE - Christian Heritage School
... functional group: group of atoms within a molecule that interacts in predictable ways with other molecules ...
... functional group: group of atoms within a molecule that interacts in predictable ways with other molecules ...
Role of Carnitine in Lipid Metabolism
... It is usually assumed that medium chain fatty acids are oxidized via a camitine independent pathway. In fact, dietary medium chain triglycerides have been suggested as a nutritional intervention modality to bypass the camitine transport mechanism in patients at risk for impaired camitine status. How ...
... It is usually assumed that medium chain fatty acids are oxidized via a camitine independent pathway. In fact, dietary medium chain triglycerides have been suggested as a nutritional intervention modality to bypass the camitine transport mechanism in patients at risk for impaired camitine status. How ...
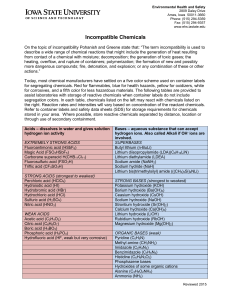
Incompatible Chemicals
... Segregate oxidizing acids (nitric, perchloric and chromic) from all other materials. Store water reactives away from water sources or aqueous solutions. Examples include metals such as sodium and potassium; acid anhydrides and acid chlorides; and fine metal powders such as zinc. Store pyrophoric che ...
... Segregate oxidizing acids (nitric, perchloric and chromic) from all other materials. Store water reactives away from water sources or aqueous solutions. Examples include metals such as sodium and potassium; acid anhydrides and acid chlorides; and fine metal powders such as zinc. Store pyrophoric che ...
Protein and Lipid Catabolism
... • NADH oxidized back to NAD+ • Uses organic compound as terminal electron acceptor – Typically pyruvate or derivative • NO oxidative phosphorylation so ATP yield is low ...
... • NADH oxidized back to NAD+ • Uses organic compound as terminal electron acceptor – Typically pyruvate or derivative • NO oxidative phosphorylation so ATP yield is low ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.