Anaerobic glycolysis
... and recycles (wastes) NADH -> NAD+ • Key enzymes of glycolysis are regulated: hexokinase, PFK-1, pyruvate kinase, PDH C ...
... and recycles (wastes) NADH -> NAD+ • Key enzymes of glycolysis are regulated: hexokinase, PFK-1, pyruvate kinase, PDH C ...
Ch. 22 Glycolysis • Explain how glucose is universal fuel, oxidized in
... Which of the following statements correctly describes an aspect of glycolysis? a. ATP is formed by oxidative phosphorylation b. Two molecules of ATP are used in the beginning of the pathway ...
... Which of the following statements correctly describes an aspect of glycolysis? a. ATP is formed by oxidative phosphorylation b. Two molecules of ATP are used in the beginning of the pathway ...
biochem ch 20 [2-9
... reaction catalyzed by succinate thiokinase (succinyl-CoA synthetase in reverse reaction) Reaction is example of substrate-level phosphorylation (formation of high-energy phosphate bond where none previously existed without use of molecular O2 [not oxidative phosphorylation]) High-energy phosphat ...
... reaction catalyzed by succinate thiokinase (succinyl-CoA synthetase in reverse reaction) Reaction is example of substrate-level phosphorylation (formation of high-energy phosphate bond where none previously existed without use of molecular O2 [not oxidative phosphorylation]) High-energy phosphat ...
Ana Maria da Silva Esteves Dissertation presented to obtain
... metabolites associated with the glycolysis or the Krebs cycle were negatively affected. To our knowledge, this is the first study on the metabolome of a hyperthermophilic organism under heat stress conditions. Further work must be done to improve the statistical significance of the results, extend t ...
... metabolites associated with the glycolysis or the Krebs cycle were negatively affected. To our knowledge, this is the first study on the metabolome of a hyperthermophilic organism under heat stress conditions. Further work must be done to improve the statistical significance of the results, extend t ...
Host Factors in the Replication of Positive
... Following translation and processing of viral proteins, (+)RNA viruses adopt a relatively conserved process for completing the RNA replication cycle in host cells. Studies of the mechanisms of (+)RNA virus replication have suggested that this process usually involves the following steps: 1) selectin ...
... Following translation and processing of viral proteins, (+)RNA viruses adopt a relatively conserved process for completing the RNA replication cycle in host cells. Studies of the mechanisms of (+)RNA virus replication have suggested that this process usually involves the following steps: 1) selectin ...
Role of CD3 /in T Cell Receptor Assembly
... have shown that glycosylation might be involved in stabilizing the structure of proteins, in modifying the functional activity of proteins, in recognition events, and in signal transduction after ligand-receptor binding (reviewed in reference 53). In addition, it has recently been demonstrated that ...
... have shown that glycosylation might be involved in stabilizing the structure of proteins, in modifying the functional activity of proteins, in recognition events, and in signal transduction after ligand-receptor binding (reviewed in reference 53). In addition, it has recently been demonstrated that ...
A horizontal gene transfer at the origin of phenylpropanoid
... Intriguingly, D. discoideum harbors two additional homologues: one is very divergent and could not be included in the analysis, while the other lies outside of the eukaryotic HAL cluster and close to the characterized PAL of P. luminescens (Figure 2, indicated by a pink arrow) and may represent a re ...
... Intriguingly, D. discoideum harbors two additional homologues: one is very divergent and could not be included in the analysis, while the other lies outside of the eukaryotic HAL cluster and close to the characterized PAL of P. luminescens (Figure 2, indicated by a pink arrow) and may represent a re ...
PD-1 Pathway, Flyer - Bio
... announce the release of its products and services portfolio for research of the PD-1 pathway. ...
... announce the release of its products and services portfolio for research of the PD-1 pathway. ...
Rapamycin increases mitochondrial efficiency by mtDNA
... OXPHOS. Levels of ROS are tightly regulated as ROS serve as a secondary messenger to ...
... OXPHOS. Levels of ROS are tightly regulated as ROS serve as a secondary messenger to ...
Anaerobic and aerobic oxidation of glucose
... enzyme lactase, which cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose. Microorganisms in the colon ferment undigested lactose to lactic acid generating methane (CH4) and hydrogen gas (H2). The gas produced creates the uncomfortable feeling of gut distention and the annoying problem of flatulence. The lac ...
... enzyme lactase, which cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose. Microorganisms in the colon ferment undigested lactose to lactic acid generating methane (CH4) and hydrogen gas (H2). The gas produced creates the uncomfortable feeling of gut distention and the annoying problem of flatulence. The lac ...
as a PDF
... glucose transport system. The amino acids can be obtained from three main sources: biosynthesis from metabolic precursors, active transport from the medium and protein degradation. Proteins could be incorporated from the surrounding medium by pynocitosis [24] and kept in reservosomes. A general sche ...
