Slide 1
... entry, and metabolism in target (fat, muscle) cells. Glucose is transported into B cells by GLUT2. The B cell oxidizes glucose, resulting in ATP, which closes ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the plasma membrane, thereby preventing K+ efflux and depolarizing the B cell. Depolarization causes voltage-sen ...
... entry, and metabolism in target (fat, muscle) cells. Glucose is transported into B cells by GLUT2. The B cell oxidizes glucose, resulting in ATP, which closes ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the plasma membrane, thereby preventing K+ efflux and depolarizing the B cell. Depolarization causes voltage-sen ...
Degradation signals within both terminal domains of the cauliflower
... (a) The UPR technique. Reference and test proteins are separated by a ubiquitin moiety. This fusion is cleaved by ubiquitin (Ub)-speci®c proteases at the Ub±test protein junction, yielding equimolar amounts of both proteins (Levy et al., 1996). For this study the system was adapted by using two stab ...
... (a) The UPR technique. Reference and test proteins are separated by a ubiquitin moiety. This fusion is cleaved by ubiquitin (Ub)-speci®c proteases at the Ub±test protein junction, yielding equimolar amounts of both proteins (Levy et al., 1996). For this study the system was adapted by using two stab ...
Poster
... observed in the UV-Vis experiment does consume molecular oxygen • Shows oxygen is necessary for formation of 4HKA ...
... observed in the UV-Vis experiment does consume molecular oxygen • Shows oxygen is necessary for formation of 4HKA ...
Biosensor - PharmaStreet
... ‘bases’ in the DNA form the basis of specificity in nucleic acid based biosensors. These sensors are capable of detecting trace amounts of microorganism DNA by comparing it to a complementary strand of known DNA. By unwinding the target DNA strand, adding the DNA probe, and annealing the two strands ...
... ‘bases’ in the DNA form the basis of specificity in nucleic acid based biosensors. These sensors are capable of detecting trace amounts of microorganism DNA by comparing it to a complementary strand of known DNA. By unwinding the target DNA strand, adding the DNA probe, and annealing the two strands ...
Cells
... Ciliary movement. Action of a single cilium. During the power stroke, the cilium is relatively stiff; during the return stroke, it bends and returns to its original position. ...
... Ciliary movement. Action of a single cilium. During the power stroke, the cilium is relatively stiff; during the return stroke, it bends and returns to its original position. ...
GEFs: master regulators of G
... homology domains in the human genome. Heptahelical G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute an enormous family of ligand-stimulated GEFs that activate heterotrimeric G proteins. In addition, exchange factors IEF1B and EFTs act upon IEF1A and EFTu, respectively, to ensure the fidelity of the in ...
... homology domains in the human genome. Heptahelical G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute an enormous family of ligand-stimulated GEFs that activate heterotrimeric G proteins. In addition, exchange factors IEF1B and EFTs act upon IEF1A and EFTu, respectively, to ensure the fidelity of the in ...
Chapter 6
... Anabolic Pathways • Synthesis of subunits from precursor metabolites – Pathways consume ATP, reducing power and precursor metabolites – Macromolecules produces once subunits are synthesized ...
... Anabolic Pathways • Synthesis of subunits from precursor metabolites – Pathways consume ATP, reducing power and precursor metabolites – Macromolecules produces once subunits are synthesized ...
Gibbs Free Energy Changes for the Glycolytic Enzymes
... the glucose transport system and is therefore trapped in the cell. There is no transport system for phosphorylated glucose. The glucose transporter is a passive transporter. Converting glucose to G6P depletes the level of glucose inside the cell, thus keeping glucose flowing inside the cell down its ...
... the glucose transport system and is therefore trapped in the cell. There is no transport system for phosphorylated glucose. The glucose transporter is a passive transporter. Converting glucose to G6P depletes the level of glucose inside the cell, thus keeping glucose flowing inside the cell down its ...
