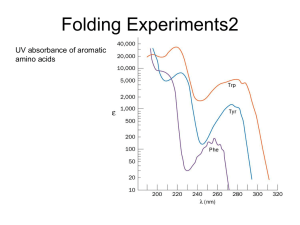
Protein Structure:
... 1. Proteins are linear polymers built of monomer units called amino acids. The construction of a vast array of macromolecules from a limited number of monomer building blocks is a recurring theme in biochemistry. Does protein function depend on the linear sequence of amino acids? The function of a p ...
... 1. Proteins are linear polymers built of monomer units called amino acids. The construction of a vast array of macromolecules from a limited number of monomer building blocks is a recurring theme in biochemistry. Does protein function depend on the linear sequence of amino acids? The function of a p ...
Antibody
... Protein Purification • The purification of proteins is an essential first step in understanding their function. • Purification should yield a sample of protein containing only one type of molecule of interest. • Proteins can be separated from one another on the basis of solubility, size, charge, an ...
... Protein Purification • The purification of proteins is an essential first step in understanding their function. • Purification should yield a sample of protein containing only one type of molecule of interest. • Proteins can be separated from one another on the basis of solubility, size, charge, an ...
DNA sequence of Exenatide to be prepared using Phosphoramidite
... of Chemical DNA Synthesis, based on its known amino acid sequence. To create the unstructured polypeptide XTEN, pairs of randomised 36 nucleotide DNA fragments encoding only for the amino acids A,E,G,P,S,T must be designed to form AGGT overhangs and subjected to ligation. Other amino acids avoided d ...
... of Chemical DNA Synthesis, based on its known amino acid sequence. To create the unstructured polypeptide XTEN, pairs of randomised 36 nucleotide DNA fragments encoding only for the amino acids A,E,G,P,S,T must be designed to form AGGT overhangs and subjected to ligation. Other amino acids avoided d ...
Recombinant Hepatitis B Surface Antigen, ayw
... Recombinant Hepatitis B Surface Antigen, ayw subtype (rHBsAg, ayw) CLHBS870 CLHBS870-2 CLHBS870-3 Introduction: HBsAg is the surface antigen of the Hepatitis-B-Virus (HBV). The capsid of a virus has different surface proteins from the rest of the virus. The antigen is a protein that binds specifical ...
... Recombinant Hepatitis B Surface Antigen, ayw subtype (rHBsAg, ayw) CLHBS870 CLHBS870-2 CLHBS870-3 Introduction: HBsAg is the surface antigen of the Hepatitis-B-Virus (HBV). The capsid of a virus has different surface proteins from the rest of the virus. The antigen is a protein that binds specifical ...
Techniques in Protein Biochemistry
... Cells are disrupted to form a homogenate, which is a mixture of all of the components of the cell, but no intact cells. The homogenate is then centrifuged at low speed to yield a pellet consisting of nuclei and a supernatant. This supernatant is then centrifuged at a higher centrifugal force to y ...
... Cells are disrupted to form a homogenate, which is a mixture of all of the components of the cell, but no intact cells. The homogenate is then centrifuged at low speed to yield a pellet consisting of nuclei and a supernatant. This supernatant is then centrifuged at a higher centrifugal force to y ...
protein - 4J Blog Server
... • How the sequence and subcomponents of proteins determine their properties. • The cellular functions of proteins. (Brief – we will come back to this in other chapters.) • The four structural levels of proteins and how changes at any level can affect the activity of the protein. • How proteins reach ...
... • How the sequence and subcomponents of proteins determine their properties. • The cellular functions of proteins. (Brief – we will come back to this in other chapters.) • The four structural levels of proteins and how changes at any level can affect the activity of the protein. • How proteins reach ...
生物物理学 I Handout No. 2 ① ② ③ ④ ⑤
... a solute. The carrier protein shown can exist in two conformational states: in state "pong" the binding sites for solute A are exposed on the outside of the bilayer; in state "ping" the same sites are exposed on the other side of the bilayer. The transition between the two states is proposed to occu ...
