simCT_RT - University of Washington
... • For every camera line-ofresponse, step a beam through the voxelized object. – Steps can be constant size or to next boundary. ...
... • For every camera line-ofresponse, step a beam through the voxelized object. – Steps can be constant size or to next boundary. ...
MR Detection of Acoustic Neuromas
... internal auditory canal may opt for a conservative approach. As these tumors typically grow very slowly (on average 1.5 mm/ year) it may take many years for a lesion to threaten life or bodily function. In these cases, periodic monitoring with audiometry and MR imaging is usually performed. Approxim ...
... internal auditory canal may opt for a conservative approach. As these tumors typically grow very slowly (on average 1.5 mm/ year) it may take many years for a lesion to threaten life or bodily function. In these cases, periodic monitoring with audiometry and MR imaging is usually performed. Approxim ...
IMAGE GUIDED THERAPY FELLOW REPORT
... ExAblate 3000 system Collected data to establish the basis for later studies that will evaluate ExAblate 3000 Clinical efficacy ...
... ExAblate 3000 system Collected data to establish the basis for later studies that will evaluate ExAblate 3000 Clinical efficacy ...
Imaging e Radioterapia
... Image-guided RT: modern linear accelerators have integrated X-ray imaging devices and conebeam CT scanners, making it possible to verify tumor position before and during treatment. The ability to check the tumor position during treatment allows for smaller safety margins and better sparing of normal ...
... Image-guided RT: modern linear accelerators have integrated X-ray imaging devices and conebeam CT scanners, making it possible to verify tumor position before and during treatment. The ability to check the tumor position during treatment allows for smaller safety margins and better sparing of normal ...
X-RAY - lucascarter
... • x-ray radiography (to find orthopedic damage, tumors, pneumonias, foreign objects, etc); • mammography1 (to image the internal structures of breasts) • CT (computed tomography)2 (to produce crosssectional images of the body) • fluoroscopy3 (to dynamically visualize the body for example to see wher ...
... • x-ray radiography (to find orthopedic damage, tumors, pneumonias, foreign objects, etc); • mammography1 (to image the internal structures of breasts) • CT (computed tomography)2 (to produce crosssectional images of the body) • fluoroscopy3 (to dynamically visualize the body for example to see wher ...
Pledge for Imaging Professionals
... To put my patients’ safety, health, and welfare first by optimizing imaging examinations to use only the radiation necessary to produce diagnostic-quality images; ...
... To put my patients’ safety, health, and welfare first by optimizing imaging examinations to use only the radiation necessary to produce diagnostic-quality images; ...
Bone Mineral Density Patient X
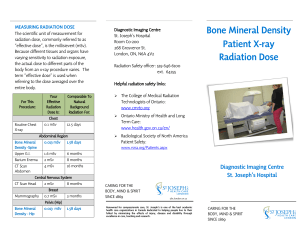
... Renowned for compassionate care, St. Joseph’s is one of the best academic health care organizations in Canada dedicated to helping people live to their fullest by minimizing the effects of injury, disease and disability through excellence in care, teaching and research. ...
... Renowned for compassionate care, St. Joseph’s is one of the best academic health care organizations in Canada dedicated to helping people live to their fullest by minimizing the effects of injury, disease and disability through excellence in care, teaching and research. ...
IGRT in CMUH
... Delivering higher doses to the tumor Maintaining acceptable doses to critical OAR Allow for dose escalation ...
... Delivering higher doses to the tumor Maintaining acceptable doses to critical OAR Allow for dose escalation ...
AHM 244 PowerPoint
... Creates cross-sectional still views or views in real time movement with help of a computer ...
... Creates cross-sectional still views or views in real time movement with help of a computer ...
An immobilization and localization technique for SRT and IMRT of
... repositioning on the order of 1 mm. The proposed system for patient localization and immobilization uses all the advantages of the SRT immobilization and localization methods 共1 mm accuracy, noninvasiveness, day-to-day patient position verification with the Depth Helmet兲. Both SRT and IMRT can be us ...
... repositioning on the order of 1 mm. The proposed system for patient localization and immobilization uses all the advantages of the SRT immobilization and localization methods 共1 mm accuracy, noninvasiveness, day-to-day patient position verification with the Depth Helmet兲. Both SRT and IMRT can be us ...
Phantom and in vivo measurements of dose exposure by image
... treatment of cancerous cells with ionizing radiation High energy x-rays in the megavolt MV range ...
... treatment of cancerous cells with ionizing radiation High energy x-rays in the megavolt MV range ...
Hendee's Radiation Therapy Physics. 4th Edition Brochure
... (IMRT) has become a routine method of radiation treatment delivery, digital imaging has replaced film–screen imaging for localization and verification, image–guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is frequently used, in many centers proton therapy has become a viable mode of radiation therapy, new approach ...
... (IMRT) has become a routine method of radiation treatment delivery, digital imaging has replaced film–screen imaging for localization and verification, image–guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is frequently used, in many centers proton therapy has become a viable mode of radiation therapy, new approach ...
