Calvin Cycle Answers
... 3. Because it needs to happen 3 times to fix enough carbon for 1 PGA/G3P. 4. Because it catalyzes 2 reactions – reduction of RuBP and regeneration of RuBP so CO2 and O2 are competing for the same active site. 5. The light reactions: cyclic and non-cyclic electron pathways. 6. NADPH is oxidized. PGAP ...
... 3. Because it needs to happen 3 times to fix enough carbon for 1 PGA/G3P. 4. Because it catalyzes 2 reactions – reduction of RuBP and regeneration of RuBP so CO2 and O2 are competing for the same active site. 5. The light reactions: cyclic and non-cyclic electron pathways. 6. NADPH is oxidized. PGAP ...
Topic I Cells - JSH Elective Science with Ms. Barbanel
... Cellular Transport • In order to survive, cells must: • Move needed materials in (nutrients, oxygen, water) • Move out toxic materials that accumulate in the cell (carbon dioxide and nitrogenous wastes) • Secrete specific materials • Cells have selectively permeable membranes, meaning they will all ...
... Cellular Transport • In order to survive, cells must: • Move needed materials in (nutrients, oxygen, water) • Move out toxic materials that accumulate in the cell (carbon dioxide and nitrogenous wastes) • Secrete specific materials • Cells have selectively permeable membranes, meaning they will all ...
Supporting Information S1 Metabolic Subsystems How the enzymes
... intensive studies of protein-protein interactions have shown that the internal cellular medium is an assembly of supra-molecular protein complexes [3], e.g., the analyses of the proteome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae have shown that at least 83% of all proteins form complexes (containing from two to e ...
... intensive studies of protein-protein interactions have shown that the internal cellular medium is an assembly of supra-molecular protein complexes [3], e.g., the analyses of the proteome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae have shown that at least 83% of all proteins form complexes (containing from two to e ...
lecture1
... Substantial biochemical efforts are needed in order to understand the choice of enzyme in the context of the process or products desired. This required fundamental research efforts into classical parameters of enzyme kinetics under working condition such as pH and temperature optimum, Km, Vmax, pres ...
... Substantial biochemical efforts are needed in order to understand the choice of enzyme in the context of the process or products desired. This required fundamental research efforts into classical parameters of enzyme kinetics under working condition such as pH and temperature optimum, Km, Vmax, pres ...
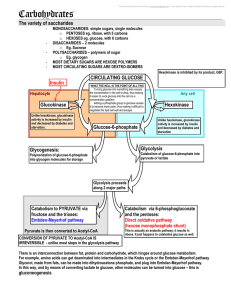
5 carbohydrates and the Krebs Cycle
... WHAT THE HELL IS THE POINT OF ALL THIS Turning glucose into something else causes the concentration in the cell to drop, thus making it easier to suck glucose into the cell via a ...
... WHAT THE HELL IS THE POINT OF ALL THIS Turning glucose into something else causes the concentration in the cell to drop, thus making it easier to suck glucose into the cell via a ...
Supplementary Material
... will diminish due to the reduced supply of NAD+ from the electron transfer chain caused by hypoxia. It is worth noting that glycolysis pathway can also be fueled by glutamate and glutamine through glutaminolysis via a section of the TCA cycle 24. Our analysis clearly shows that the accumulation of g ...
... will diminish due to the reduced supply of NAD+ from the electron transfer chain caused by hypoxia. It is worth noting that glycolysis pathway can also be fueled by glutamate and glutamine through glutaminolysis via a section of the TCA cycle 24. Our analysis clearly shows that the accumulation of g ...
Toll/Imd pathways link to insects cellular immune response via
... Insects utilize innate immune response exclusively which are divided into humoral and cellular reaction. Humoral immunity contains antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) systhesis and plasma melanization by phenoloxidase (PO) activity. Cellular immunity contains phagocytosis, nodule formation and encapsulati ...
