Executive Stress Formula
... In the human body, hundreds of chemical reactions occur during the course of normal metabolic processes. Many chemical reactions require significant energy in order to take place, and therefore need a catalyst to allow the reaction to proceed. The catalyst acts to lower the energy needed for the rea ...
... In the human body, hundreds of chemical reactions occur during the course of normal metabolic processes. Many chemical reactions require significant energy in order to take place, and therefore need a catalyst to allow the reaction to proceed. The catalyst acts to lower the energy needed for the rea ...
Comparison of Free Total Amino Acid Compositions and
... Amino acid composition is a reliable indicator of the nutritional value of food. Free amino acids are the main constituents of functionally essential compounds that are found in mushrooms. The most typical mushroom taste can be given by the nonvolatile compounds, such as free amino acids and soluble ...
... Amino acid composition is a reliable indicator of the nutritional value of food. Free amino acids are the main constituents of functionally essential compounds that are found in mushrooms. The most typical mushroom taste can be given by the nonvolatile compounds, such as free amino acids and soluble ...
chapter_6_-_plus_ch_review
... 2. Structure of proteins a. Amino acids b. Protein folding into 3-D shape c. Denaturing a protein 3. Some amino acids are essential (9/20) 4. Digestion and absorption 5. How much protein do you need a. AMDR, RDA b. Nitrogen balance 6. Rating protein quality 7. Too much or too little protein 8. Veget ...
... 2. Structure of proteins a. Amino acids b. Protein folding into 3-D shape c. Denaturing a protein 3. Some amino acids are essential (9/20) 4. Digestion and absorption 5. How much protein do you need a. AMDR, RDA b. Nitrogen balance 6. Rating protein quality 7. Too much or too little protein 8. Veget ...
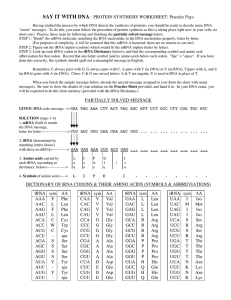
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
Synthesis of a Glutathione Analogue Using 2-α-Methyl-β
... groups. This characteristic is known as chirality, and the α-carbon is considered to be the chiral center. The spatial arrangement of the groups around the chiral center can be oriented in two different ways, meaning that the amino acid has two possible enantiomers, or non-superimposable mirror imag ...
... groups. This characteristic is known as chirality, and the α-carbon is considered to be the chiral center. The spatial arrangement of the groups around the chiral center can be oriented in two different ways, meaning that the amino acid has two possible enantiomers, or non-superimposable mirror imag ...
BCHM 562, Biochemistry II
... carrying electrons from one reaction to another. 3. NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced, to form NADH. 4. NADH is a reducing agent – it can donate electrons. 5. Electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD+. 6. NADPH is NADH with an ...
... carrying electrons from one reaction to another. 3. NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced, to form NADH. 4. NADH is a reducing agent – it can donate electrons. 5. Electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD+. 6. NADPH is NADH with an ...
Document
... fragments to give ___________________________ -chymotrypsin consists of 3 polypeptide chains joined by 2 of the 5 original disulfide bonds • changes in 1°structure that accompany the change from chymotrypsinogen to -chymotrypsin result in changes in ____________________________________ as well. ...
... fragments to give ___________________________ -chymotrypsin consists of 3 polypeptide chains joined by 2 of the 5 original disulfide bonds • changes in 1°structure that accompany the change from chymotrypsinogen to -chymotrypsin result in changes in ____________________________________ as well. ...
Gene Section RBM15 (RNA binding motif protein 15) in Oncology and Haematology
... 5' OTT - 3' MAL, comprisng most of OTT fused to most of MAL; the reciprocal 5' MAL - 3' OTT may or may not be present. Abnormal protein Includes most of OTT with the RNA recognition motifs and the SPOC domain in N-term, and most of MAL, with the scaffold attachment factor box in C-term. Oncogenesis ...
... 5' OTT - 3' MAL, comprisng most of OTT fused to most of MAL; the reciprocal 5' MAL - 3' OTT may or may not be present. Abnormal protein Includes most of OTT with the RNA recognition motifs and the SPOC domain in N-term, and most of MAL, with the scaffold attachment factor box in C-term. Oncogenesis ...
221_exam_2_2003
... produces multiple fermentation products replenishes key intermediates of the TCA cycle fixes carbon dioxide ...
... produces multiple fermentation products replenishes key intermediates of the TCA cycle fixes carbon dioxide ...