AbstractID: 10105 Title: Managing the Imaging Dose during Image-Guided Radiation Therapy
... AbstractID: 10105 Title: Managing the Imaging Dose during Image-Guided Radiation Therapy Radiographic image guidance has emerged as the new paradigm for patient positioning, target localization, and external beam alignment in radiotherapy. Today, image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) can involve 3DCT for ...
... AbstractID: 10105 Title: Managing the Imaging Dose during Image-Guided Radiation Therapy Radiographic image guidance has emerged as the new paradigm for patient positioning, target localization, and external beam alignment in radiotherapy. Today, image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) can involve 3DCT for ...
Energy selective computed tomography: a potential revolution for
... sections (e.g., the effective atomic number, the mean excitation energy, etc.). What makes proton therapy different from common radiotherapy which uses photons (i.e., X-ray or gammarays) is the fact that the beam stops at a certain range in the patient instead of being gradually attenuated until lea ...
... sections (e.g., the effective atomic number, the mean excitation energy, etc.). What makes proton therapy different from common radiotherapy which uses photons (i.e., X-ray or gammarays) is the fact that the beam stops at a certain range in the patient instead of being gradually attenuated until lea ...
IMAGE GUIDED RADIATION THERAPY (IGRT)
... (protons)) Placed Inside a powerful magnetic field protons align with the direction of the magnetic field Additional RF electromagnetic field is briefly turned on causing the protons to absorb some of its energy When this field is turned off protons release this energy at radio frequency which is th ...
... (protons)) Placed Inside a powerful magnetic field protons align with the direction of the magnetic field Additional RF electromagnetic field is briefly turned on causing the protons to absorb some of its energy When this field is turned off protons release this energy at radio frequency which is th ...
Nuclear Medicine Primer What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear
... (ie. Gallium-67 for gut transit studies – 78 hours). Additionally, not all radioisotopes can be used with all ligands due to their chemical properties. Gallium 67 cannot be attached to MDP or Sestamibi. Technetium-99m is the most widely used radioisotope because it can be easily attached to a vast a ...
... (ie. Gallium-67 for gut transit studies – 78 hours). Additionally, not all radioisotopes can be used with all ligands due to their chemical properties. Gallium 67 cannot be attached to MDP or Sestamibi. Technetium-99m is the most widely used radioisotope because it can be easily attached to a vast a ...
Medical Physics-Radiation Physics (Spring Semester)
... statistical measurements, atomic and nuclear structure, radioactive decay with emphasis on radioactive sources used in biomedical sciences, Interaction of ionizing radiation-matter and its applications in Medicine and Radiation Protection, Quality assurance and quality control in medical laboratorie ...
... statistical measurements, atomic and nuclear structure, radioactive decay with emphasis on radioactive sources used in biomedical sciences, Interaction of ionizing radiation-matter and its applications in Medicine and Radiation Protection, Quality assurance and quality control in medical laboratorie ...
Slide 1
... developed by Georges Charpak, a Ukranian Scientist, which is able to detect individual photons. This counting mechanism is far more efficient than using film, which requires a greater number of photons to act on the ...
... developed by Georges Charpak, a Ukranian Scientist, which is able to detect individual photons. This counting mechanism is far more efficient than using film, which requires a greater number of photons to act on the ...
ISDE Resolution on Radiologic Risk from Medical Diagnostic Imaging
... Understanding that medical diagnostic radiation with (x and γ rays in radiology and nuclear medicine) is a proven class I carcinogen (1) even at the lowest doses; that the level of this exposure is continuously rising(2) and totals the dose equivalent to at least 100 chest x-rays per person per year ...
... Understanding that medical diagnostic radiation with (x and γ rays in radiology and nuclear medicine) is a proven class I carcinogen (1) even at the lowest doses; that the level of this exposure is continuously rising(2) and totals the dose equivalent to at least 100 chest x-rays per person per year ...
A B
... HPI: A 62-year-old right-handed male in his usual state of health, when he suddenly awoke in his home, screaming, and in a state of confusion. The family took him to the hospital where he had a grand mal seizure. Neuro-imaging revealed a 3-cm enhancing left temporal lobe mass. Two weeks later, he u ...
... HPI: A 62-year-old right-handed male in his usual state of health, when he suddenly awoke in his home, screaming, and in a state of confusion. The family took him to the hospital where he had a grand mal seizure. Neuro-imaging revealed a 3-cm enhancing left temporal lobe mass. Two weeks later, he u ...
Reliability Study of ExacTrac® System Image Isocenter Using an On
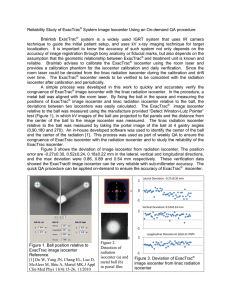
... technique to guide the initial patient setup, and uses kV x-ray imaging technique for target localization. It is important to know the accuracy of such system not only depends on the accuracy of image registration through bony anatomy or fiducial marks, but also depends on the assumption that the ge ...
... technique to guide the initial patient setup, and uses kV x-ray imaging technique for target localization. It is important to know the accuracy of such system not only depends on the accuracy of image registration through bony anatomy or fiducial marks, but also depends on the assumption that the ge ...