Topics To Know For Chapters 8-10
... - glucose - carbon fixation - NADPH & NADP - CO2 reduction - ATP & ADP + phosphate group - ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 26. Name two catabolic pathways. - aerobic respiration - NAD - fermentation - FAD - redox reactions 27. Know the three main stages of aerobic cell respiration and where do they tak ...
... - glucose - carbon fixation - NADPH & NADP - CO2 reduction - ATP & ADP + phosphate group - ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 26. Name two catabolic pathways. - aerobic respiration - NAD - fermentation - FAD - redox reactions 27. Know the three main stages of aerobic cell respiration and where do they tak ...
27.1 Digestion of Proteins 27.2 Amino Acid Metabolism: An
... – Biologically, it lowers blood pressure, kills invading bacteria, and enhances memory. – Nitric oxide is synthesized from oxygen and the amino acid arginine. – In blood vessels, NO activates reactions in smooth muscle cells that cause dilation and a resulting decrease in blood pressure. © 2013 Pear ...
... – Biologically, it lowers blood pressure, kills invading bacteria, and enhances memory. – Nitric oxide is synthesized from oxygen and the amino acid arginine. – In blood vessels, NO activates reactions in smooth muscle cells that cause dilation and a resulting decrease in blood pressure. © 2013 Pear ...
The Metabolism of Triglycerides by Spores of Penic
... synthetic triglycerides containing C, to CI2fatty acids to the corresponding methylketones with one less carbon atom (Acklin, 1929; Thaler & Eisenlohr, 1941). The first step in the oxidation is presumably the hydrolysis of the triglyceride, since the formation of extracellular esterases is well docu ...
... synthetic triglycerides containing C, to CI2fatty acids to the corresponding methylketones with one less carbon atom (Acklin, 1929; Thaler & Eisenlohr, 1941). The first step in the oxidation is presumably the hydrolysis of the triglyceride, since the formation of extracellular esterases is well docu ...
chirality
... is that each amino acid contains one stereocenter in its structure. All natural amino acids exist as a single enantiomer (the L isomer); this enantiomeric purity allows proteins (amino acid polymers) to form stable three dimensional structures. When determining how life on this planet began, the que ...
... is that each amino acid contains one stereocenter in its structure. All natural amino acids exist as a single enantiomer (the L isomer); this enantiomeric purity allows proteins (amino acid polymers) to form stable three dimensional structures. When determining how life on this planet began, the que ...
CHAPTER 6
... – This is a cytosolic enzyme (whereas CPS I is mitochondrial and used for the urea cycle) – Substrates are HCO3-, glutamine (not NH4+), 2 ATP – In mammals, CPS-II can be viewed as the committed step in pyrimidine synthesis – Bacteria have but one CPS; thus, the committed step is the next reaction, w ...
... – This is a cytosolic enzyme (whereas CPS I is mitochondrial and used for the urea cycle) – Substrates are HCO3-, glutamine (not NH4+), 2 ATP – In mammals, CPS-II can be viewed as the committed step in pyrimidine synthesis – Bacteria have but one CPS; thus, the committed step is the next reaction, w ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... Lipoic Acid functions to couple acyl-group transfer and electron transfer during oxidation and decarboxylation of αketo acids. It is found in pyruvate dehydrogenase and αketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Lipoic acid is covalently bound to relevant enzymes through amide bond formation with the εNH2 group ...
... Lipoic Acid functions to couple acyl-group transfer and electron transfer during oxidation and decarboxylation of αketo acids. It is found in pyruvate dehydrogenase and αketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Lipoic acid is covalently bound to relevant enzymes through amide bond formation with the εNH2 group ...
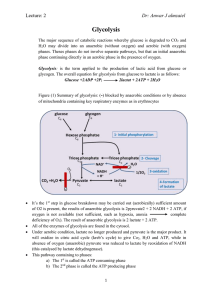
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... of O2 is present, the results of anaerobic glycolysis is 2pyruvate2 + 2 NADH + 2 ATP, if oxygen is not available (not sufficient, such as hypoxia, anoxia complete deficiency of O2). The result of anaerobic glycolysis is 2 lactate + 2 ATP. All of the enzymes of glycolysis are found in the cytosol. Un ...
... of O2 is present, the results of anaerobic glycolysis is 2pyruvate2 + 2 NADH + 2 ATP, if oxygen is not available (not sufficient, such as hypoxia, anoxia complete deficiency of O2). The result of anaerobic glycolysis is 2 lactate + 2 ATP. All of the enzymes of glycolysis are found in the cytosol. Un ...
