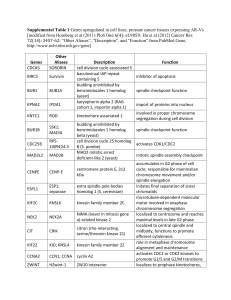
12672_2014_177_MOESM1_ESM
... centrosome;tumorigenesis may occur when this protein fails to degrade and produces excess centrosomes resulting in aberrant mitotic spindles duplication control of cell cycle; this protein and E2F4 interact with tumor suppressor proteins p130 and p107, but not with pRB involved in the initiation of ...
... centrosome;tumorigenesis may occur when this protein fails to degrade and produces excess centrosomes resulting in aberrant mitotic spindles duplication control of cell cycle; this protein and E2F4 interact with tumor suppressor proteins p130 and p107, but not with pRB involved in the initiation of ...
051607
... • Cooperativity – Multiple binding sites – Two states: high affinity (R for Hb) & low (T) – Different factors influence the R↔T equil • Oxygen: allosteric activator (positive) • BPG, H+, etc.: allosteric inhibitors ...
... • Cooperativity – Multiple binding sites – Two states: high affinity (R for Hb) & low (T) – Different factors influence the R↔T equil • Oxygen: allosteric activator (positive) • BPG, H+, etc.: allosteric inhibitors ...
The Complement system
... • The complement works as a cascade system. – Cascade is when one reaction triggers another reaction which trigger others and so on. These types of systems can grow exponentially very fast. ...
... • The complement works as a cascade system. – Cascade is when one reaction triggers another reaction which trigger others and so on. These types of systems can grow exponentially very fast. ...
ARPE-19 retinal pigment epithelia cells as an in vitro model
... enzyme, HO-1 in differentiated ARPE-19 cells. As expected, preincubation with AA attenuated significantly light induced cell damage. Not expected was the increase of HO-1 expression more than 2-fold on the protein level in AA-supplemented cells after light-induced cell damage. AA upregulates HO-1 si ...
... enzyme, HO-1 in differentiated ARPE-19 cells. As expected, preincubation with AA attenuated significantly light induced cell damage. Not expected was the increase of HO-1 expression more than 2-fold on the protein level in AA-supplemented cells after light-induced cell damage. AA upregulates HO-1 si ...
7.4mb ppt - UCLA.edu
... For Class II the polymorphisms are also concentrated in the binding pocket with the -chain showing more variability than the -chain ...
... For Class II the polymorphisms are also concentrated in the binding pocket with the -chain showing more variability than the -chain ...
Stress and Brain Development
... For each hormone, a specific receptor exists within the cell. It is important to note one fundamental difference, however, between the steroid hormones and the other signaling molecules. The receptors for growth factors and neurotransmitters lie on the outer surface of the cell and directly bind the ...
... For each hormone, a specific receptor exists within the cell. It is important to note one fundamental difference, however, between the steroid hormones and the other signaling molecules. The receptors for growth factors and neurotransmitters lie on the outer surface of the cell and directly bind the ...
Chapter 6 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Overview All living
... exception of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate, we will not learn the other intermediate molecules. This process effectively uses oxygen to break the C-C bonds found in the acetyl-CoA (which was pyruvate). As the bonds are broken, energy may be harvested (to form ATP), but usually electrons are released a ...
... exception of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate, we will not learn the other intermediate molecules. This process effectively uses oxygen to break the C-C bonds found in the acetyl-CoA (which was pyruvate). As the bonds are broken, energy may be harvested (to form ATP), but usually electrons are released a ...
G:\CLASSES\BI 205\Biol205_S10\exams\Final_S10.wpd
... (6 points) The citric acid cycle generates NADH+H+ and FADH2, which are then used in the process of oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. If the citric acid cycle (which does not use oxygen) and oxphos are separate processes, as they are, then why is it that the citric acid cycle stops almost immed ...
... (6 points) The citric acid cycle generates NADH+H+ and FADH2, which are then used in the process of oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. If the citric acid cycle (which does not use oxygen) and oxphos are separate processes, as they are, then why is it that the citric acid cycle stops almost immed ...
Document
... • Control coefficient determined for each enzyme. = activity / enzyme concentration. • Enzymes with large control coefficients impt to overall regulation. • Recent finding suggest that the control of most pathways is shared by multiple pathway enzymes ...
... • Control coefficient determined for each enzyme. = activity / enzyme concentration. • Enzymes with large control coefficients impt to overall regulation. • Recent finding suggest that the control of most pathways is shared by multiple pathway enzymes ...
Supplementary Material (doc 44K)
... prepared in the presence of protease inhibitor cocktail mix (Roche), 40 mM Nmethylmaleimide (NEM) and benzonase (Sigma-Aldrich). Protein concentrations in the lysate were determined by Bradford assays and confirmed by applying 10% of the lysate to SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. IP was carried ...
... prepared in the presence of protease inhibitor cocktail mix (Roche), 40 mM Nmethylmaleimide (NEM) and benzonase (Sigma-Aldrich). Protein concentrations in the lysate were determined by Bradford assays and confirmed by applying 10% of the lysate to SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. IP was carried ...
Mechanisms of Hormonal Action
... receptors with KD values ranging from 10-12 to 10-6 M. Only a minute amount of the hormones are required to induce response. The binding of the hormone stimulates a chemical activity that is communicated into the cell. Steroids are another type of hormone. Steroids are derived from cholesterol and r ...
... receptors with KD values ranging from 10-12 to 10-6 M. Only a minute amount of the hormones are required to induce response. The binding of the hormone stimulates a chemical activity that is communicated into the cell. Steroids are another type of hormone. Steroids are derived from cholesterol and r ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... function, enzyme catalysis, an overview of energy metabolism, and the maintenance and expression of genetic information. I. PRE-REQUISITE: CHEM 302 Organic Chemistry II J. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES: Upon completion the student will be able to: Course Objective 1. Describe the molecular basis of life ...
