Selective Internal Radiation Therapy
... have the highest weighting factor (0.2) as they are the most sensitive to radiation, whilst skin is least sensitive (0.01) (total sum of weighting factors across all tissues = 1). Allows for comparison of radiation of different types to different regions ...
... have the highest weighting factor (0.2) as they are the most sensitive to radiation, whilst skin is least sensitive (0.01) (total sum of weighting factors across all tissues = 1). Allows for comparison of radiation of different types to different regions ...
Vascular and Interventional Radiology
... treatment is dismal. The median survival of such patients is only 6–9 months. ...
... treatment is dismal. The median survival of such patients is only 6–9 months. ...
Catalyst article on Medical Imaging
... broken bone. X-rays are particularly good at generating images of teeth and bones because they cannot pass easily through the calcium in these hard tissues. Bones and teeth absorb X-rays more than soft tissues, such as muscle and fat, so they show up on an X-ray image as shadows. In the 110 years si ...
... broken bone. X-rays are particularly good at generating images of teeth and bones because they cannot pass easily through the calcium in these hard tissues. Bones and teeth absorb X-rays more than soft tissues, such as muscle and fat, so they show up on an X-ray image as shadows. In the 110 years si ...
Released: 2/28/2008 5:40 PM EST Source: American Institute of
... In the last 50 years, medical physicists have spearheaded the development and application of particle accelerators for cancer treatment. Once confined only to physics laboratories, linear accelerators are sophisticated high energy machines that can now deliver beams of energetic electrons or X rays ...
... In the last 50 years, medical physicists have spearheaded the development and application of particle accelerators for cancer treatment. Once confined only to physics laboratories, linear accelerators are sophisticated high energy machines that can now deliver beams of energetic electrons or X rays ...
Iowa Institute for Biomedical Imaging PhD thesis defense 9:00 – 11
... Abstract: Cancer is the second deadliest disease in the United States with an estimated 1.69 million new cases in 2017. Medical imaging systems are widely used in clinical medicine to non-invasively identify, diagnosis, plan treatment, and monitor tumors within the body. Advances in imaging research ...
... Abstract: Cancer is the second deadliest disease in the United States with an estimated 1.69 million new cases in 2017. Medical imaging systems are widely used in clinical medicine to non-invasively identify, diagnosis, plan treatment, and monitor tumors within the body. Advances in imaging research ...
What is Nuclear Medicine?
... I131 (≤800 MBq for treatment of thyrotoxicosis): 4 months P32 (≤200 MBq for treatment of polycythemia): 3 months Sr89 (≤150 MBq for treatment of bone metastases): 24 months ...
... I131 (≤800 MBq for treatment of thyrotoxicosis): 4 months P32 (≤200 MBq for treatment of polycythemia): 3 months Sr89 (≤150 MBq for treatment of bone metastases): 24 months ...
Enlarged Axilary Lymph Nodes
... most consistent with adenocarcinoma. A breast primary would be most likely and since her mammogram was negative her surgeon ordered an MRI of both breasts which was also negative for any abnormalities in her breasts. There are no specific NCCN guidelines to search for unknown primary cancers, but im ...
... most consistent with adenocarcinoma. A breast primary would be most likely and since her mammogram was negative her surgeon ordered an MRI of both breasts which was also negative for any abnormalities in her breasts. There are no specific NCCN guidelines to search for unknown primary cancers, but im ...
Angie Gelli, Ph.D. - The Hartwell Foundation
... 80%. This high morbidity associated with surgery and radiation to treat brain tumors is unacceptable. In glioblastoma multiforme, the most common and most aggressive malignant primary brain tumor in children, the inability to deliver chemotherapeutic drugs into the brain is cited as the single most ...
... 80%. This high morbidity associated with surgery and radiation to treat brain tumors is unacceptable. In glioblastoma multiforme, the most common and most aggressive malignant primary brain tumor in children, the inability to deliver chemotherapeutic drugs into the brain is cited as the single most ...
Address of the donor - British Institute of Radiology
... “Choosing Wisely” initiative to encourage doctors to consider the value of treatments and avoid “over medicalising” patients. The BIR agrees that, for a range of reasons inappropriate clinical interventions are made which are not evidence based and which do not help with patient management or wellbe ...
... “Choosing Wisely” initiative to encourage doctors to consider the value of treatments and avoid “over medicalising” patients. The BIR agrees that, for a range of reasons inappropriate clinical interventions are made which are not evidence based and which do not help with patient management or wellbe ...
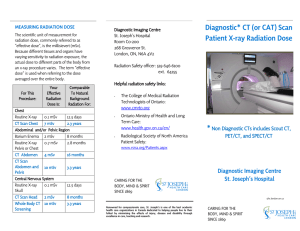
Diagnostic CT or CAT Scan Patient X
... machine. As they slowly slide out of the tunnel, they are exposed to x-rays originating from a source that circles around the body area being assessed (e.g. head and/or spine and/or hip). A detector circling the tunnel registers the x-rays penetrating the body area being imaged. Patients are scanned ...
... machine. As they slowly slide out of the tunnel, they are exposed to x-rays originating from a source that circles around the body area being assessed (e.g. head and/or spine and/or hip). A detector circling the tunnel registers the x-rays penetrating the body area being imaged. Patients are scanned ...
Positron Emission Tomography
... patient. Signal from detectors used by computer to build a functional image of organs such as the brain. ...
... patient. Signal from detectors used by computer to build a functional image of organs such as the brain. ...