... Insects utilize innate immune response exclusively which are divided into humoral and cellular reaction. Humoral immunity contains antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) systhesis and plasma melanization by phenoloxidase (PO) activity. Cellular immunity contains phagocytosis, nodule formation and encapsulati ...
UNIT 7 Metabolism and generation of ATP
... nearly through the interior of the mitochondrion. Understanding the function of the inner mitochondrial membrane is a key to understanding how the mitochondrion works. Processes occurring inside the mitochondrial matrix include pyruvate oxidation, fatty acid oxidation, amino acid metabolism, and the ...
... nearly through the interior of the mitochondrion. Understanding the function of the inner mitochondrial membrane is a key to understanding how the mitochondrion works. Processes occurring inside the mitochondrial matrix include pyruvate oxidation, fatty acid oxidation, amino acid metabolism, and the ...
Protocol S11 – Experimental validations of functional
... annotated and orphan gene sets putatively linked to either cell wall assembly or protein translation (see Table S18). The annotated gene sets were represented by the positive gold standards generated for the COGs function terms “M -Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis” and “J-Translation/ribosomal ...
... annotated and orphan gene sets putatively linked to either cell wall assembly or protein translation (see Table S18). The annotated gene sets were represented by the positive gold standards generated for the COGs function terms “M -Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis” and “J-Translation/ribosomal ...
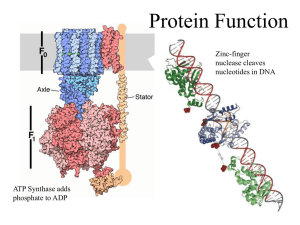
Protein Function - Gleason Chemistry
... • Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up more than a third of the body’s protein. • Composed of 3 chains in a helix. The sequence normally follows the pattern “Gly-Pro-X” and can span over 1,400 residues per chain. • It is the major structural protein of connective tissues (e.g. ...
... • Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up more than a third of the body’s protein. • Composed of 3 chains in a helix. The sequence normally follows the pattern “Gly-Pro-X” and can span over 1,400 residues per chain. • It is the major structural protein of connective tissues (e.g. ...
Functional genomics: assigning functions to genome sequences
... Functional linkages relate all 3 components of cytochrome oxidase complex and also CtaB, the cytochrome oxidase assembly factor These genes are at four different chromosomal locations Membrane proteins linked to soluble proteins ...
... Functional linkages relate all 3 components of cytochrome oxidase complex and also CtaB, the cytochrome oxidase assembly factor These genes are at four different chromosomal locations Membrane proteins linked to soluble proteins ...
Crosstalk between Notch signaling Pathway and Glutamine uptake
... T cells controls the adaptive immune response and are critical for immunological memory. When quiescent naive T cells are stimulated by an antigen, they are activated, which causes cell growth, proliferation and cytokine production (Smith-Garvin. 2009[1] ). One of the main adaptations during T cell ...
... T cells controls the adaptive immune response and are critical for immunological memory. When quiescent naive T cells are stimulated by an antigen, they are activated, which causes cell growth, proliferation and cytokine production (Smith-Garvin. 2009[1] ). One of the main adaptations during T cell ...
幻灯片 1
... and occupy distinct zones where the environmental conditions favour their specific activities. ...
... and occupy distinct zones where the environmental conditions favour their specific activities. ...
Slides
... • GADD45 was initially identified as a gene whose transcription rapidly increases in cells treated with DNA-damage causing agents. • Takekawa and Saito previously isolated three GADD45-like cDNAs (GADD45α, GADD45β, and GADD45γ) that encode for three similar proteins that bind to MAP3K4. – MAP3K4 med ...
... • GADD45 was initially identified as a gene whose transcription rapidly increases in cells treated with DNA-damage causing agents. • Takekawa and Saito previously isolated three GADD45-like cDNAs (GADD45α, GADD45β, and GADD45γ) that encode for three similar proteins that bind to MAP3K4. – MAP3K4 med ...
www.invertebrate.us
... Use second messengers, therefore, take longer to create the response Also, the response lasts longer In addition to working on ion channels, these responses may modify existing cell proteins or regulate the production of new cell proteins Found in growth and development of neurons and may be a mecha ...
