Title Metabolism of fluoroorganic compounds in microorganisms
... and catechol substituted with a trifluoromethyl group, which the most widely used fluorinated moiety in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals (Engesser et al. 1988; Engesser et al. 1990). No strain has yet been shown to grow on these compounds, but co-metabolism is possible via ortho- and meta-cleavage ...
... and catechol substituted with a trifluoromethyl group, which the most widely used fluorinated moiety in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals (Engesser et al. 1988; Engesser et al. 1990). No strain has yet been shown to grow on these compounds, but co-metabolism is possible via ortho- and meta-cleavage ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... • For example, cholesterol enters the liver's cholesterol pool from a number of sources including dietary cholesterol, as well as cholesterol synthesized de novo by extrahepatic tissues and by the liver itself. • Cholesterol is eliminated from the liver as unmodified cholesterol in the bile, or it ...
... • For example, cholesterol enters the liver's cholesterol pool from a number of sources including dietary cholesterol, as well as cholesterol synthesized de novo by extrahepatic tissues and by the liver itself. • Cholesterol is eliminated from the liver as unmodified cholesterol in the bile, or it ...
DISCOVERY OF ENZYMES RESPONSIBLE FOR AN ALTERNATE
... inhibited by hymeglusin, a specific inhibitor of bacterial and eukaryotic HMGCS, with experimentally determined Ki of 570 ± 120 nM and kinact of 17 ± 3 min-1. Hymeglusin also prevents the growth of H. volcanii cells in vivo suggesting the essentiality of the enzyme and the mevalonate pathway in the ...
... inhibited by hymeglusin, a specific inhibitor of bacterial and eukaryotic HMGCS, with experimentally determined Ki of 570 ± 120 nM and kinact of 17 ± 3 min-1. Hymeglusin also prevents the growth of H. volcanii cells in vivo suggesting the essentiality of the enzyme and the mevalonate pathway in the ...
- World Journal of Gastroenterology
... 11 proteins in the human proteome, as shown in Table 1. In this review, we will refer to aminotransferase genes as to GPT and GOT, including their related isoforms. While there are two isoforms of human ALT, namely ALT1 and ALT2, when referring to the protein, we will use the ALT name. The gene that ...
... 11 proteins in the human proteome, as shown in Table 1. In this review, we will refer to aminotransferase genes as to GPT and GOT, including their related isoforms. While there are two isoforms of human ALT, namely ALT1 and ALT2, when referring to the protein, we will use the ALT name. The gene that ...
Ox bile, dried
... salts. The bile salts in fresh bile are mainly totally conjugated as peptides formed from bile acid, glycine or taurine. The selective activity of fully conjugated bile acids is less than that of free acids. Deoxycholic acid is the most active of the bile acids. Bacterial enzymes hydrolyse bile conj ...
... salts. The bile salts in fresh bile are mainly totally conjugated as peptides formed from bile acid, glycine or taurine. The selective activity of fully conjugated bile acids is less than that of free acids. Deoxycholic acid is the most active of the bile acids. Bacterial enzymes hydrolyse bile conj ...
Hydroxy carboxylic acids
... At room temperature, citric acid is a white crystalline powder. It can exist either in an anhydrous (waterfree) form or as a monohydrate. The anhydrous form crystallizes from hot water, whereas the monohydrate forms when citric acid is crystallized from cold water. The monohydrate can be converted t ...
... At room temperature, citric acid is a white crystalline powder. It can exist either in an anhydrous (waterfree) form or as a monohydrate. The anhydrous form crystallizes from hot water, whereas the monohydrate forms when citric acid is crystallized from cold water. The monohydrate can be converted t ...
Prokaryotic features of a nucleus
... GAPDHs in that it contains two insertions, probably Lys53A and Glu-68A (see Fig. 3). It has a calculated M , of 36768, which is somewhat smaller than expected from its electrophoretic mobility in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels, suggesting a M , of approximately 39000 [34]. The calculated amino acid com ...
... GAPDHs in that it contains two insertions, probably Lys53A and Glu-68A (see Fig. 3). It has a calculated M , of 36768, which is somewhat smaller than expected from its electrophoretic mobility in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels, suggesting a M , of approximately 39000 [34]. The calculated amino acid com ...