... function, enzyme catalysis, an overview of energy metabolism, and the maintenance and expression of genetic information. I. PRE-REQUISITE: CHEM 302 Organic Chemistry II J. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES: Upon completion the student will be able to: Course Objective 1. Describe the molecular basis of life ...
Exam 2 for Review - philipdarrenjones.com
... 38) A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the volume of blood lost, is transferred directly into one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A) It will have no unfavorable effec ...
... 38) A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the volume of blood lost, is transferred directly into one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A) It will have no unfavorable effec ...
Introduction - Northern Illinois University
... Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes • The defining difference between prokaryote and eukaryote is that eukaryotes have their DNA stored in a membranebound nucleus, while prokaryotes have their DNA floating freely in the cytoplasm. • Prokaryotes are single celled organisms that are simpler than eukaryotes. T ...
... Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes • The defining difference between prokaryote and eukaryote is that eukaryotes have their DNA stored in a membranebound nucleus, while prokaryotes have their DNA floating freely in the cytoplasm. • Prokaryotes are single celled organisms that are simpler than eukaryotes. T ...
AP Biology Study Guide Part II: Cells Describe the structure and
... diagrams to support your response. 5. How are electrochemical gradients formed and how do they function? 6. Differentiate between exergonic and endergonic reactions and give examples of each. Include a discussion of free energy in your response. 7. Describe how enzymes function. Discuss factors that ...
... diagrams to support your response. 5. How are electrochemical gradients formed and how do they function? 6. Differentiate between exergonic and endergonic reactions and give examples of each. Include a discussion of free energy in your response. 7. Describe how enzymes function. Discuss factors that ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... - A component of ATP, nucleic acids, coenzymes, phospholipids, teichoic acid, capsular polysaccharides; also is required for signal transduction. - Phosphate (PO43-) is usually used as the P source. ...
... - A component of ATP, nucleic acids, coenzymes, phospholipids, teichoic acid, capsular polysaccharides; also is required for signal transduction. - Phosphate (PO43-) is usually used as the P source. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 30. What allows for hormones released into the bloodstream to only trigger responses in certain cell types and organs? - Hormones act only on cells that express the appropriate receptor. - Target cells respond to a particular hormone because they contain a receptor for that hormone. 31. How does a c ...
... 30. What allows for hormones released into the bloodstream to only trigger responses in certain cell types and organs? - Hormones act only on cells that express the appropriate receptor. - Target cells respond to a particular hormone because they contain a receptor for that hormone. 31. How does a c ...
1984 BS, Seoul National University, Korea
... residues of the N-end rule pathway include the N-terminal arginine (Arg) residue which can be post-translationally created by ATE1-encoded Arg-tRNA transferases (R-transferases) that transfer the amino acid L-Arg from Arg-tRNAArg to the N-termini. Recognins that recognize the N-terminal Arg residue ...
... residues of the N-end rule pathway include the N-terminal arginine (Arg) residue which can be post-translationally created by ATE1-encoded Arg-tRNA transferases (R-transferases) that transfer the amino acid L-Arg from Arg-tRNAArg to the N-termini. Recognins that recognize the N-terminal Arg residue ...
ß-arrestin signaling and regulation of transcription
... susceptible to endotoxic shock. -arrestins may regulate IL1R signaling through interaction with TRAF6 and/or IB␣, since IL1R signaling also converges at IB␣–NF-B. However, stimulation of 2-adrenergic receptors has no effect on the interaction of -arrestin and TRAF6 (Wang et al., 2006), which s ...
... susceptible to endotoxic shock. -arrestins may regulate IL1R signaling through interaction with TRAF6 and/or IB␣, since IL1R signaling also converges at IB␣–NF-B. However, stimulation of 2-adrenergic receptors has no effect on the interaction of -arrestin and TRAF6 (Wang et al., 2006), which s ...
G-protein linked receptor
... G-protein coupled receptors also activate IP3 and Ca2+-mediated signaling pathways Activate receptor acts as GEF Activated Ga activates phospholipase C (PLC) Active PLC cleaves PIP2 to IP3 and diacylglycerol (DAG) IP3 opens Ca2+ channels in ER releasing Ca2+ to cytoplasm ...
... G-protein coupled receptors also activate IP3 and Ca2+-mediated signaling pathways Activate receptor acts as GEF Activated Ga activates phospholipase C (PLC) Active PLC cleaves PIP2 to IP3 and diacylglycerol (DAG) IP3 opens Ca2+ channels in ER releasing Ca2+ to cytoplasm ...
How does the structure of the cell membrane contribute to its function?
... Proteins Membrane Proteins: 1. Structural Proteins: ...
... Proteins Membrane Proteins: 1. Structural Proteins: ...
T cell receptors, T cell function and signaling
... called Igα and Igβ, forming the BCR • The TCR is in a complex with invariant transmembrane proteins called CD3ε, δ, γ, and TCRζ • Igα, Igβ, CD3ε, CD3δ, CD3γ, and TCRζ each contain ITAM motifs • B cells express a co-receptor composed of CD21, CD18, and CD81 that binds complement, increasing B cell si ...
... called Igα and Igβ, forming the BCR • The TCR is in a complex with invariant transmembrane proteins called CD3ε, δ, γ, and TCRζ • Igα, Igβ, CD3ε, CD3δ, CD3γ, and TCRζ each contain ITAM motifs • B cells express a co-receptor composed of CD21, CD18, and CD81 that binds complement, increasing B cell si ...























