Overview on Reactions with Multi
... most important issues of the 21st century, the chemical industry has to adapt to new rules and laws. It is important to develop new processes that will generate less waste, use less energy, resources and water, which will also positively affect the environment, and lower the process costs as well. T ...
... most important issues of the 21st century, the chemical industry has to adapt to new rules and laws. It is important to develop new processes that will generate less waste, use less energy, resources and water, which will also positively affect the environment, and lower the process costs as well. T ...
Crude protein and amino acids content in some common
... and Arginine (2.4 to 3.4 %). In general, the EP2R has higher essential amino acids level compared to other diets. The results showed that the alternative feeds tested in this study had nine types of essential amino acids. However, the values of essential amino acids were not significantly different ...
... and Arginine (2.4 to 3.4 %). In general, the EP2R has higher essential amino acids level compared to other diets. The results showed that the alternative feeds tested in this study had nine types of essential amino acids. However, the values of essential amino acids were not significantly different ...
Krebs Cycle
... substrate and the product are identical (oxaloacetate), or simply put, the substrate ultimately cycles to itself in a series of reactions—this is in contrast to a pathway in which a substrate undergoes conversion to a chemically-distinct product! - Krebs cycle is comprised of a total of eight enzyma ...
... substrate and the product are identical (oxaloacetate), or simply put, the substrate ultimately cycles to itself in a series of reactions—this is in contrast to a pathway in which a substrate undergoes conversion to a chemically-distinct product! - Krebs cycle is comprised of a total of eight enzyma ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. • Carbon-based molecules have three general types of structures. – straight chain – branched chain – ring ...
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. • Carbon-based molecules have three general types of structures. – straight chain – branched chain – ring ...
Gluconeogenesis
... humans. In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. The human brain alone requires 120 g of glucose each day, more than half of which is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. ...
... humans. In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. The human brain alone requires 120 g of glucose each day, more than half of which is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. ...
Urea
... hyperammonemia & CNS toxicity will occur • To solve this problem, ammonia is transported from peripheral tissues to liver via formation of: Glutamine (most tissues) Alanine (muscle) ...
... hyperammonemia & CNS toxicity will occur • To solve this problem, ammonia is transported from peripheral tissues to liver via formation of: Glutamine (most tissues) Alanine (muscle) ...
7.014 Section Problem:
... c) How could you design a similar enzyme to cleave after aspartic acid? d) Speculate on the effect of changing the aspartic acid in protease B to a glutamic acid. e) There are three amino acids required for the active site to function and three amino acids involved in substrate recognition – why th ...
... c) How could you design a similar enzyme to cleave after aspartic acid? d) Speculate on the effect of changing the aspartic acid in protease B to a glutamic acid. e) There are three amino acids required for the active site to function and three amino acids involved in substrate recognition – why th ...
Chemistry/Biology 302 – Biochemistry: Exam 1 Practice Problems
... these questions come from several years of past Biochem tests. Over those years, we've used several different textbooks, and some of them use different approximate pKa values for buffers and amino acids. I've tried to update these questions so that they all use consistent pKa values, but if I've mis ...
... these questions come from several years of past Biochem tests. Over those years, we've used several different textbooks, and some of them use different approximate pKa values for buffers and amino acids. I've tried to update these questions so that they all use consistent pKa values, but if I've mis ...
Tyrocidine Biosynthesis by Three Complementary Fractions from
... (0.2 ml of a 0.5% solution) was added prior to precipitation. After 20 min, the suspension was centrifuged at 15OOg for 10 min. The precipitate was resuspended in 2 ml of 7 % trichloroacetic acid and recentrifuged. It was similarly washed in 2 ml of ethanol-ether (25 :75, v/v) and 2 ml of ether, bef ...
... (0.2 ml of a 0.5% solution) was added prior to precipitation. After 20 min, the suspension was centrifuged at 15OOg for 10 min. The precipitate was resuspended in 2 ml of 7 % trichloroacetic acid and recentrifuged. It was similarly washed in 2 ml of ethanol-ether (25 :75, v/v) and 2 ml of ether, bef ...
