
Principles of sorting and assembly of peroxisomal alcohol
... the cytosol to its target organelle is generally present within the primary amino acid sequence of the protein. This information (for instance a short sequence of a few amino acids) is recognized by a receptor that brings the protein to the correct target organelle. Sorting of proteins to organelles ...
... the cytosol to its target organelle is generally present within the primary amino acid sequence of the protein. This information (for instance a short sequence of a few amino acids) is recognized by a receptor that brings the protein to the correct target organelle. Sorting of proteins to organelles ...
Solutions to 7
... hydrophobic acid with another hydrophobic amino acid and the van der Waals forces remain. e) Substitution of one amino acid, Cys75 Gly, leads to dimerization of the receptors with or without growth factor. Provide a brief explanation for this observation. This substitution positions two cysteine r ...
... hydrophobic acid with another hydrophobic amino acid and the van der Waals forces remain. e) Substitution of one amino acid, Cys75 Gly, leads to dimerization of the receptors with or without growth factor. Provide a brief explanation for this observation. This substitution positions two cysteine r ...
... The study evaluated the performance and carcass composition index of Nile tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus ) fed with diets containing increasing levels of spray-dried blood meal (SDBM) and vat-dried blood meal (VDBM) and formulated based on digestible amino acids. Two hundred and fifty-two fingerlin ...
Protein Malnutrition - MSUD Family Support Group
... nutritional problems usually involve proteins and their component parts, the amino acids. For that reason, this discussion will be limited to protein and amino acid malnutrition. Proteins are associated with all forms of life and have many different functions in the body. Proteins act as catalysts f ...
... nutritional problems usually involve proteins and their component parts, the amino acids. For that reason, this discussion will be limited to protein and amino acid malnutrition. Proteins are associated with all forms of life and have many different functions in the body. Proteins act as catalysts f ...
Protein Structure
... huge number of different 3D shapes they adopt: function follows structure; function is determined by structure • Proteins are the most structurally complex and functionally sophisticated molecules known ...
... huge number of different 3D shapes they adopt: function follows structure; function is determined by structure • Proteins are the most structurally complex and functionally sophisticated molecules known ...
AP Biology
... – Proteins are molecules composed of chains of amino acids – Proteins have a variety of functions ...
... – Proteins are molecules composed of chains of amino acids – Proteins have a variety of functions ...
Chapter 17 Power Point
... • Silent mutations – have no effect on the encoded protein • Missense mutations – change one amino acid to another; might still code for the correct amino acid • Nonsense mutations – change a regular amino acid codon into a stop codon ...
... • Silent mutations – have no effect on the encoded protein • Missense mutations – change one amino acid to another; might still code for the correct amino acid • Nonsense mutations – change a regular amino acid codon into a stop codon ...
BIOCHEMISTRY NOTES
... 1. This is a type of regulation that occurs when the inhibitory molecule binds to the enzyme at a site other than the active site (the allosteric site). 2. This causes the enzyme to either become active or inactive (the opposite of whatever it currently is) D. Feedback Inhibition - this is a type of ...
... 1. This is a type of regulation that occurs when the inhibitory molecule binds to the enzyme at a site other than the active site (the allosteric site). 2. This causes the enzyme to either become active or inactive (the opposite of whatever it currently is) D. Feedback Inhibition - this is a type of ...
Unit 2 Metabolism and Survival Glossary
... ATP synthase an enzyme which produces ATP Biological catalysts catalysts made of protein that are only found in living cells Calorimeter a piece of equipment used to measure heat generation from an organism to allow metabolic rate to be calculate Catabolic a reaction which releases energy and breaks ...
... ATP synthase an enzyme which produces ATP Biological catalysts catalysts made of protein that are only found in living cells Calorimeter a piece of equipment used to measure heat generation from an organism to allow metabolic rate to be calculate Catabolic a reaction which releases energy and breaks ...
Macromolecules - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... You are what you eat! • SWBAT define macromolecule and name the four biological macromolecules found in all living organisms • SWBAT identify the monomers that compose each of the major macromolecules • SWBAT describe the main functions of each of the macromolecules ...
... You are what you eat! • SWBAT define macromolecule and name the four biological macromolecules found in all living organisms • SWBAT identify the monomers that compose each of the major macromolecules • SWBAT describe the main functions of each of the macromolecules ...
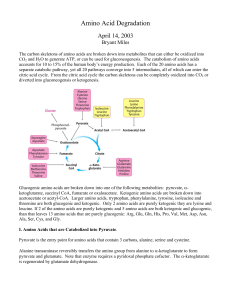
Amino Acid Degradation
... a similar manner that pyruvate dehydrogenase is phosphorylated and inactivated. The intake of dietary branched amino acids activates a phosphatase which activates this enzyme. A genetic deficiency in the branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase enzyme is called maple syrup urine disease. The deficien ...