... Use second messengers, therefore, take longer to create the response Also, the response lasts longer In addition to working on ion channels, these responses may modify existing cell proteins or regulate the production of new cell proteins Found in growth and development of neurons and may be a mecha ...
Biology Cells Lecture B. Rife SOHI 2001
... - conversion of energy from one form to another Support, movement, and communication: Cytoskeleton, Cell walls, Cell surfaces, Cell junctions - relationships with extracellular environments Within each of the four categories there are structural similarities that underlie their functions. All four c ...
... - conversion of energy from one form to another Support, movement, and communication: Cytoskeleton, Cell walls, Cell surfaces, Cell junctions - relationships with extracellular environments Within each of the four categories there are structural similarities that underlie their functions. All four c ...
BOTANY DEPARTMENT - university of nairobi staff profiles
... Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactions. Evaluate the function of A ...
... Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactions. Evaluate the function of A ...
Assessing the Impact of Autophagy on Cellular Metabolism
... Autophagy is a highly conserved, homeostatic degradation pathway that involves the breaking down and salvaging of cellular components. Autophagy is a pro-survival process that involves the digestion and recycling of damaged or exhausted organelles, or other cellular components via lysosomes. First d ...
... Autophagy is a highly conserved, homeostatic degradation pathway that involves the breaking down and salvaging of cellular components. Autophagy is a pro-survival process that involves the digestion and recycling of damaged or exhausted organelles, or other cellular components via lysosomes. First d ...
Gene Section SRSF3 (serine/arginine rich splicing factor 3) -
... Diagram of protein structure of SRSF3. The numbers below the diagram are the amino acid positions in SRSF3 protein. SRSF3 has an RNA recognition motifs (RRM) in the N-terminus and an arginine/serine-rich domain (RS) at the C-terminus. RRM motif identifies and binds specific RNA sequences. RS domain ...
... Diagram of protein structure of SRSF3. The numbers below the diagram are the amino acid positions in SRSF3 protein. SRSF3 has an RNA recognition motifs (RRM) in the N-terminus and an arginine/serine-rich domain (RS) at the C-terminus. RRM motif identifies and binds specific RNA sequences. RS domain ...
TOPIC B1: CELL LEVEL SYSTEMS B1.3 RESPIRATION
... By the end of this unit you should be able to: ...
... By the end of this unit you should be able to: ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Materials
... O. Vacuoles are the largest organelle in plants taking up most of the space 1. Serves as a storage area for proteins, ions, wastes, and cell products such as glucose 2. May contain poisons to keep animals from eating them 3. Animal vacuoles are smaller & used for digestion P. Cytoskeleton consists ...
... O. Vacuoles are the largest organelle in plants taking up most of the space 1. Serves as a storage area for proteins, ions, wastes, and cell products such as glucose 2. May contain poisons to keep animals from eating them 3. Animal vacuoles are smaller & used for digestion P. Cytoskeleton consists ...
Document
... is a bottleneck… In our pursuit to engage with experimentalists for lead discovery or optimization, our efforts become restricted in the absence of an experimental structure of the receptor protein/enzyme. When we analyze, it occurred to us that most of these ‘important target receptors’ whose struc ...
... is a bottleneck… In our pursuit to engage with experimentalists for lead discovery or optimization, our efforts become restricted in the absence of an experimental structure of the receptor protein/enzyme. When we analyze, it occurred to us that most of these ‘important target receptors’ whose struc ...
anatomi sistem saraf dan indera a
... within the cochlea) are stimulated by sound vibrations transmitted through air, membranes, and fluids • Deafness is any degree of hearing loss. Conduction deafness results when the transmission of sound vibrations through the external and middle ears is hindered. Sensorineural deafness occurs when t ...
... within the cochlea) are stimulated by sound vibrations transmitted through air, membranes, and fluids • Deafness is any degree of hearing loss. Conduction deafness results when the transmission of sound vibrations through the external and middle ears is hindered. Sensorineural deafness occurs when t ...