Sec"on 8 - Small World Initiative
... • The large and small subunit associate only in the presence of mRNA • The mRNA passes through a “tunnel” created by the mature ribosome • This tunnel contains the ac$ve A, P, and E sites where ...
... • The large and small subunit associate only in the presence of mRNA • The mRNA passes through a “tunnel” created by the mature ribosome • This tunnel contains the ac$ve A, P, and E sites where ...
Introduction to Enzymes - Rose
... different forms of lactate dehydrogenase are isoforms, while the M and H polypeptides are isozymes, because they are produced from separate genes. Why do organisms use more than one enzyme with the same activity? Different isozymes may be expressed in different tissues. This is important, because, i ...
... different forms of lactate dehydrogenase are isoforms, while the M and H polypeptides are isozymes, because they are produced from separate genes. Why do organisms use more than one enzyme with the same activity? Different isozymes may be expressed in different tissues. This is important, because, i ...
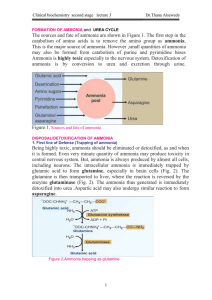
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... Regulation of the Urea Cycle 1. Coarse Regulation The enzyme levels change with the protein content of diet. During starvation, the activity of urea cycle enzymes is elevated to meet the increased rate of protein catabolism. 2. Fine Regulation The major regulatory step is catalyzed by CPS-I where th ...
... Regulation of the Urea Cycle 1. Coarse Regulation The enzyme levels change with the protein content of diet. During starvation, the activity of urea cycle enzymes is elevated to meet the increased rate of protein catabolism. 2. Fine Regulation The major regulatory step is catalyzed by CPS-I where th ...
ProteinShop: A tool for protein structure prediction and modeling
... form regular structures, called secondary structures The secondary structures fold together to form a compact 3-dimensional shape, called the tertiary structure ...
... form regular structures, called secondary structures The secondary structures fold together to form a compact 3-dimensional shape, called the tertiary structure ...
description - In
... FUNCTION: Natural PEG-free and hydrolyzed protein free Soft and Emollient Emulsifier of vegetal origin DESCRIPTION: A new non-ethoxylated, vegetal derived emulsifier that combines the unique lipidic chains of olive oil with the glutamic acid called Olivoyl Glutamate, a lipo-aminoacid with a fatty am ...
... FUNCTION: Natural PEG-free and hydrolyzed protein free Soft and Emollient Emulsifier of vegetal origin DESCRIPTION: A new non-ethoxylated, vegetal derived emulsifier that combines the unique lipidic chains of olive oil with the glutamic acid called Olivoyl Glutamate, a lipo-aminoacid with a fatty am ...
5)qualitative_tests_of_proteins
... proteins are enzymes or subunits of enzymes, catalyzing chemical reactions. Other proteins play structural or mechanical roles, such as those that form the struts and joints of the cytoskeleton, serving as biological scaffolds for the mechanical integrity and tissue signaling functions. - Proteins c ...
... proteins are enzymes or subunits of enzymes, catalyzing chemical reactions. Other proteins play structural or mechanical roles, such as those that form the struts and joints of the cytoskeleton, serving as biological scaffolds for the mechanical integrity and tissue signaling functions. - Proteins c ...
Improved RP-HPLC and anion-exchange chromatography methods
... (Fuc) was obtained by Acros. An amino acid standard H (Pierce Perbio) with the following 17 amino acids L-alanine (Ala), L-arginine (Arg), L-aspartic acid (Asp), L-glutamic acid (Glu), glycine (Gly), L-histidine (His), L-isoleucine (Ile), L-leucine (Leu), L-methionine (Met), L-phenylalanine (Phe), L ...
... (Fuc) was obtained by Acros. An amino acid standard H (Pierce Perbio) with the following 17 amino acids L-alanine (Ala), L-arginine (Arg), L-aspartic acid (Asp), L-glutamic acid (Glu), glycine (Gly), L-histidine (His), L-isoleucine (Ile), L-leucine (Leu), L-methionine (Met), L-phenylalanine (Phe), L ...
Document
... accumulation of the end-product in a particular pathway inhibits the first enzyme’s activity in the pathway – Regulate cell’s production of amino acids, vitamins, purines, and pyrimidines – Mechanism stops the cell from wasting chemical resources – Allosteric inhibitors play a role ...
... accumulation of the end-product in a particular pathway inhibits the first enzyme’s activity in the pathway – Regulate cell’s production of amino acids, vitamins, purines, and pyrimidines – Mechanism stops the cell from wasting chemical resources – Allosteric inhibitors play a role ...
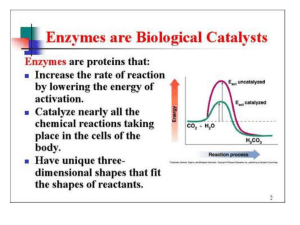
What Are Enzymes?
... • Are reusable • There are about 2000 different enzymes in each one of your cells ...