A Proteome Reference Map and Proteomic Analysis
... and diversity as well as predicted genetic features such as exo- and endo-glycosyl hydrolases and high affinity oligosaccharide transporters. These features likely help B. longum compete for uptake of structurally diverse oligosaccharides released from digestion of plant fibers. Several studies cond ...
... and diversity as well as predicted genetic features such as exo- and endo-glycosyl hydrolases and high affinity oligosaccharide transporters. These features likely help B. longum compete for uptake of structurally diverse oligosaccharides released from digestion of plant fibers. Several studies cond ...
Early Development of Vertebrates
... Establishment of the dorsal-ventral axis in mammals is not well defined. - the hypoblast forms on the side of the ICM exposed to blastocyst fluid - the dorsal axis forms from ICM cells in contact with the trophoblast and amnionic cavity ...
... Establishment of the dorsal-ventral axis in mammals is not well defined. - the hypoblast forms on the side of the ICM exposed to blastocyst fluid - the dorsal axis forms from ICM cells in contact with the trophoblast and amnionic cavity ...
Unit F214 - Communication, homeostasis and energy
... The ADH molecule attaches to receptors on the ................................................. of these cells and causes protein channels known as ................................................. to insert themselves into the membrane. Water passes through these channels by ....................... ...
... The ADH molecule attaches to receptors on the ................................................. of these cells and causes protein channels known as ................................................. to insert themselves into the membrane. Water passes through these channels by ....................... ...
View/Open - Oregon State University
... undefined media, they are still inappropriate for most biochemical and phenotypic testing. In addition, most biochemical tests are designed for identification of enteric bacteria and do not reveal useful information about free-living bacteria in their natural environment (O’Hara et al., 1992; Torsvi ...
... undefined media, they are still inappropriate for most biochemical and phenotypic testing. In addition, most biochemical tests are designed for identification of enteric bacteria and do not reveal useful information about free-living bacteria in their natural environment (O’Hara et al., 1992; Torsvi ...
OMB No. 0925-0001/0002 (Rev. 08/12), Biographical Sketch Format
... ’14 Keynote Speaker, Fraunhofer Forum International Symposium on Cell-free Protein Synthesis, Berlin C. Contribution to Science 1. Pioneering development of versatile, practical cell-free protein synthesis technology. Primarily started after I came to Stanford in 1998, the program focused on develop ...
... ’14 Keynote Speaker, Fraunhofer Forum International Symposium on Cell-free Protein Synthesis, Berlin C. Contribution to Science 1. Pioneering development of versatile, practical cell-free protein synthesis technology. Primarily started after I came to Stanford in 1998, the program focused on develop ...
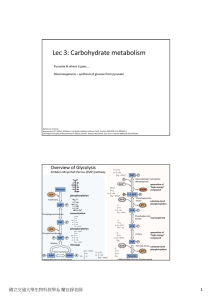
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... Conditions that promote glycolysis inhibit gluconeogenesis, and vice versa. ...
... Conditions that promote glycolysis inhibit gluconeogenesis, and vice versa. ...
Systemic Organ Wasting Induced by Localized Expression of the
... of diseases, including cancers. We have developed a model for organ wasting in adult Drosophila, whereby overproliferation induced by activation of Yorkie, the Yap1 oncogene ortholog, in intestinal stem cells leads to wasting of the ovary, fat body, and muscle. These organ-wasting phenotypes are ass ...
... of diseases, including cancers. We have developed a model for organ wasting in adult Drosophila, whereby overproliferation induced by activation of Yorkie, the Yap1 oncogene ortholog, in intestinal stem cells leads to wasting of the ovary, fat body, and muscle. These organ-wasting phenotypes are ass ...