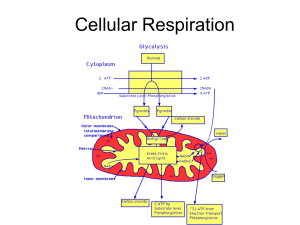
Carbohydrate Catabolism Cellular Respiration
... – Involves splitting of a six-carbon glucose into two three-carbon sugar molecules – Net gain of two ATP molecules – Two molecules of NADH ...
... – Involves splitting of a six-carbon glucose into two three-carbon sugar molecules – Net gain of two ATP molecules – Two molecules of NADH ...
Lactic acid fermentation
... electrons to – NAD+, forming NADH. However, there is only a limited supply of NAD+ available in a cell. For glycolysis to continue, NADH must be oxidized – that is, have electrons taken away – to regenerate the NAD+. This is usually done through an electron transport chain in a process called oxidat ...
... electrons to – NAD+, forming NADH. However, there is only a limited supply of NAD+ available in a cell. For glycolysis to continue, NADH must be oxidized – that is, have electrons taken away – to regenerate the NAD+. This is usually done through an electron transport chain in a process called oxidat ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration • The process by which mitochondria break down glucose to make ATP • Two types – Aerobic respiration: requires oxygen and carried out by plants, animals, and some bacteria – Anaerobic respiration: requires no oxygen and carried out by yeast, some bacteria, and sometimes animals ...
... Cellular Respiration • The process by which mitochondria break down glucose to make ATP • Two types – Aerobic respiration: requires oxygen and carried out by plants, animals, and some bacteria – Anaerobic respiration: requires no oxygen and carried out by yeast, some bacteria, and sometimes animals ...
Bio Chemistry (Power Point File) - Homoeopathy Clinics In India
... specialized transferases that regulate metabolism by transferring phosphate from ATP to other molecules. ...
... specialized transferases that regulate metabolism by transferring phosphate from ATP to other molecules. ...
Introduction Milk is the exclusive nutrient source for the neonate. ... practices and availability of highly selected sows have allowed for...
... Alternative fates of BCAA in the mammary gland, depending upon the amino acid, may include synthesis of cellular protein, synthesis of nonessential amino acids, utilization in fatty acid synthesis, and oxidization as an energy source. Animal nutrition studies do not usually account for these alterna ...
... Alternative fates of BCAA in the mammary gland, depending upon the amino acid, may include synthesis of cellular protein, synthesis of nonessential amino acids, utilization in fatty acid synthesis, and oxidization as an energy source. Animal nutrition studies do not usually account for these alterna ...
Acid - Net Texts
... acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (used in baking). As these Zinc, a typical metal, reacting with hydrochloric three examples show, acids can be solutions, liquids, or solids. Gases acid, a typical acid such as hydrogen chloride can be acids as well. Strong acids and some concentrated ...
... acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (used in baking). As these Zinc, a typical metal, reacting with hydrochloric three examples show, acids can be solutions, liquids, or solids. Gases acid, a typical acid such as hydrogen chloride can be acids as well. Strong acids and some concentrated ...
effect of -fluorination of valproic acid on valproyl- s-acyl
... Covalent binding was abolished in cells pretreated with 4-pentenoic acid (a potent inhibitor of -oxidation) and increased in incubations with hepatocytes from rats pretreated with clofibrate (an inducer of -oxidation) (Porubek et al., 1989). In addition, similar studies in isolated rat liver mitoc ...
... Covalent binding was abolished in cells pretreated with 4-pentenoic acid (a potent inhibitor of -oxidation) and increased in incubations with hepatocytes from rats pretreated with clofibrate (an inducer of -oxidation) (Porubek et al., 1989). In addition, similar studies in isolated rat liver mitoc ...
File - Principles of Biology 103
... 3. Which of the following metabolic pathways require(s) molecular oxygen: A. Aerobic respiration B. Lactate fermentation C. Alcoholic fermentation D. All of the above 4. What occurs when molecules are broken apart in respiration: A. ADP is released as a waste product B. The oxygen in the compounds t ...