... • Are reusable • There are about 2000 different enzymes in each one of your cells ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Lipids are nonpolar molecules that include fats, oils, and cholesterol. – Many contain carbon chains called fatty acids. – Fats and oils contain fatty acids bonded to glycerol. Triglyceride ...
... • Lipids are nonpolar molecules that include fats, oils, and cholesterol. – Many contain carbon chains called fatty acids. – Fats and oils contain fatty acids bonded to glycerol. Triglyceride ...
Metabol Nutri-ClinEnz Med 2_6 Nov 2012
... The normal levels reflect the balance between the rate of synthesis and release into plasma during cell turnover, and the rate of clearance from the circulation. The enzyme level in plasma may be: •increased due to proliferation of cells, an increase in rate of cell turnover or damage or in enzyme s ...
... The normal levels reflect the balance between the rate of synthesis and release into plasma during cell turnover, and the rate of clearance from the circulation. The enzyme level in plasma may be: •increased due to proliferation of cells, an increase in rate of cell turnover or damage or in enzyme s ...
Various University Examination Questions on Fatty acid
... 17. Write the reaction, with cofactors if any, catalyzed by Acetyl CoA carboxylase. ...
... 17. Write the reaction, with cofactors if any, catalyzed by Acetyl CoA carboxylase. ...
Chapter 4 The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins
... Answer: Because a protein may be denatured through the disruption of hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions by salts or organic solvents, removal of those conditions will reestablish the original aqueous environment, often permitting the protein to fold once again into its native conformation. ...
... Answer: Because a protein may be denatured through the disruption of hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions by salts or organic solvents, removal of those conditions will reestablish the original aqueous environment, often permitting the protein to fold once again into its native conformation. ...
Review Questions for Advanced Biochemistry Course
... 31. Which of the following statements about the TCA cycle is CORRECT? A. Citrate is frequently used for gluconeogenesis in the liver B. The production of oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase is one of several anaplerotic reactions for the TCA cycle C. Succinyl CoA is used to create a neurotransmitte ...
... 31. Which of the following statements about the TCA cycle is CORRECT? A. Citrate is frequently used for gluconeogenesis in the liver B. The production of oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase is one of several anaplerotic reactions for the TCA cycle C. Succinyl CoA is used to create a neurotransmitte ...
Lipid Metabolism
... Free fatty acid will be converted to the acyl-CoA by the reaction of Acyl-CoA synthetase. The long chain acyl-CoA produces metabolic feedback inhibition of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase which is the key enzyme for the fatty acids synthesis. 13. STATINS (LIKE LOVASTATIN) AND THYROID HORMONES (AS IN HYPE ...
... Free fatty acid will be converted to the acyl-CoA by the reaction of Acyl-CoA synthetase. The long chain acyl-CoA produces metabolic feedback inhibition of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase which is the key enzyme for the fatty acids synthesis. 13. STATINS (LIKE LOVASTATIN) AND THYROID HORMONES (AS IN HYPE ...
Study Questions for Chapter 1 – The Cell
... 4. When plotting the velocity (V) of an enzymatic reaction against the substrate concentration, one sees “saturable” kinetics. That is, at some substrate concentration, the enzyme is functioning at its maximal rate (Vmax) and cannot operate any faster. The substrate concentration that results in ...
... 4. When plotting the velocity (V) of an enzymatic reaction against the substrate concentration, one sees “saturable” kinetics. That is, at some substrate concentration, the enzyme is functioning at its maximal rate (Vmax) and cannot operate any faster. The substrate concentration that results in ...
Metabolism: the Degradation and Synthesis of Living Cells
... as a series of enzyme-catalyzed linear, branched or circular reactions, or pathways. • Highly coupled and interconnected (“Every road leads to Rome”). • Highly regulated (often reciprocally) to achieve the best economy (“Balanced supply and demand”). • The number of reactions is large (over 1000), h ...
... as a series of enzyme-catalyzed linear, branched or circular reactions, or pathways. • Highly coupled and interconnected (“Every road leads to Rome”). • Highly regulated (often reciprocally) to achieve the best economy (“Balanced supply and demand”). • The number of reactions is large (over 1000), h ...
introduction - WordPress.com
... It plays a starring role in both the process of energy production and biosynthesis. The cycle finishes the sugar-breaking job started in glycolysis and fuels the production of ATP in the process. It is also a central hub in biosynthetic reactions, pro viding intermediates that are used to build amin ...
... It plays a starring role in both the process of energy production and biosynthesis. The cycle finishes the sugar-breaking job started in glycolysis and fuels the production of ATP in the process. It is also a central hub in biosynthetic reactions, pro viding intermediates that are used to build amin ...
chapter-02
... Proteins Amino Acids • Amino Acids are linked together by peptide bonds • Dipeptide – two amino acids bonded together • Polypeptide – several amino acids linked together Amino acid ...
... Proteins Amino Acids • Amino Acids are linked together by peptide bonds • Dipeptide – two amino acids bonded together • Polypeptide – several amino acids linked together Amino acid ...