Urea Cycle Defect: A Case Study
... The abnormal values given in the chart on the previous page are characteristic of a deficiency of the urea cycle enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC). The primary function of OTC is to catalyze the second reaction seen in the first figure of the urea cycle. In this reaction carbamylphosphate is c ...
... The abnormal values given in the chart on the previous page are characteristic of a deficiency of the urea cycle enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC). The primary function of OTC is to catalyze the second reaction seen in the first figure of the urea cycle. In this reaction carbamylphosphate is c ...
Electron-Transport Chain and ATP production
... Electron-Transport Chain and ATP production Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane where NADH and FADH2 are oxidized back to NAD+ and FAD. They transfer their e- in a series of steps and ultimately to O2: O2 + 4e- + 4H+ → 2H2O The energy released in these e- transfers is used to pump H+ (protons ...
... Electron-Transport Chain and ATP production Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane where NADH and FADH2 are oxidized back to NAD+ and FAD. They transfer their e- in a series of steps and ultimately to O2: O2 + 4e- + 4H+ → 2H2O The energy released in these e- transfers is used to pump H+ (protons ...
structure and function of bio- molecules - Aditya K Panda, PhD
... therefore two optical isomers (threonine and isoleucine have, e.g., two optical C-atoms). The basis for the nomenclature is D/L-glycerine aldehyde. Protein forming amino acids are all of the L-type. D-type amino acids are also known in nature but do not occur in proteins. In the case of amino acids ...
... therefore two optical isomers (threonine and isoleucine have, e.g., two optical C-atoms). The basis for the nomenclature is D/L-glycerine aldehyde. Protein forming amino acids are all of the L-type. D-type amino acids are also known in nature but do not occur in proteins. In the case of amino acids ...
Gluconeogenesis
... The phosphopentose epimerase reaction interconverts ribulose-5-P and xylulose-5-phosphate. The mechanism involves an enediol intermediate and occurs with inversion at C-3. ...
... The phosphopentose epimerase reaction interconverts ribulose-5-P and xylulose-5-phosphate. The mechanism involves an enediol intermediate and occurs with inversion at C-3. ...
CHAPTER 8 CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... 5. Only a small amount of NAD+ is needed in cells because each NAD+ molecule is used over and over. 6. FAD coenzyme of oxidation-reduction can replace NAD+; FAD accepts two electrons and becomes FADH2. C. Phases of Complete Glucose Breakdown 1. Cellular respiration includes four phases: a. Glycolysi ...
... 5. Only a small amount of NAD+ is needed in cells because each NAD+ molecule is used over and over. 6. FAD coenzyme of oxidation-reduction can replace NAD+; FAD accepts two electrons and becomes FADH2. C. Phases of Complete Glucose Breakdown 1. Cellular respiration includes four phases: a. Glycolysi ...
lecture 5
... the “factories” in which the synthesis of proteins occurs. -The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes formation of the peptide bonds that link amino acid residues in a protein. -The small subunit binds mRNA and is responsible for the accuracy of translation by ensuring correct base-pairing between the c ...
... the “factories” in which the synthesis of proteins occurs. -The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes formation of the peptide bonds that link amino acid residues in a protein. -The small subunit binds mRNA and is responsible for the accuracy of translation by ensuring correct base-pairing between the c ...
The Regulation of Acetyl Coenzyme A Synthesis in Chloroplasts
... The enzymatic activities of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) and acetyl-CoA synthe tase (ACS) have been compared in extracts of plastids isolated from spinach leaves and from both green and etiolated pea seedlings. A ll plastid preparations were shown to be capable of synthesizing acetyl-Co ...
... The enzymatic activities of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) and acetyl-CoA synthe tase (ACS) have been compared in extracts of plastids isolated from spinach leaves and from both green and etiolated pea seedlings. A ll plastid preparations were shown to be capable of synthesizing acetyl-Co ...
Connection of Propionyl-CoA Metabolism to Polyketide
... known about the cellular parameters controlling polyketide biosynthesis in fungi. We recently presented data suggesting that perturbations in the acyl-CoA pool can impair polyketide biosynthesis in A. nidulans. We found that blockage of propionate metabolism by mutation in the mcsA gene (encoding me ...
... known about the cellular parameters controlling polyketide biosynthesis in fungi. We recently presented data suggesting that perturbations in the acyl-CoA pool can impair polyketide biosynthesis in A. nidulans. We found that blockage of propionate metabolism by mutation in the mcsA gene (encoding me ...
