Growth and gas exchange in field-grown and greenhouse
... year and the greenhouse allowed to assume natural photoperiods and near ambient temperatures. Watering and fertilization were also reduced during this time. Normal growing conditions were resumed the following May. Ultraviolet-B radiation treatments—greenhouse experiment Supplemental UV-B radiation ...
... year and the greenhouse allowed to assume natural photoperiods and near ambient temperatures. Watering and fertilization were also reduced during this time. Normal growing conditions were resumed the following May. Ultraviolet-B radiation treatments—greenhouse experiment Supplemental UV-B radiation ...
The Radiologic Assessment of Trigeminal Neuropathy
... variety of symptoms including facial pain , numbness, masticator muscle spasm and weakness, trismus, and trigeminal neuralgia. Lesions producing these symptoms may occur anywhere along the protracted course of the fifth cranial nerve from its distal facial ramifications to its nuclear columns in the ...
... variety of symptoms including facial pain , numbness, masticator muscle spasm and weakness, trismus, and trigeminal neuralgia. Lesions producing these symptoms may occur anywhere along the protracted course of the fifth cranial nerve from its distal facial ramifications to its nuclear columns in the ...
Part 1 - Canadian Association of Nuclear Medicine
... prostatectomy (Gleason score 8). Coronal (left), axial (middle), and sagittal (right) fused image projections of PET/CT scans. Focal 11C-choline uptake (a) in right (bold arrow) and left (thin arrow) iliac region revealed lymph node involvement, not observed with 18F-FDG PET (b). ...
... prostatectomy (Gleason score 8). Coronal (left), axial (middle), and sagittal (right) fused image projections of PET/CT scans. Focal 11C-choline uptake (a) in right (bold arrow) and left (thin arrow) iliac region revealed lymph node involvement, not observed with 18F-FDG PET (b). ...
CT Scanner Acceptance Testing
... Figure 8: Perspex (PMMA) Head and body phantoms for measurement of CTDI. Both phantoms are ≥ 140 mm in z-axis length. The body phantom placed on the patient table and the head phantom is supported in the head rest. Phantoms are aligned centred at the scan isocentre. The ion chamber is inserted into ...
... Figure 8: Perspex (PMMA) Head and body phantoms for measurement of CTDI. Both phantoms are ≥ 140 mm in z-axis length. The body phantom placed on the patient table and the head phantom is supported in the head rest. Phantoms are aligned centred at the scan isocentre. The ion chamber is inserted into ...
Acceptance Testing and Quality Control of Dental Imaging
... It is important to properly perform tests for image quality and safety purposes right after the installation and during routine operation of a dental x-ray unit. Having a quality control (QC) program for dental x-ray facilities is instrumental in ensuring that patients are not receiving excessive ra ...
... It is important to properly perform tests for image quality and safety purposes right after the installation and during routine operation of a dental x-ray unit. Having a quality control (QC) program for dental x-ray facilities is instrumental in ensuring that patients are not receiving excessive ra ...
dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging
... and/or edema or may be invaded by diffuse tumor growth. When perfusion is measured with other techniques (e.g. O15-PET, SPECT, and arterial spin labelling [ASL] MRI) the cerebellum has often been used as a reference region (10 –12). These techniques measure CBF but usually not CBV. Thus the measurem ...
... and/or edema or may be invaded by diffuse tumor growth. When perfusion is measured with other techniques (e.g. O15-PET, SPECT, and arterial spin labelling [ASL] MRI) the cerebellum has often been used as a reference region (10 –12). These techniques measure CBF but usually not CBV. Thus the measurem ...
Controlling exposure to ionising radiation in the medical imaging
... in which radioguided procedures are performed (cardiology, neurology, surgery, etc.). The first appraisal of ASN's inspections in interventional radiology, based on those carried out in 2009, reveals disparities in the implementation of radiation protection in healthcare establishments and in servic ...
... in which radioguided procedures are performed (cardiology, neurology, surgery, etc.). The first appraisal of ASN's inspections in interventional radiology, based on those carried out in 2009, reveals disparities in the implementation of radiation protection in healthcare establishments and in servic ...
09. Quality Assurance in Paediatric Radiological - RPOP
... imaging aims to ensure quality during all phases of the operation the service • One aspect of such programmes focuses on the operation of equipment, and is required by the BSS, many governments, the EU and recommended by numerous professional bodies • A quality assurance programme may be seen as par ...
... imaging aims to ensure quality during all phases of the operation the service • One aspect of such programmes focuses on the operation of equipment, and is required by the BSS, many governments, the EU and recommended by numerous professional bodies • A quality assurance programme may be seen as par ...
article in press - The EndoExperience
... diagnostics and surgery planning [1,2]. Conventional CT protocols are generally associated with relatively high radiation dose levels and even clinical protocols for multi-slice CT (MSCT) still show high doses [3,4]. The introduction of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) holds promising potential ...