Development of Software Package for Determining Protein
... Effects, and Counterion Binding—A Review of the Poisson– Boltzmann Counterion Binding—A Review." Wiley ...
... Effects, and Counterion Binding—A Review of the Poisson– Boltzmann Counterion Binding—A Review." Wiley ...
The Effects of Whey Protein and Leucine Supplementation
... protein or carbohydrate supplement in the morning and once again in the evening. The NON-SUP group did not receive any supplement. The subjects were encouraged to continue with their normal dietary habits with the addition of the protein or carbohydrate supplement as this would be similar to the way ...
... protein or carbohydrate supplement in the morning and once again in the evening. The NON-SUP group did not receive any supplement. The subjects were encouraged to continue with their normal dietary habits with the addition of the protein or carbohydrate supplement as this would be similar to the way ...
Reactive cysteine in proteins: Protein folding - Genoma
... which is related to the fact that their pKa is around 8,5 (Benesch and Benesch, 1955). In contrast, some redox proteins possess a reactive cysteine that is stabilized in the thiolate form by a basic residue, in most cases a lysine or an arginine residue (Copley et al., 2004). In conclusion, reactive ...
... which is related to the fact that their pKa is around 8,5 (Benesch and Benesch, 1955). In contrast, some redox proteins possess a reactive cysteine that is stabilized in the thiolate form by a basic residue, in most cases a lysine or an arginine residue (Copley et al., 2004). In conclusion, reactive ...
PSLDoc: Protein subcellular localization prediction based on
... a neighboring bi-gram descriptor. However, AA and Dip cannot represent information between two gapped amino acids. The use of n-peptide to capture long distance amino acid information will result in a high-dimensional vector space. For example, the feature number of a vector is 3,200,000 (5 205), wh ...
... a neighboring bi-gram descriptor. However, AA and Dip cannot represent information between two gapped amino acids. The use of n-peptide to capture long distance amino acid information will result in a high-dimensional vector space. For example, the feature number of a vector is 3,200,000 (5 205), wh ...
Protease Activity of a 90-kDa Protein Isolated from Scallop Shells
... protease activity was observed in a single peak, which was eluted around the 0.3 M NaCl fraction. SDSPAGE analysis of this peak did not show any bands by CBB staining, but showed a main band with a molecular weight of approximately 90 kDa by Stainsall staining (Figure 1C). To purify the protease fur ...
... protease activity was observed in a single peak, which was eluted around the 0.3 M NaCl fraction. SDSPAGE analysis of this peak did not show any bands by CBB staining, but showed a main band with a molecular weight of approximately 90 kDa by Stainsall staining (Figure 1C). To purify the protease fur ...
The Family of Berberine Bridge Enzyme-like
... a site directed mutagenesis study was conducted to probe the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme. Sequence alignments reveal that four different active site compositions are present in the 28 different AtBBE-like proteins. 14 out of 28 AtBBE-like proteins share the AtBBE-like protein 15 active site co ...
... a site directed mutagenesis study was conducted to probe the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme. Sequence alignments reveal that four different active site compositions are present in the 28 different AtBBE-like proteins. 14 out of 28 AtBBE-like proteins share the AtBBE-like protein 15 active site co ...
Respiratory enzyme activity and regulation of respiration pathway in
... plant rhizosphere (Armstrong et al., 1994; Blom, 1999; Jackson and Armstrong, 1999; Kozlowski, 1997; Vartapetian and Jackson, 1997). The function of mitochondrion, which plays an essential role in different plant metabolic activities, has been shown sensitive to adverse conditions (Hadži-Tašković Šu ...
... plant rhizosphere (Armstrong et al., 1994; Blom, 1999; Jackson and Armstrong, 1999; Kozlowski, 1997; Vartapetian and Jackson, 1997). The function of mitochondrion, which plays an essential role in different plant metabolic activities, has been shown sensitive to adverse conditions (Hadži-Tašković Šu ...
tRNA-derived short RNAs bind to Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... amounts of tRNA fragments pool, we have shown the differential processing of almost all individual tRNA isoforms. The mode of gene expression regulation by tRNA cleavage is not well understood yet, but similarly to its biogenesis it seems to differ between higher eukaryotes and other organisms. One ...