Ervin B. Podgoršak, Recipient of the Coolidge
... own unique technique and called it dynamic stereotactic radiosurgery. We also introduced other techniques in radiotherapy treatment and radiation dosimetry, and this placed us on the forefront of medical physics in Canada as well as in North America in general. ...
... own unique technique and called it dynamic stereotactic radiosurgery. We also introduced other techniques in radiotherapy treatment and radiation dosimetry, and this placed us on the forefront of medical physics in Canada as well as in North America in general. ...
Drugs Today (Barc) - hem
... choline measured with (1)H MRS showed that in tumors a large fraction of the choline signal (>54 +/- 36%) was not accounted for by PC and GPC. The fraction of unaccounted choline was particularly large in PNET (>78 +/- 7%). The pH of tumor tissue was higher than the pH of normal brain tissue (7.06 + ...
... choline measured with (1)H MRS showed that in tumors a large fraction of the choline signal (>54 +/- 36%) was not accounted for by PC and GPC. The fraction of unaccounted choline was particularly large in PNET (>78 +/- 7%). The pH of tumor tissue was higher than the pH of normal brain tissue (7.06 + ...
EGTOGET Seminar Topics
... X-rays were discovered by the German physicist Will elm Konrad Rontgen in November 1895. He called the 'new kind of ray' or X-rays, X for the unknown. their usefulness to visualize the internal anatomy of humans was established. Today, imaging with X-rays is perhaps the most commonly used diagnostic ...
... X-rays were discovered by the German physicist Will elm Konrad Rontgen in November 1895. He called the 'new kind of ray' or X-rays, X for the unknown. their usefulness to visualize the internal anatomy of humans was established. Today, imaging with X-rays is perhaps the most commonly used diagnostic ...
Imaging Highlights
... • Used to visualize and examine internal body structures The three most common: 1.Radiography (x-ray) 2.Computed Tomography (CT) 3.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ...
... • Used to visualize and examine internal body structures The three most common: 1.Radiography (x-ray) 2.Computed Tomography (CT) 3.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ...
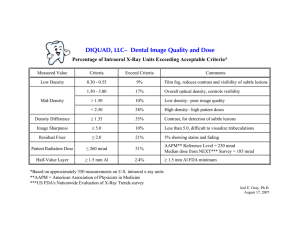
DIQUAD, LLC– Dental Image Quality and Dose
... this value—those using radiation exposures between 260 mR and 634 mR. It should be stressed that the median NEXT radiation exposure is 185 mR which means that some facilities are using radiation exposures which are 3.4 times higher than that used by the typical facility. According to the attached ta ...
... this value—those using radiation exposures between 260 mR and 634 mR. It should be stressed that the median NEXT radiation exposure is 185 mR which means that some facilities are using radiation exposures which are 3.4 times higher than that used by the typical facility. According to the attached ta ...
X-rays
... X-rays and γ-rays are ionizing waves, Such photons are able to ionize an atom, i.e., to release an electron from the atom. Even at very low X-ray doses the energy deposited by ionizing radiation, such as X-rays, may be sufficient to damage or destroy cells. We have two types of effects , Non det ...
... X-rays and γ-rays are ionizing waves, Such photons are able to ionize an atom, i.e., to release an electron from the atom. Even at very low X-ray doses the energy deposited by ionizing radiation, such as X-rays, may be sufficient to damage or destroy cells. We have two types of effects , Non det ...
Applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in radiotherapy
... imaging in improving the planning of radiotherapy for head and neck cancer [22, 23], and other important contributions on functional imaging [24, 25]. Two papers [26, 27] attempted to provide a clinical context for the use of imaging. Both suggested that, for follow-up at least, excessive imaging of ...
... imaging in improving the planning of radiotherapy for head and neck cancer [22, 23], and other important contributions on functional imaging [24, 25]. Two papers [26, 27] attempted to provide a clinical context for the use of imaging. Both suggested that, for follow-up at least, excessive imaging of ...
The Role of MRI in Radiation Treatment Planning
... Years of research and technological development have gone into CTtreatment planning ...
... Years of research and technological development have gone into CTtreatment planning ...
New Technologies in 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy: Introduction
... metastatic disease has yet occurred; thus, these patients can be considered to be potentially curable. Nevertheless, about one-third of these patients (18% of all cancer patients) cannot be cured, because therapy fails to stop tumor growth. This is the point where new technologies in radiation oncol ...
... metastatic disease has yet occurred; thus, these patients can be considered to be potentially curable. Nevertheless, about one-third of these patients (18% of all cancer patients) cannot be cured, because therapy fails to stop tumor growth. This is the point where new technologies in radiation oncol ...
20141201124090
... • During gamma decay, the atomic number and mass number of the atom remain the same, but the energy of the nucleus decreases. • Gamma often accompanies alpha or beta decay. • Gamma rays are much more penetrating than either alpha particles or beta particles. • It can take several centimeters of lead ...
... • During gamma decay, the atomic number and mass number of the atom remain the same, but the energy of the nucleus decreases. • Gamma often accompanies alpha or beta decay. • Gamma rays are much more penetrating than either alpha particles or beta particles. • It can take several centimeters of lead ...
Access to Information About Hazardous and Toxic Substances Act
... manufacturing and construction industries, radiographers and other radioisotope users. As an Atomic Energy Act Agreement State, Maryland has the state level authority to function exactly as the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission in issuing and inspecting RAM licenses and pursuing penalty assessments ...
... manufacturing and construction industries, radiographers and other radioisotope users. As an Atomic Energy Act Agreement State, Maryland has the state level authority to function exactly as the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission in issuing and inspecting RAM licenses and pursuing penalty assessments ...