Biochemistry Test Review
... What is the connection between bond polarity and hydrophobic vs. hydrophilic molecules? Why are most compounds with ionic bonds also hydrophilic? What are hydrogen bonds? How do they differ from ionic and covalent bonds? List at least four emergent properties of water and describe them. Compare cohe ...
... What is the connection between bond polarity and hydrophobic vs. hydrophilic molecules? Why are most compounds with ionic bonds also hydrophilic? What are hydrogen bonds? How do they differ from ionic and covalent bonds? List at least four emergent properties of water and describe them. Compare cohe ...
Nutrition
... A) Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle where it combines with oxaloacetic acid to create citric acid B) As the cycle moves around, citric acid is rearranged to produce different intermediate molecules called keto acids C) At the end of the cycle, the resulting molecule is oxaloacetic acid which is now ...
... A) Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle where it combines with oxaloacetic acid to create citric acid B) As the cycle moves around, citric acid is rearranged to produce different intermediate molecules called keto acids C) At the end of the cycle, the resulting molecule is oxaloacetic acid which is now ...
Translation webquest
... Once you have made an RNA strand, read the new text under the animation and find the start codon in your RNA strand. Make sure you use your mouse to place the green box on the start codon. When you have located the start sequence, click on the start codon to continue. Read the new text under the a ...
... Once you have made an RNA strand, read the new text under the animation and find the start codon in your RNA strand. Make sure you use your mouse to place the green box on the start codon. When you have located the start sequence, click on the start codon to continue. Read the new text under the a ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Lipids are nonpolar molecules that include fats, oils, and cholesterol. – Many contain carbon chains called fatty acids. – Fats and oils contain fatty acids bonded to glycerol. Triglyceride ...
... • Lipids are nonpolar molecules that include fats, oils, and cholesterol. – Many contain carbon chains called fatty acids. – Fats and oils contain fatty acids bonded to glycerol. Triglyceride ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 1: Structure and Function in Biochemistry
... and two of the propionate side chains have been decarboxylated to form vinyl side chains –CH=CH2. The four pyrrole N atoms form a square planar array at ideal spacing to act as ligands for metal ions such as Fe2+. This locks Fe2+ in place with high affinity, so all cellular Fe2+ will effectively be ...
... and two of the propionate side chains have been decarboxylated to form vinyl side chains –CH=CH2. The four pyrrole N atoms form a square planar array at ideal spacing to act as ligands for metal ions such as Fe2+. This locks Fe2+ in place with high affinity, so all cellular Fe2+ will effectively be ...
Document
... Oxidation of one glucose yields 2840 kJ/mole energy Energy obtained by biological engine: 32ATP X 30.5 kJ/Mol = 976 kJ/mol Thus 34% efficiency is obtained if calculations are done using standard conditions. But if concentrations in the cellular condition are taken in account, the efficiency is close ...
... Oxidation of one glucose yields 2840 kJ/mole energy Energy obtained by biological engine: 32ATP X 30.5 kJ/Mol = 976 kJ/mol Thus 34% efficiency is obtained if calculations are done using standard conditions. But if concentrations in the cellular condition are taken in account, the efficiency is close ...
Amino Acid Metabolism 1 Key Concepts
... reaction is run in the reverse direction as a way to deaminate glutamate and form nitrogenous waste products such as urea and uric acid. A second, and more common way that plants and bacteria incorporate NH4+ into metabolites, is through a two reaction mechanism that functions when NH4+ concentratio ...
... reaction is run in the reverse direction as a way to deaminate glutamate and form nitrogenous waste products such as urea and uric acid. A second, and more common way that plants and bacteria incorporate NH4+ into metabolites, is through a two reaction mechanism that functions when NH4+ concentratio ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
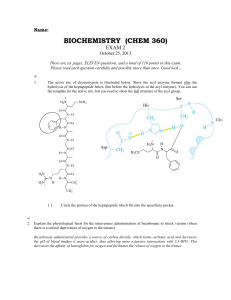
... derivatives, an example of which is given below. Describe two structural features of penicillin, to which the inhibitory activity can be attributed. (1) the structure resembles D-ala.D-ala moiety (2) nucleophilic attack by the carboxypeptidase is more likely to occur to the -lactam ring than the al ...
... derivatives, an example of which is given below. Describe two structural features of penicillin, to which the inhibitory activity can be attributed. (1) the structure resembles D-ala.D-ala moiety (2) nucleophilic attack by the carboxypeptidase is more likely to occur to the -lactam ring than the al ...
Balancing Reactions 1
... 5. Write balanced formula unit equations for the following redox reactions: a. Aluminum reacts with sulfuric acid, H2SO4, to produce aluminum sulfate and hydrogen. b. Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia, NH3 c. Zinc sulfide, ZnS, reacts with oxygen to from zinc oxide and sulfur dioxide ...