... amounts of tRNA fragments pool, we have shown the differential processing of almost all individual tRNA isoforms. The mode of gene expression regulation by tRNA cleavage is not well understood yet, but similarly to its biogenesis it seems to differ between higher eukaryotes and other organisms. One ...
Hydrolysis of Bradykinin by Angiotensin
... removed, the rate of Phe-Arg release should parallel the loss of biological activity (bradykininase activity). Thus, it is difficult to understand why the chloride effect has not been observed by other investigators (4, 5) using biological assays. It is not known whether the pulmonary converting enz ...
... removed, the rate of Phe-Arg release should parallel the loss of biological activity (bradykininase activity). Thus, it is difficult to understand why the chloride effect has not been observed by other investigators (4, 5) using biological assays. It is not known whether the pulmonary converting enz ...
Nature template
... phosphoglyceric acid (PGA), while C-2 and C-3 are almost unlabeled. If CO2 is fixed via the cyclic reductive pentose phosphate pathway (Calvin cycle), label would be distributed among all three carbon positions. The “bypass” scheme shown in figure S1 explains how this can occur. After growing the em ...
... phosphoglyceric acid (PGA), while C-2 and C-3 are almost unlabeled. If CO2 is fixed via the cyclic reductive pentose phosphate pathway (Calvin cycle), label would be distributed among all three carbon positions. The “bypass” scheme shown in figure S1 explains how this can occur. After growing the em ...
Correlation of Hyperglycemia and Succinate dehydrogenase Activity
... The carbohydrate metabolism of various vertebrate hosts, infected with helminth parasites has been studied by numerous investigators[6-8]. But information on the reflection of carbohydrate metabolism on the Kreb’s cycle enzymes in the helminth infected hosts is meager and scattered. Succinate dehydr ...
... The carbohydrate metabolism of various vertebrate hosts, infected with helminth parasites has been studied by numerous investigators[6-8]. But information on the reflection of carbohydrate metabolism on the Kreb’s cycle enzymes in the helminth infected hosts is meager and scattered. Succinate dehydr ...
Landick R, Yanofsky C. 1987. Transcription
... segment of the leader region. While the polymerase pauses in the leader region, the opportunity is provided for loading of a ribosome at the leader peptide ribosome-binding site of the leader transcript. After a ribosome loads and begins translation, it approaches the paused polymerase. As it nears ...
... segment of the leader region. While the polymerase pauses in the leader region, the opportunity is provided for loading of a ribosome at the leader peptide ribosome-binding site of the leader transcript. After a ribosome loads and begins translation, it approaches the paused polymerase. As it nears ...
Decreased expression of plastidial adenylate kinase in potato tubers
... Fig. 2. Metabolite levels in 10-week-old tubers from the StpADK transgenic plants. Data are shown as the average of six plants per line. An asterisk denotes significant difference from wild type (P <0.05). ...
... Fig. 2. Metabolite levels in 10-week-old tubers from the StpADK transgenic plants. Data are shown as the average of six plants per line. An asterisk denotes significant difference from wild type (P <0.05). ...
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs
... A water soluble vitamin of the B family; nicotinamide is not active Once converted to the amide, it is incorporated into NAD ...
... A water soluble vitamin of the B family; nicotinamide is not active Once converted to the amide, it is incorporated into NAD ...
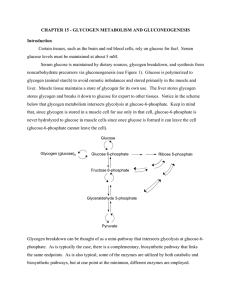
CHAPTER 15 - GLYCOGEN METABOLISM AND
... This enzyme, distinct from the debranching enzyme, creates a branch by transferring a 7residue from one non-reducing end of a chain to the 6-OH group of a glucose residue on either the same or another chain (see Figure 15-11) Control of glycogen metabolism Control of glycogen metabolism is more elab ...
... This enzyme, distinct from the debranching enzyme, creates a branch by transferring a 7residue from one non-reducing end of a chain to the 6-OH group of a glucose residue on either the same or another chain (see Figure 15-11) Control of glycogen metabolism Control of glycogen metabolism is more elab ...