... a similar manner that pyruvate dehydrogenase is phosphorylated and inactivated. The intake of dietary branched amino acids activates a phosphatase which activates this enzyme. A genetic deficiency in the branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase enzyme is called maple syrup urine disease. The deficien ...
Document
... chain of amino acids held together by a peptide bond. This chain may be 10’s, 100’s, or even 1000’s long and has a specific function (i.e. tubulin microtubules, catalase in cells, helicase to unwind DNA, etc.). There are only 20 amino acids; we are able to make 12 in our bodies (termed nonessential) ...
... chain of amino acids held together by a peptide bond. This chain may be 10’s, 100’s, or even 1000’s long and has a specific function (i.e. tubulin microtubules, catalase in cells, helicase to unwind DNA, etc.). There are only 20 amino acids; we are able to make 12 in our bodies (termed nonessential) ...
Chapter 3 Problem Set
... Lys) then the pI of the protein will be high. Conversely, if it has a relatively large number of acidic residues (Asp, Glu), then the protein will have a low pI. Histones have high pI values because they have large numbers of His, Arg, and Lys residues. Because the side-chains of these residues are ...
... Lys) then the pI of the protein will be high. Conversely, if it has a relatively large number of acidic residues (Asp, Glu), then the protein will have a low pI. Histones have high pI values because they have large numbers of His, Arg, and Lys residues. Because the side-chains of these residues are ...
Microbiology(Hons)[Paper-IV] - Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira
... b) What are thermoduric microorganisms? c) How does TMAO reduces shelf life of modified atmosphere packaged fish? d) What are the antimicrobial barriers present in egg white? e) Write down the advantages and disadvantages of slow freezing in food preservation. ...
... b) What are thermoduric microorganisms? c) How does TMAO reduces shelf life of modified atmosphere packaged fish? d) What are the antimicrobial barriers present in egg white? e) Write down the advantages and disadvantages of slow freezing in food preservation. ...
2.3 and 2.4 Notes
... Proteins are also called polypeptide chains. ◦ This is because the bond is called a peptide bond. ...
... Proteins are also called polypeptide chains. ◦ This is because the bond is called a peptide bond. ...
Cladograms and Evolutionary Relationships
... 1. Which animal has all of the derived traits? ____________________________________ 2. What is the least common derived trait? _____________________________________ ...
... 1. Which animal has all of the derived traits? ____________________________________ 2. What is the least common derived trait? _____________________________________ ...
Summary of Metabolism
... • Typically associated with enzymes that catalyze irreversible reactions • Allosteric regulators can cause feed back or feedforward regualtion ...
... • Typically associated with enzymes that catalyze irreversible reactions • Allosteric regulators can cause feed back or feedforward regualtion ...
Protein_Structure_Final_Powerpoint
... Molecular interactions determine tertiary and quaternary structures DNA mutations can affect protein function Unconserved regions are predicted to serve as key sites where ...
... Molecular interactions determine tertiary and quaternary structures DNA mutations can affect protein function Unconserved regions are predicted to serve as key sites where ...
Metabolism of BCAAs
... allows BCAAs to be an ideal reserve for both carbon skeletons and nitrogen for glutamate synthesis. However, this near equilibrium status also means that for the reaction to proceed, rather than cycle between BCAAs and BCKAs, BCKAs must be eliminated. This can occur via simple removal from the cell ...
... allows BCAAs to be an ideal reserve for both carbon skeletons and nitrogen for glutamate synthesis. However, this near equilibrium status also means that for the reaction to proceed, rather than cycle between BCAAs and BCKAs, BCKAs must be eliminated. This can occur via simple removal from the cell ...
Slide 1
... 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
... 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
Why plants need nutrients
... Primary nutrients: N, P, K Nitrogen atoms are needed to make amino acids and proteins (including enzymes) and other important biological molecules. Nitrogen promotes green, leafy growth and the formation of stems. Crops with high nitrogen demands include grasses and leafy vegetables such as lettuce, ...
... Primary nutrients: N, P, K Nitrogen atoms are needed to make amino acids and proteins (including enzymes) and other important biological molecules. Nitrogen promotes green, leafy growth and the formation of stems. Crops with high nitrogen demands include grasses and leafy vegetables such as lettuce, ...
ENERGY METABOLISM
... The surplus amino acids ARE NOT STORED, but are either: a. released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis, b. they are with the resulting carbon skeletons being degraded by the liver pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates, these metabolites can be oxidized for energy o ...
... The surplus amino acids ARE NOT STORED, but are either: a. released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis, b. they are with the resulting carbon skeletons being degraded by the liver pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates, these metabolites can be oxidized for energy o ...












![Microbiology(Hons)[Paper-IV] - Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017635075_1-cacd0a5e5aa4de554a7e55477a5947cd-300x300.png)