... 5. Write balanced formula unit equations for the following redox reactions: a. Aluminum reacts with sulfuric acid, H2SO4, to produce aluminum sulfate and hydrogen. b. Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia, NH3 c. Zinc sulfide, ZnS, reacts with oxygen to from zinc oxide and sulfur dioxide ...
HPER 334 Nutrition Exam 2
... b. It is a precursor for bile, vitamin D, and sex hormone synthesis c. It is not formed in the body when provided by the diet d. It is found in abundance in tropical fats such as palm oil 32. Which of the following cannot be found in plants? a. Cholesterol b. Triglycerides c. Essential fatty acids d ...
... b. It is a precursor for bile, vitamin D, and sex hormone synthesis c. It is not formed in the body when provided by the diet d. It is found in abundance in tropical fats such as palm oil 32. Which of the following cannot be found in plants? a. Cholesterol b. Triglycerides c. Essential fatty acids d ...
Lecture 6
... • Urea cycle 1) Formation of carbamoyl phosphate from ammonia and Co2 2) Addition of aspartate 3) Production of fumarate (Kreb’s cycle intermediate) 4) Produces Urea ...
... • Urea cycle 1) Formation of carbamoyl phosphate from ammonia and Co2 2) Addition of aspartate 3) Production of fumarate (Kreb’s cycle intermediate) 4) Produces Urea ...
Biomolecule Review Worksheet
... group. Some “R” groups are very small, others are large, and even others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. 4. How many different amino acids are there? 5. What part of the amino acid varies from one amino acid to another? ...
... group. Some “R” groups are very small, others are large, and even others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. 4. How many different amino acids are there? 5. What part of the amino acid varies from one amino acid to another? ...
selenium 01% brochure 2015
... Methionine is convertible to cysteine. But as methionine is a limiting essential amino acid, and cysteine is a common, non-essential amino acid, in the animal there practically exists a RARE NEED TO CONVERT METHIONINE TO CYSTEINE. ...
... Methionine is convertible to cysteine. But as methionine is a limiting essential amino acid, and cysteine is a common, non-essential amino acid, in the animal there practically exists a RARE NEED TO CONVERT METHIONINE TO CYSTEINE. ...
63KB - NZQA
... transcribes the code for a polypeptide from the DNA. The purpose of transcription is explained: mRNA transcribes the code for a polypeptide from the DNA in the nucleus and carries it to the ribosomes / cytoplasm. So that the original DNA does not get damaged leaving the nucleus. The purpose of trans ...
... transcribes the code for a polypeptide from the DNA. The purpose of transcription is explained: mRNA transcribes the code for a polypeptide from the DNA in the nucleus and carries it to the ribosomes / cytoplasm. So that the original DNA does not get damaged leaving the nucleus. The purpose of trans ...
enzymes - BEHS Science
... Mimic molecules compete with the substrate and bind to the active site ...
... Mimic molecules compete with the substrate and bind to the active site ...
Nutrition
... • Unsaturated fats, called oils, come from plants – Contains one or more double bonds – Missing one or more pairs of hydrogen ...
... • Unsaturated fats, called oils, come from plants – Contains one or more double bonds – Missing one or more pairs of hydrogen ...
5-PDH-and-TCA-cycle - WatCut
... in the citric acid cycle 3. synthesis of amino acids, e.g., transamination to alanine 4. reduction to lactate ...
... in the citric acid cycle 3. synthesis of amino acids, e.g., transamination to alanine 4. reduction to lactate ...
Proteins determine what?
... 25.What are the 4 steps of translation? • 1. mRNA goes to ribosome • 2. tRNA temporarily pair with mRNA • 3. the amino acids at the end of the tRNA bond together and the tRNA leaves • 4. translation stops when STOP codon is ...
... 25.What are the 4 steps of translation? • 1. mRNA goes to ribosome • 2. tRNA temporarily pair with mRNA • 3. the amino acids at the end of the tRNA bond together and the tRNA leaves • 4. translation stops when STOP codon is ...
Lesson Plan in Word Format
... that have one of the letters A C T G on them. They have now become nucleotides. The students will then create a DNA double helix strand matching up the letters by holding hands across from each other. One strand will then pull away from the other strand of DNA. Half of the students can then flip the ...
... that have one of the letters A C T G on them. They have now become nucleotides. The students will then create a DNA double helix strand matching up the letters by holding hands across from each other. One strand will then pull away from the other strand of DNA. Half of the students can then flip the ...
Flexibility of a polypeptide chain
... hydrophobic amino acids are yellow, charged ones are blue, others are white cross-section ...
... hydrophobic amino acids are yellow, charged ones are blue, others are white cross-section ...