... diagnostics and surgery planning [1,2]. Conventional CT protocols are generally associated with relatively high radiation dose levels and even clinical protocols for multi-slice CT (MSCT) still show high doses [3,4]. The introduction of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) holds promising potential ...
Finding the Great Mimicker: Pheochromocytoma
... *Focus on the navy box surrounding the difference benign and suspicious appearance of adrenal masses found on CT. These imaging characteristics often dictate appropriate subsequent biochemistry/surgical work up. From Young, WF. The Incidentally Discovered Adrenal Mass. New England Journal of Medicin ...
... *Focus on the navy box surrounding the difference benign and suspicious appearance of adrenal masses found on CT. These imaging characteristics often dictate appropriate subsequent biochemistry/surgical work up. From Young, WF. The Incidentally Discovered Adrenal Mass. New England Journal of Medicin ...
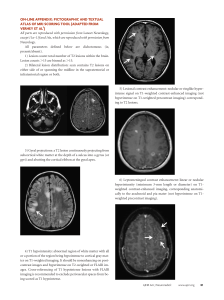
ON-LINE APPENDIX: PICTOGRAPHIC AND TEXTUAL ATLAS OF
... enhancement may be present in small-vessel primary angiitis of the CNS,11 in CNS infections,12,13 and in neoplasm,14 –16 but is not a feature of CNS demyelination. 7) Diffusion restriction: The presence of decreased diffusion supports the diagnosis of an arterial ischemic event,17-19 in which the cl ...
... enhancement may be present in small-vessel primary angiitis of the CNS,11 in CNS infections,12,13 and in neoplasm,14 –16 but is not a feature of CNS demyelination. 7) Diffusion restriction: The presence of decreased diffusion supports the diagnosis of an arterial ischemic event,17-19 in which the cl ...
radiation protection in diagnostic radiology
... collimation. Otherwise the patient would be over-irradiated, by receiving radiation over a larger volume. Irradiating a smaller volume also minimizes the amount of scattered radiation and improves image contrast. • When using equipment without automatic X Ray beam collimation, it should be verified ...
... collimation. Otherwise the patient would be over-irradiated, by receiving radiation over a larger volume. Irradiating a smaller volume also minimizes the amount of scattered radiation and improves image contrast. • When using equipment without automatic X Ray beam collimation, it should be verified ...
PET evaluation of fatty tumors in the extremity: Possibility of using
... Objective: The relative utility of various preoperative diagnostic imaging modalities, including PET (utilizing FDG and FMT), CT, and MR imaging, for evaluation of lipoma and liposarcoma, especially well-differentiated liposarcoma, was investigated. Methods: Imaging findings in 32 patients with hist ...
... Objective: The relative utility of various preoperative diagnostic imaging modalities, including PET (utilizing FDG and FMT), CT, and MR imaging, for evaluation of lipoma and liposarcoma, especially well-differentiated liposarcoma, was investigated. Methods: Imaging findings in 32 patients with hist ...
Medical Radioisotopes Production Without A Nuclear Reactor
... EMI, a company best known today for its music and recording business. It was later known as computed axial tomography (CAT or CT scan) and body section röntgenography. Although the term computed tomography could be used to describe positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tom ...
... EMI, a company best known today for its music and recording business. It was later known as computed axial tomography (CAT or CT scan) and body section röntgenography. Although the term computed tomography could be used to describe positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tom ...
radiation pressure cross section for fluffy aggregates
... computer simulations based on the assumption that the sticking probabilities are unity.53 The individual monomers forming the aggregates are assumed to be compact spheres identical in size and material composition. If the radius r. of the spherical monomer is larger than the wavelength of the incide ...
... computer simulations based on the assumption that the sticking probabilities are unity.53 The individual monomers forming the aggregates are assumed to be compact spheres identical in size and material composition. If the radius r. of the spherical monomer is larger than the wavelength of the incide ...
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS)
... necrotic tumors. In the prospective study, a 3-tesla MR unit was used to perform proton MR spectroscopy, diffusion and perfusion imaging in 20 patients with cerebral abscesses and 26 patients who had solitary brain tumors (14 high-grade gliomas and 12 metastases). The proton spectra obtained reveale ...
... necrotic tumors. In the prospective study, a 3-tesla MR unit was used to perform proton MR spectroscopy, diffusion and perfusion imaging in 20 patients with cerebral abscesses and 26 patients who had solitary brain tumors (14 high-grade gliomas and 12 metastases). The proton spectra obtained reveale ...