BI0 120 cell and tissues
... B. matrix of the mitochondria. C. membranes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. D. intermembrane space of mitochondria. E. inner membrane of the chloroplasts. 38. What is the fate of the carbon fragment that proceeds through the citric acid cycle? A. conversion to heat. B. synthesis of glucose. C. i ...
... B. matrix of the mitochondria. C. membranes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. D. intermembrane space of mitochondria. E. inner membrane of the chloroplasts. 38. What is the fate of the carbon fragment that proceeds through the citric acid cycle? A. conversion to heat. B. synthesis of glucose. C. i ...
Endocrinology – glucose homeostasis
... by indirectly inhibiting gluconeogenesis via inhibition of fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue. Second, it increases the rate of uptake of glucose into all insulin-sensitive tissues, notably muscle, adipose tissue and the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (the “satiety centre”). It do ...
... by indirectly inhibiting gluconeogenesis via inhibition of fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue. Second, it increases the rate of uptake of glucose into all insulin-sensitive tissues, notably muscle, adipose tissue and the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (the “satiety centre”). It do ...
Polar amino acids with negative charge
... • Proteins are the machines that drive cells and, ultimately, organisms. ...
... • Proteins are the machines that drive cells and, ultimately, organisms. ...
Synthesis of a Glutathione Analogue Using 2-α-Methyl-β
... Glutathione plays an important role in the treatment of malaria in people. Malaria can be caused by the parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Recently, antimalarial agents have been met with resistance from the parasite. It has been shown that elevated GSH content in Plasmodium falciparum infected cells l ...
... Glutathione plays an important role in the treatment of malaria in people. Malaria can be caused by the parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Recently, antimalarial agents have been met with resistance from the parasite. It has been shown that elevated GSH content in Plasmodium falciparum infected cells l ...
my handy vitamin review
... Required for collagen synthesis, and as a cofactor for several enzymes. Also scavenges oxygen radicals. In almost all organisms, ascorbic acid is synthesized from glucose in 4 steps. A relatively recent (40 million years ago) mutation in the ancestor of humans made us unable to make ascorbic acid. S ...
... Required for collagen synthesis, and as a cofactor for several enzymes. Also scavenges oxygen radicals. In almost all organisms, ascorbic acid is synthesized from glucose in 4 steps. A relatively recent (40 million years ago) mutation in the ancestor of humans made us unable to make ascorbic acid. S ...
Lecture 4 POWERPOINT here
... However, unlike a bottle factory, where the same robot performs the identical function, with these biological systems the subunits have to be added in a set sequence because we have more than one flavour! 4 subunits in NA; 20 subunits in P’; many many in polysaccarides ...
... However, unlike a bottle factory, where the same robot performs the identical function, with these biological systems the subunits have to be added in a set sequence because we have more than one flavour! 4 subunits in NA; 20 subunits in P’; many many in polysaccarides ...
Repetition Summary of last lecture Energy Cell Respiration
... In a c ti v e tra n s c ri p ti o n fa c to r ...
... In a c ti v e tra n s c ri p ti o n fa c to r ...
Combinatorial mutagenesis to restrict amino acid usage in an
... the function of a large protein can also be fabricated with a limited set of amino acids. It is still unclear, therefore, whether the principles deduced from the studies with the small proteins can be applied to much larger and topologically more complex proteins. Thus, we have developed an effectiv ...
... the function of a large protein can also be fabricated with a limited set of amino acids. It is still unclear, therefore, whether the principles deduced from the studies with the small proteins can be applied to much larger and topologically more complex proteins. Thus, we have developed an effectiv ...
Related Metabolic Processes
... 1. Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the help of oxygen • Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons to any electron acceptor, not just to oxygen. • In glycolysis, glucose is oxidized to two pyruvate molecules with NAD+ as the oxidizing agent, not O2. • Some energy from this oxi ...
... 1. Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the help of oxygen • Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons to any electron acceptor, not just to oxygen. • In glycolysis, glucose is oxidized to two pyruvate molecules with NAD+ as the oxidizing agent, not O2. • Some energy from this oxi ...
Amino acid profile of organically grown alternative agricultural
... Abstract. Human nutrition recently has mainly focused on animal products; particularly processed products with large amounts of various synthetic additives. The benefit of fruits and vegetables for human health has been already shown and consumer interest in organic food products has increased. Ther ...
... Abstract. Human nutrition recently has mainly focused on animal products; particularly processed products with large amounts of various synthetic additives. The benefit of fruits and vegetables for human health has been already shown and consumer interest in organic food products has increased. Ther ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.