... 3. Which of the following metabolic pathways require(s) molecular oxygen: A. Aerobic respiration B. Lactate fermentation C. Alcoholic fermentation D. All of the above 4. What occurs when molecules are broken apart in respiration: A. ADP is released as a waste product B. The oxygen in the compounds t ...
Nutritional Requirements in Fermentation
... S, go into making up the molecules of living matter. All living cells on earth contain water as their predominant constituent. The remainder of the cell consists largely of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates, along with a few common salts. A few smaller compounds are very ubiquitous ...
... S, go into making up the molecules of living matter. All living cells on earth contain water as their predominant constituent. The remainder of the cell consists largely of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates, along with a few common salts. A few smaller compounds are very ubiquitous ...
Enzymes - Best Friends of Flours The Miller`s Little Helpers
... The enzyme glucose oxidase (GOD) is usually derived from the mould Aspergillus, sometimes from Penecillium species. Honey is also a rich source of GOD. The enzyme stems from the pharyngeal glands of the bees. However, its suitability is rather restricted by the taste of its carrier. One effect of GO ...
... The enzyme glucose oxidase (GOD) is usually derived from the mould Aspergillus, sometimes from Penecillium species. Honey is also a rich source of GOD. The enzyme stems from the pharyngeal glands of the bees. However, its suitability is rather restricted by the taste of its carrier. One effect of GO ...
gluconeogenesis
... The brain alone requires about 120 g of glucose each day—more than half of all the glucose stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. However, the supply of glucose from these stores is not always sufficient; between meals and during longer fasts, or after vigorous exercise, glycogen is depleted. For t ...
... The brain alone requires about 120 g of glucose each day—more than half of all the glucose stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. However, the supply of glucose from these stores is not always sufficient; between meals and during longer fasts, or after vigorous exercise, glycogen is depleted. For t ...
Lecture 7 - Columbus Labs
... rather than N-formylmethionine. However, as in prokaryotes, a special tRNA participates in initiation. 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is always AUG. Eukaryotes, in contrast with prokaryotes, do not use a specific purine-rich sequence (RBS) on the 5′ side to distinguish initiator A ...
... rather than N-formylmethionine. However, as in prokaryotes, a special tRNA participates in initiation. 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is always AUG. Eukaryotes, in contrast with prokaryotes, do not use a specific purine-rich sequence (RBS) on the 5′ side to distinguish initiator A ...
Amino acid composition of the aerial part of G. pratense L., G
... Typically, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is used for the analysis of amino acids [3]. Amino acids lack chromophores and do not give a UV-Vis response, hence amino acids require derivatization prior to HPLC analysis performed with UV-Vis detectors. A method to determine free amino aci ...
... Typically, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is used for the analysis of amino acids [3]. Amino acids lack chromophores and do not give a UV-Vis response, hence amino acids require derivatization prior to HPLC analysis performed with UV-Vis detectors. A method to determine free amino aci ...
Review Questions for Advanced Biochemistry Course
... 31. Which of the following statements about the TCA cycle is CORRECT? A. Citrate is frequently used for gluconeogenesis in the liver B. The production of oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase is one of several anaplerotic reactions for the TCA cycle C. Succinyl CoA is used to create a neurotransmitte ...
... 31. Which of the following statements about the TCA cycle is CORRECT? A. Citrate is frequently used for gluconeogenesis in the liver B. The production of oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase is one of several anaplerotic reactions for the TCA cycle C. Succinyl CoA is used to create a neurotransmitte ...
Topics To Know For Chapters 8-10
... - glucose - carbon fixation - NADPH & NADP - CO2 reduction - ATP & ADP + phosphate group - ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 26. Name two catabolic pathways. - aerobic respiration - NAD - fermentation - FAD - redox reactions 27. Know the three main stages of aerobic cell respiration and where do they tak ...
... - glucose - carbon fixation - NADPH & NADP - CO2 reduction - ATP & ADP + phosphate group - ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 26. Name two catabolic pathways. - aerobic respiration - NAD - fermentation - FAD - redox reactions 27. Know the three main stages of aerobic cell respiration and where do they tak ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.