SERIES IAEA HUMAN HEALTH SERIES
... therapy treatment. The clinical relevance of the technology and the recent rapid technological developments have brought about extensive increases in the use of this diagnostic tool generally, and in an increasing number of Member States. The complexity of this technology continues to increase, as d ...
... therapy treatment. The clinical relevance of the technology and the recent rapid technological developments have brought about extensive increases in the use of this diagnostic tool generally, and in an increasing number of Member States. The complexity of this technology continues to increase, as d ...
Patient Dose in common CT examinations-2003
... Since the discovery of X rays and radioactivity more than 100 years ago, different ways of producing radiation and radioactive materials artificially have been found. The first use of X rays was in medical diagnosis, within six months of their discovery in 1895. Diagnostic radiology is concerned wit ...
... Since the discovery of X rays and radioactivity more than 100 years ago, different ways of producing radiation and radioactive materials artificially have been found. The first use of X rays was in medical diagnosis, within six months of their discovery in 1895. Diagnostic radiology is concerned wit ...
IMPLEMENTATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CONE-BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY USING A COBALT-60
... Cobalt-60 (Co-60) radiation therapy is a simple and reliable method of treating cancer by irradiating treatment volumes within the patient with high energy gamma rays. Medical linear accelerators (linacs) began to replace Co-60 units during the 1960’s in more developed countries, but Co-60 has remai ...
... Cobalt-60 (Co-60) radiation therapy is a simple and reliable method of treating cancer by irradiating treatment volumes within the patient with high energy gamma rays. Medical linear accelerators (linacs) began to replace Co-60 units during the 1960’s in more developed countries, but Co-60 has remai ...
Innova X-ray Dose Efficiency: Objective Evidence
... In evaluating any scientific study of a complex subject, it is important to assess the clarity of the objectives and metrics, the methods for managing confounding factors, and the strength of the objective evidence to support the conclusions. In the case of studies of patient dose in interventional ...
... In evaluating any scientific study of a complex subject, it is important to assess the clarity of the objectives and metrics, the methods for managing confounding factors, and the strength of the objective evidence to support the conclusions. In the case of studies of patient dose in interventional ...
(mIBG) Scintigraphy - Society of Nuclear Medicine
... and Paediatric Committee of the EANM have been taken into consideration, and partially integrated with this text. The same has been done with the most relevant literature on this topic, and the final result has been discussed within a group of distinguished experts. ...
... and Paediatric Committee of the EANM have been taken into consideration, and partially integrated with this text. The same has been done with the most relevant literature on this topic, and the final result has been discussed within a group of distinguished experts. ...
Pretreatment Evaluation of Prostate Cancer: Role of MR Imaging
... Prostate cancer is the most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death in American men. The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2004, 230,110 new cases of prostate cancer will be diagnosed in the United States and 29,900 people will die of the disease, increases of 4.5% and 3.5 ...
... Prostate cancer is the most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death in American men. The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2004, 230,110 new cases of prostate cancer will be diagnosed in the United States and 29,900 people will die of the disease, increases of 4.5% and 3.5 ...
Optimization of image acquisition techniques for dual
... consistent with the demands of chest radiography, however, promises to remove conventional limitations, permitting high-performance DE imaging at total dose equivalent to that of a single chest radiograph. Over the last ⬃5 years, clinical DE systems based on FPDs have become available,15,19 renewing ...
... consistent with the demands of chest radiography, however, promises to remove conventional limitations, permitting high-performance DE imaging at total dose equivalent to that of a single chest radiograph. Over the last ⬃5 years, clinical DE systems based on FPDs have become available,15,19 renewing ...
- Surrey Research Insight Open Access
... stochastic model for normal brain images and simultaneously detects MS lesions as outliers that are not well explained by the model. Many other lesion segmentation studies based on multi-spectral anatomical MRI scans were reported in [28-34]. However, in the majority of clinical situations only one ...
... stochastic model for normal brain images and simultaneously detects MS lesions as outliers that are not well explained by the model. Many other lesion segmentation studies based on multi-spectral anatomical MRI scans were reported in [28-34]. However, in the majority of clinical situations only one ...
ICRP Publication 105
... similar patients rather than individuals, are used to ensure that doses do not deviate significantly from those achieved at peer departments for that procedure unless there is a known, relevant, and acceptable reason for the deviation. This is in contrast to the Commission’s usual balancing of utilit ...
... similar patients rather than individuals, are used to ensure that doses do not deviate significantly from those achieved at peer departments for that procedure unless there is a known, relevant, and acceptable reason for the deviation. This is in contrast to the Commission’s usual balancing of utilit ...