... glucose transport system. The amino acids can be obtained from three main sources: biosynthesis from metabolic precursors, active transport from the medium and protein degradation. Proteins could be incorporated from the surrounding medium by pynocitosis [24] and kept in reservosomes. A general sche ...
Genetic engineering of lactic acid bacteria to produce
... the general secretory pathway surface layer homology domain teichoic acid twin-arginine translocation pathway transmembrane domain transmembrane segment teichuronic acid cell wall polysaccharides WXG100 secretion system wall teichoic acid ...
... the general secretory pathway surface layer homology domain teichoic acid twin-arginine translocation pathway transmembrane domain transmembrane segment teichuronic acid cell wall polysaccharides WXG100 secretion system wall teichoic acid ...
Glycolysis
... Hexokinase, Phosphofructokinase & Pyruvate Kinase. Local control of metabolism involves regulatory effects of varied concentrations of pathway substrates or intermediates, to benefit the cell. Global control is for the benefit of the whole organism, & often involves hormone-activated signal casc ...
... Hexokinase, Phosphofructokinase & Pyruvate Kinase. Local control of metabolism involves regulatory effects of varied concentrations of pathway substrates or intermediates, to benefit the cell. Global control is for the benefit of the whole organism, & often involves hormone-activated signal casc ...
Glycolysis
... Hexokinase, Phosphofructokinase & Pyruvate Kinase. Local control of metabolism involves regulatory effects of varied concentrations of pathway substrates or intermediates, to benefit the cell. Global control is for the benefit of the whole organism, & often involves hormone-activated signal casc ...
... Hexokinase, Phosphofructokinase & Pyruvate Kinase. Local control of metabolism involves regulatory effects of varied concentrations of pathway substrates or intermediates, to benefit the cell. Global control is for the benefit of the whole organism, & often involves hormone-activated signal casc ...
12. Molecular Recognition: The Thermodynamics of
... Figure 12.6 Binding isotherm for estrogen binding to its receptor. (A) The generation of a binding isotherm relies on a method for detecting how much ligand is bound to the protein at any given concentration of ligand. There are many different ways of determining the extent of binding, and any such ...
... Figure 12.6 Binding isotherm for estrogen binding to its receptor. (A) The generation of a binding isotherm relies on a method for detecting how much ligand is bound to the protein at any given concentration of ligand. There are many different ways of determining the extent of binding, and any such ...
Potassium starvation responses in yeast highlight novel potassium-related functions
... especially for microorganisms. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been used over the years as a model organism for study the processes that control intracellular cation levels. Potassium is the major intracellular cation in yeast and it has been associated with various relevant cellular processe ...
... especially for microorganisms. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been used over the years as a model organism for study the processes that control intracellular cation levels. Potassium is the major intracellular cation in yeast and it has been associated with various relevant cellular processe ...
709_2010_211_MOESM2_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
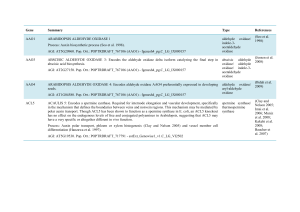
... RESPONSE REGULATOR 6: Encodes a Type-A response regulator that is responsive to cytokinin treatment. Its C-ter domain is very short in comparison to other Arabidopsis ARRs (17 total). Arr6 protein is stabilized by cytokinin. Process: Cytokinin mediated signaling pathway (Hwang et al. 2002; To et al. ...
... RESPONSE REGULATOR 6: Encodes a Type-A response regulator that is responsive to cytokinin treatment. Its C-ter domain is very short in comparison to other Arabidopsis ARRs (17 total). Arr6 protein is stabilized by cytokinin. Process: Cytokinin mediated signaling pathway (Hwang et al. 2002; To et al. ...
5 Molecular basis of type-2 diabetes
... Insulin stimulates the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/ extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). This pathway involves the tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS proteins and/or Shc, which in turn interact with the adapter protein Grb2, recruiting the Son-of-sevenless (SOS) exchange protein to t ...
... Insulin stimulates the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/ extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). This pathway involves the tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS proteins and/or Shc, which in turn interact with the adapter protein Grb2, recruiting the Son-of-sevenless (SOS) exchange protein to t ...
Engineering Acetyl Coenzyme A Supply: Functional Expression of a
... the mitochondrial matrix. However, in this yeast, acetyl-CoA generated in the mitochondrion cannot meet the requirement for cytosolic acetyl-CoA. Instead, a separate pathway known as the pyruvate dehydrogenase bypass, which involves pyruvate decarboxylase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, and acetyl-CoA ...
... the mitochondrial matrix. However, in this yeast, acetyl-CoA generated in the mitochondrion cannot meet the requirement for cytosolic acetyl-CoA. Instead, a separate pathway known as the pyruvate dehydrogenase bypass, which involves pyruvate decarboxylase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, and acetyl-CoA ...