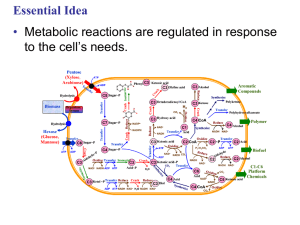
Metabolism - University of Lethbridge
... 3) Every metabolic pathway has a first committing step 4) All metabolic pathways are regulated Additional characteristic of eucaryotic metabolic pathways: Occur in specific cellular locations ...
... 3) Every metabolic pathway has a first committing step 4) All metabolic pathways are regulated Additional characteristic of eucaryotic metabolic pathways: Occur in specific cellular locations ...
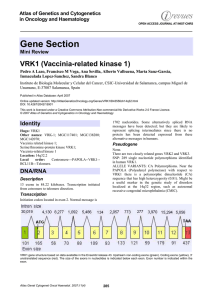
Gene Section VRK1 (Vaccinia-related kinase 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... hypersensitive site located between VRK1 and BCL11B genes; but the structure, or expression, of VRK1 does not appear to be affected. In this translocation there is a dysregulation of TLX3 and NKX2-5 homeobox genes (both on chromosome 5). ...
... hypersensitive site located between VRK1 and BCL11B genes; but the structure, or expression, of VRK1 does not appear to be affected. In this translocation there is a dysregulation of TLX3 and NKX2-5 homeobox genes (both on chromosome 5). ...
ángeles garcía pardo
... many of the metabolic pathways that reside in mitochondria such as decarboxylation of pyruvate, the TCA cycle, β-oxidation of fatty acids and oxidative phosphorylation are very much diminished during proliferation whereas the activity of glycolysis and of the pentose phosphate pathway are profoundly ...
... many of the metabolic pathways that reside in mitochondria such as decarboxylation of pyruvate, the TCA cycle, β-oxidation of fatty acids and oxidative phosphorylation are very much diminished during proliferation whereas the activity of glycolysis and of the pentose phosphate pathway are profoundly ...
Moore_Timothy_LIfe Science Semester 1 Assessment
... Which of these is not one of the domains of life? Eukarya Bacteria Protozoa Archaea Starches are an example of which type of organic molecule? carbohydrate protein nucleic acid lipid Which part of the eukaryotic cell contains information to direct the cell’s functions? ribosome cytoplasm mitochondri ...
... Which of these is not one of the domains of life? Eukarya Bacteria Protozoa Archaea Starches are an example of which type of organic molecule? carbohydrate protein nucleic acid lipid Which part of the eukaryotic cell contains information to direct the cell’s functions? ribosome cytoplasm mitochondri ...
chapter outline - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... is reduced to nitrogen gas, the process is called denitrification C. Anaerobic respiration is not as efficient in ATP synthesis as aerobic respiration because the alternative electron acceptors do not have as positive a reduction potential as O2; despite this, anaerobic respiration is useful because ...
... is reduced to nitrogen gas, the process is called denitrification C. Anaerobic respiration is not as efficient in ATP synthesis as aerobic respiration because the alternative electron acceptors do not have as positive a reduction potential as O2; despite this, anaerobic respiration is useful because ...
G protein
... • Many other pathways can lead to activation of heterotrimeric G proteins, including - Wnts, which act through seven-pass receptors known as Frizzleds - Hedgehog, which acts through a different sevenpass protein called Smoothened ...
... • Many other pathways can lead to activation of heterotrimeric G proteins, including - Wnts, which act through seven-pass receptors known as Frizzleds - Hedgehog, which acts through a different sevenpass protein called Smoothened ...
Cellular Respiration
... during cellular respiration –C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • Glucose is oxidized, O2 is reduced, and e-s lose potential E • Molecules that have an abundance of hydrogen are excellent fuels because their bonds are a source of “hilltop” e-s that “fall” closer to O2 ...
... during cellular respiration –C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • Glucose is oxidized, O2 is reduced, and e-s lose potential E • Molecules that have an abundance of hydrogen are excellent fuels because their bonds are a source of “hilltop” e-s that “fall” closer to O2 ...