β-catenin: a key mediator of Wnt signaling Karl
... the degradation of β-catenin by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway [30•]. Interestingly, several colon carcinoma and melanoma cell lines contain elevated levels of β-catenin; in some of these cell lines the increased stability can be attributed to point mutations in β-catenin that change the serine an ...
... the degradation of β-catenin by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway [30•]. Interestingly, several colon carcinoma and melanoma cell lines contain elevated levels of β-catenin; in some of these cell lines the increased stability can be attributed to point mutations in β-catenin that change the serine an ...
Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways
... of NF-κB-inducing stimuli further extends to physical, physiological and oxidative stresses, and its additional functions include regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation and survival4,5. As a consequence, dysregulation of NF-κB activity is linked to inflammatory disorders, autoimmune and m ...
... of NF-κB-inducing stimuli further extends to physical, physiological and oxidative stresses, and its additional functions include regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation and survival4,5. As a consequence, dysregulation of NF-κB activity is linked to inflammatory disorders, autoimmune and m ...
enzymes-regulation-text
... Polyubiquitylated proteins are targeted to a HUGE protein complex called the proteasome: ...
... Polyubiquitylated proteins are targeted to a HUGE protein complex called the proteasome: ...
Chapter 6 – How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Standard 1.g
... The efficiency of cellular respiration – a typical cell stores around 40% of the chemical energy released in ATP, the rest is released as heat ATP is produced in 2 ways 1. The movement of electrons along an electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane. The protons di ...
... The efficiency of cellular respiration – a typical cell stores around 40% of the chemical energy released in ATP, the rest is released as heat ATP is produced in 2 ways 1. The movement of electrons along an electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane. The protons di ...
The Molecules of Movement
... Differences from skeletal muscle: Timing of ventricular action potential and isometric force Action potential lasts as long as isometric force Force is already relaxing during membrane’s refractory period o Therefore cannot produced fused tetanus (sustained, summated force) o Designed for pumping No ...
... Differences from skeletal muscle: Timing of ventricular action potential and isometric force Action potential lasts as long as isometric force Force is already relaxing during membrane’s refractory period o Therefore cannot produced fused tetanus (sustained, summated force) o Designed for pumping No ...
An hierarchical artificial neural network system for the classification
... An hierarchical artificial neural network system for the classification of transmembrane proteins ...
... An hierarchical artificial neural network system for the classification of transmembrane proteins ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... therefore believed to be ancient in origin. What can be said about the origin of the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain, and the F1 ATPase? ...
... therefore believed to be ancient in origin. What can be said about the origin of the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain, and the F1 ATPase? ...
PDF
... the exact mode of CO2 fixation is largely unsolved. Ribulose-1,5bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenases (Rubisco) from diatoms have half-saturation constants for CO2 of 30–60 mM [5] despite the fact that typical sea water contains about 10 mM CO2 [6]. To prevent potential CO2 limitation, most diatoms ha ...
... the exact mode of CO2 fixation is largely unsolved. Ribulose-1,5bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenases (Rubisco) from diatoms have half-saturation constants for CO2 of 30–60 mM [5] despite the fact that typical sea water contains about 10 mM CO2 [6]. To prevent potential CO2 limitation, most diatoms ha ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... water do not mix. Oils are dominated by quite symmetric C–H bonds and have dielectric constants below 10. Water is dominated by the electrically asymmetric O–H bonds and has a dielectric constant of 80. It requires considerable energy to dissolve an oil molecule in water because to do so involves br ...
... water do not mix. Oils are dominated by quite symmetric C–H bonds and have dielectric constants below 10. Water is dominated by the electrically asymmetric O–H bonds and has a dielectric constant of 80. It requires considerable energy to dissolve an oil molecule in water because to do so involves br ...
$doc.title
... All these past attempts to create novel-coloured flowers have focused on the manipulation of the flavonoid pigmentation pathways that exist in flowers (Elomaa and Holton, 1994; Forkmann and Martens, 2001). To create black flowers, for example, researchers tried to increase the concentrations of fl ...
... All these past attempts to create novel-coloured flowers have focused on the manipulation of the flavonoid pigmentation pathways that exist in flowers (Elomaa and Holton, 1994; Forkmann and Martens, 2001). To create black flowers, for example, researchers tried to increase the concentrations of fl ...
Cell Respiration
... converted into glucose three-phosphate, which requires two ATP molecules. The remaining four steps involve splitting the six-carbon molecule into two three-carbon molecules. B. Glucose, a six-carbon sugar, enters the cell by active transport and is primed and converted into glucose three-phosphate, ...
... converted into glucose three-phosphate, which requires two ATP molecules. The remaining four steps involve splitting the six-carbon molecule into two three-carbon molecules. B. Glucose, a six-carbon sugar, enters the cell by active transport and is primed and converted into glucose three-phosphate, ...
Biochemical Journal
... The first member of the p38 MAPK family was independently identified by four groups as a 38 kDa protein (p38) that was rapidly phosphorylated on tyrosine in response to LPS (lipopolysaccharide) stimulation [5], as a target of pyridinylimidazole drugs [CSBP (cytokine-suppressive anti-inflammatory dru ...
... The first member of the p38 MAPK family was independently identified by four groups as a 38 kDa protein (p38) that was rapidly phosphorylated on tyrosine in response to LPS (lipopolysaccharide) stimulation [5], as a target of pyridinylimidazole drugs [CSBP (cytokine-suppressive anti-inflammatory dru ...