... a solute. The carrier protein shown can exist in two conformational states: in state "pong" the binding sites for solute A are exposed on the outside of the bilayer; in state "ping" the same sites are exposed on the other side of the bilayer. The transition between the two states is proposed to occu ...
Document
... bond to give mixed disulfide) 2) Protein SH attacks protein-PDI mixed S-S bond to give protein S-S bond 3) Continues until protein in native S-S configuration and PDI cannot bind to exposed hydrophobic patches on the protein ...
... bond to give mixed disulfide) 2) Protein SH attacks protein-PDI mixed S-S bond to give protein S-S bond 3) Continues until protein in native S-S configuration and PDI cannot bind to exposed hydrophobic patches on the protein ...
Lab Techniques for Systems Biology
... Select a gene from a genome. Make lots of that gene. Insert the gene into a vector. Insert the vector into a cell. The cell makes lots of the protein. Purify the protein. Perform quality control. ...
... Select a gene from a genome. Make lots of that gene. Insert the gene into a vector. Insert the vector into a cell. The cell makes lots of the protein. Purify the protein. Perform quality control. ...
Ch7 Membranes homework
... fluid. The hydrophobic _______ face each other. Another type of lipid present in the plasma membrane is _______________ which stabilizes membrane fluidity. The proteins found in the plasma membrane may be ____________ proteins, which penetrate the membrane, or _____________ proteins, which occur eit ...
... fluid. The hydrophobic _______ face each other. Another type of lipid present in the plasma membrane is _______________ which stabilizes membrane fluidity. The proteins found in the plasma membrane may be ____________ proteins, which penetrate the membrane, or _____________ proteins, which occur eit ...
PowerPoint Slides
... All alpha proteins All beta proteins Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) Alpha and beta proteins (a+b) Multi-domain proteins Membrane and cell surface proteins Small proteins ...
... All alpha proteins All beta proteins Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) Alpha and beta proteins (a+b) Multi-domain proteins Membrane and cell surface proteins Small proteins ...
Enzyme Regulation - University of San Diego Home Pages
... - most kinases are regulated - phosphatases generally not regulated - can lead to large amplification of original signal Four general classes of protein kinases, based on substrate (both sequence and amino acid phosphorylated), homology and regulation mechanisms (thousands of kinases) Protein Kinase ...
... - most kinases are regulated - phosphatases generally not regulated - can lead to large amplification of original signal Four general classes of protein kinases, based on substrate (both sequence and amino acid phosphorylated), homology and regulation mechanisms (thousands of kinases) Protein Kinase ...
lecture notes endomembrane system 1
... whereas the ER extends from the nucleus far out into the cytosol. Organelle positioning is highly dependent on the cytoskeleton, and disruption of the cytoskeleton leads to breakdown of the internal organisation of the organelles. How proteins move between compartments. ...
... whereas the ER extends from the nucleus far out into the cytosol. Organelle positioning is highly dependent on the cytoskeleton, and disruption of the cytoskeleton leads to breakdown of the internal organisation of the organelles. How proteins move between compartments. ...
Recall basic cell physiology
... Extracellular matrix - Biological “glue.” 3 protein fibers are interwoven in this matrix: collagen, elastin, fibronectin. Secreted by cells Desmosomes – “Rivets” to anchor adjacent cells that are not touching ...
... Extracellular matrix - Biological “glue.” 3 protein fibers are interwoven in this matrix: collagen, elastin, fibronectin. Secreted by cells Desmosomes – “Rivets” to anchor adjacent cells that are not touching ...
lab2 precipitation of casein at isoelectric point
... PH = Pka + log{ (casein acetate sodium )÷ (acetic acid)} Maximum precipitation can be obtained at the isoelectric point by addition of some reagents such as, ethanol which dehydrates the molecule and allow neutralization of charge ...
... PH = Pka + log{ (casein acetate sodium )÷ (acetic acid)} Maximum precipitation can be obtained at the isoelectric point by addition of some reagents such as, ethanol which dehydrates the molecule and allow neutralization of charge ...