Combining Inductive Logic Programming, Active
... discover what facts are missing to form one consistent hypothesis Lateral Thinking Puzzles Presented with a confusing situation There is an Oracle that knows what happened You can only ask yes or no questions ...
... discover what facts are missing to form one consistent hypothesis Lateral Thinking Puzzles Presented with a confusing situation There is an Oracle that knows what happened You can only ask yes or no questions ...
File
... Tumor cells have a higher requirement for glucose due to a lower efficiency in energy production from glycolysis. • Complete oxidation of CO2 in healthy cells under aerobic conditions yields ~30 ATP per glucose. • Anaerobic metabolism of glucose in tumor cells yields 2 ATP per glucose. – Glucose tra ...
... Tumor cells have a higher requirement for glucose due to a lower efficiency in energy production from glycolysis. • Complete oxidation of CO2 in healthy cells under aerobic conditions yields ~30 ATP per glucose. • Anaerobic metabolism of glucose in tumor cells yields 2 ATP per glucose. – Glucose tra ...
LP - Columbia University
... PROTEINS. These are the most important class of macromolecules in the cell, and we will discuss them now in detail. The monomers that make up proteins are the amino acids, of which there are 20. The same 20 in E. coli and in elephants and eggplant. The general structure of an amino acid is: Note t ...
... PROTEINS. These are the most important class of macromolecules in the cell, and we will discuss them now in detail. The monomers that make up proteins are the amino acids, of which there are 20. The same 20 in E. coli and in elephants and eggplant. The general structure of an amino acid is: Note t ...
Chemistry of Life: The Four Macromolecules
... • controlling the rate of reactions and regulating cell processes (act as enzymes) • forming cellular structures • transporting substances into or out of cells • and helping to fight disease. ...
... • controlling the rate of reactions and regulating cell processes (act as enzymes) • forming cellular structures • transporting substances into or out of cells • and helping to fight disease. ...
Structure and physical-chemical properties of enzymes
... - At a fixed enzyme concentration [E], the initial velocity Vo is almost linearly proportional to substrate concentration [S] when [S] is small but is nearly independent of [S] when [S] is large ...
... - At a fixed enzyme concentration [E], the initial velocity Vo is almost linearly proportional to substrate concentration [S] when [S] is small but is nearly independent of [S] when [S] is large ...
Microbiology bio 123
... 2. Some are competitive inhibitors, they compete for the enzyme. (i.e. a→b→c→PABA+E→folic acid, Sulfonamide (synthetic antibiotics) competes with PABA for enzyme E.) Metabolism includes two major types of reactions: 1. Endergonic reactions require energy to be placed into the reaction to complete th ...
... 2. Some are competitive inhibitors, they compete for the enzyme. (i.e. a→b→c→PABA+E→folic acid, Sulfonamide (synthetic antibiotics) competes with PABA for enzyme E.) Metabolism includes two major types of reactions: 1. Endergonic reactions require energy to be placed into the reaction to complete th ...
Phylogenetic and genetic analysis of envelope gene of the
... A fresh wave of Dengue infection, particularly Dengue serotype 1and 3, have been observed all across India in recent times and has led to several fatalities. Since the surface situated envelope protein of the dengue virion is responsible for virus entry into the host cell, we have laid special empha ...
... A fresh wave of Dengue infection, particularly Dengue serotype 1and 3, have been observed all across India in recent times and has led to several fatalities. Since the surface situated envelope protein of the dengue virion is responsible for virus entry into the host cell, we have laid special empha ...
Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... just a few small monomers, by varying number, sequence and bonding arrangements. Our biological macromolecules are grouped into four categories: proteins, nucleic acids, lipids and carbohydrates. We shall discuss structure and functions of each group. Most of our biological molecules are assembled o ...
... just a few small monomers, by varying number, sequence and bonding arrangements. Our biological macromolecules are grouped into four categories: proteins, nucleic acids, lipids and carbohydrates. We shall discuss structure and functions of each group. Most of our biological molecules are assembled o ...
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... Electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are funneled into the electron transport chain reducing O2 to H2O and producing ATP in the process of oxidative phosphorylation ...
... Electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are funneled into the electron transport chain reducing O2 to H2O and producing ATP in the process of oxidative phosphorylation ...
Lecture 26
... A multienzyme complexes are groups of non covalently associated enzymes that catalyze two or more sequential steps in a metabolic pathway. Molecular weight of 4,600,000 Da E. coli ...
... A multienzyme complexes are groups of non covalently associated enzymes that catalyze two or more sequential steps in a metabolic pathway. Molecular weight of 4,600,000 Da E. coli ...