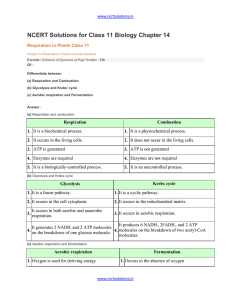
chapter_14_respiration_in_plants
... ETS or electron transport system is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It helps in releasing and utilizing the energy stored in NADH+H+ and FADH2. NADH + H+, which is formed during glycolysis and citric acid cycle, gets oxidized by NADH dehydrogenase (complex I). The electrons so generated ...
... ETS or electron transport system is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It helps in releasing and utilizing the energy stored in NADH+H+ and FADH2. NADH + H+, which is formed during glycolysis and citric acid cycle, gets oxidized by NADH dehydrogenase (complex I). The electrons so generated ...
CHAPTER 7, CELLULAR RESPIRATION In Eukaryotic Cells, the
... 7. The Energy they LOSE is used to PUMP Protons of the Hydrogen Atoms from the Mitochondrial Matrix to the other side of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane. 8. The Pumping builds up a High Concentration (A Concentration Gradient) of Protons in the space Between the INNER and OUTER Mitochondrial Membr ...
... 7. The Energy they LOSE is used to PUMP Protons of the Hydrogen Atoms from the Mitochondrial Matrix to the other side of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane. 8. The Pumping builds up a High Concentration (A Concentration Gradient) of Protons in the space Between the INNER and OUTER Mitochondrial Membr ...
Taste
... (“short”) sensory receptors. Differentiate from basal stem cells in the taste bud. Turnover about every 10 days. ...
... (“short”) sensory receptors. Differentiate from basal stem cells in the taste bud. Turnover about every 10 days. ...
144803525 - BORA
... Finally, my family deserves special recognition, specially my parents Ram Bahadur KC and Sabitri KC. Your unconditional love and support have been my driving force of going forward. I feel blessed with all your love, encouragement and faith in me. ...
... Finally, my family deserves special recognition, specially my parents Ram Bahadur KC and Sabitri KC. Your unconditional love and support have been my driving force of going forward. I feel blessed with all your love, encouragement and faith in me. ...
GENERATION OF K581A MUTATION AND PRODUCTION OF RECOMBINANT JAK2 PROTEIN
... Protein kinases (PKs) are a large group of enzymes which catalyze transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP to the hydroxyl group of tyrosine, threonine or serine residue of their substrates (Choreschi K. et al. 2009) Vertebrate genome consist s of approximately 2000 different protein kinase ...
... Protein kinases (PKs) are a large group of enzymes which catalyze transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP to the hydroxyl group of tyrosine, threonine or serine residue of their substrates (Choreschi K. et al. 2009) Vertebrate genome consist s of approximately 2000 different protein kinase ...
Final Exam - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... b) How does the synthesis of ornithine proceed, taking into consideration that one reaction requires NAD+, another is catalyzed by a transaminase, and yet another produces ADP as one of its products (Note: all reactions have been discussed in class in a different context)? Draw the structures of the ...
... b) How does the synthesis of ornithine proceed, taking into consideration that one reaction requires NAD+, another is catalyzed by a transaminase, and yet another produces ADP as one of its products (Note: all reactions have been discussed in class in a different context)? Draw the structures of the ...
The protein acetylome and the regulation of metabolism - Serval
... (NatB) contains the subunits N-Acetyl Transferase 3 (Nat3) and Mitochondrial Distribution and Morphology 20 (Mdm20), while the N-Acetyl Transferase C complex (NatC) contains the Maintenance of Killer proteins Mak3, Mak10 and Mak31. Homologs to all these subunits are present in plants, and complement ...
... (NatB) contains the subunits N-Acetyl Transferase 3 (Nat3) and Mitochondrial Distribution and Morphology 20 (Mdm20), while the N-Acetyl Transferase C complex (NatC) contains the Maintenance of Killer proteins Mak3, Mak10 and Mak31. Homologs to all these subunits are present in plants, and complement ...
Derived copy of Bis2A 07.3 Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid
... liver. This form produces GTP. GTP is energetically equivalent to ATP; however, its use is more restricted. In particular, protein synthesis primarily uses GTP. Step 6. Step six is a dehydration process that converts succinate into fumarate. Two hydrogen atoms are transferred to FAD, producing FADH2 ...
... liver. This form produces GTP. GTP is energetically equivalent to ATP; however, its use is more restricted. In particular, protein synthesis primarily uses GTP. Step 6. Step six is a dehydration process that converts succinate into fumarate. Two hydrogen atoms are transferred to FAD, producing FADH2 ...
Deletion mutant of FGFR4 induces onion
... invagination of ER-derived membrane stacks into the nucleus. ...
... invagination of ER-derived membrane stacks into the nucleus. ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... FIGURE 12.8 Central role of astrocytes in brain homeostasis. Orange: pH buffering. Abundant carbonic anhydrase (CA) in astrocytes converts CO 2 to H+ andHCO3−. TwoHCO3– are transported into the extracellular space along with one Na+ via the Na+-HCO3− cotransporter (NBC), thereby increasing the extr ...
... FIGURE 12.8 Central role of astrocytes in brain homeostasis. Orange: pH buffering. Abundant carbonic anhydrase (CA) in astrocytes converts CO 2 to H+ andHCO3−. TwoHCO3– are transported into the extracellular space along with one Na+ via the Na+-HCO3− cotransporter (NBC), thereby increasing the extr ...