Lecture 1: Fundamentals of Protein Structure
... • Evolution conserves amino acids that are important to protein structure and function across species. Sequence comparison of multiple “homologs” of a particular protein reveals highly ...
... • Evolution conserves amino acids that are important to protein structure and function across species. Sequence comparison of multiple “homologs” of a particular protein reveals highly ...
When it comes to reliable automation of protein digestion for LC and
... protein digestion followed by sample preparation for LC-MS, the choice is simple. The ProPrep LC is the only instrument that has been specifically designed for this purpose. The ProPrep LC gives you peace of mind and your samples the best treatment. The ProPrep LC comes standard with one reaction bl ...
... protein digestion followed by sample preparation for LC-MS, the choice is simple. The ProPrep LC is the only instrument that has been specifically designed for this purpose. The ProPrep LC gives you peace of mind and your samples the best treatment. The ProPrep LC comes standard with one reaction bl ...
Three Dimensional Protein Structures
... Glu) are normally located on the surface of the protein in contact with water. • Uncharged polar residues (Ser, Thr, Asn, Gln, and Tyr) are usually on the protein surface but also occur in the interior of the protein. ...
... Glu) are normally located on the surface of the protein in contact with water. • Uncharged polar residues (Ser, Thr, Asn, Gln, and Tyr) are usually on the protein surface but also occur in the interior of the protein. ...
Biochemistry Chapter 17
... contain almost every vitamin and mineral you need. The egg white or albumen contains lots of protein (ovalbumin) and not much else. The egg yolk contains all of the fat and most of the other nutrients found in eggs. It is also high in protein (livetin). ...
... contain almost every vitamin and mineral you need. The egg white or albumen contains lots of protein (ovalbumin) and not much else. The egg yolk contains all of the fat and most of the other nutrients found in eggs. It is also high in protein (livetin). ...
LS1a Fall 09
... Section Activity #3: You have developed a cell-free (“in vitro”) translation system to study the players involved in the translation of secreted proteins. A series of control experiments are shown below. Microsomes are vesicles derived from ER membranes. Protein X is a known peptide hormone that is ...
... Section Activity #3: You have developed a cell-free (“in vitro”) translation system to study the players involved in the translation of secreted proteins. A series of control experiments are shown below. Microsomes are vesicles derived from ER membranes. Protein X is a known peptide hormone that is ...
Proteins - Boardworks
... Proteins are a diverse group of large and complex polymer molecules, made up of long chains of amino acids. They have a wide range of biological roles, including: ...
... Proteins are a diverse group of large and complex polymer molecules, made up of long chains of amino acids. They have a wide range of biological roles, including: ...
PDF
... dye following registration by a laser scanner [4]. Expression Proteomics is based on 2-dimensional (2-D) gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. 2-D gel electrophoresis allows the separation of thousands of proteins by isoelectrofocusing followed by electrophoresis in gradient polyacrylamide gel ...
... dye following registration by a laser scanner [4]. Expression Proteomics is based on 2-dimensional (2-D) gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. 2-D gel electrophoresis allows the separation of thousands of proteins by isoelectrofocusing followed by electrophoresis in gradient polyacrylamide gel ...
Protein purification
Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells, tissues or whole organisms. Protein purification is vital for the characterization of the function, structure and interactions of the protein of interest. The purification process may separate the protein and non-protein parts of the mixture, and finally separate the desired protein from all other proteins. Separation of one protein from all others is typically the most laborious aspect of protein purification. Separation steps usually exploit differences in protein size, physico-chemical properties, binding affinity and biological activity. The pure result may be termed protein isolate.The methods used in protein purification can roughly be divided into analytical and preparative methods. The distinction is not exact, but the deciding factor is the amount of protein that can practically be purified with that method. Analytical methods aim to detect and identify a protein in a mixture, whereas preparative methods aim to produce large quantities of the protein for other purposes, such as structural biology or industrial use. In general, the preparative methods can be used in analytical applications, but not the other way around.