Proteins
... The instructions for arranging amino acids into many different proteins are stored in DNA. Protein Molecule ...
... The instructions for arranging amino acids into many different proteins are stored in DNA. Protein Molecule ...
Document
... Adjustments in the rate of reactions catalyzed by regulatory enzymes allow the cell to meet changing needs for energy and for biomolecules required in growth an maintenance. ...
... Adjustments in the rate of reactions catalyzed by regulatory enzymes allow the cell to meet changing needs for energy and for biomolecules required in growth an maintenance. ...
NF96-251 A Comparative Study of Fiber Digestion and Subsequent
... smaller, one-compartment stomach (proventriculus) in avian and ratite species. The rumen is where most of the microbial digestion of fiber occurs in cattle. The rumen is located strategically before the small intestine where the majority of the essential nutrients such as amino acids, lipids, minera ...
... smaller, one-compartment stomach (proventriculus) in avian and ratite species. The rumen is where most of the microbial digestion of fiber occurs in cattle. The rumen is located strategically before the small intestine where the majority of the essential nutrients such as amino acids, lipids, minera ...
Feature based Protein Function Prediction by Using Random Forest
... Proteins are main building blocks of our Life. They are responsible for catalyzing and regulating biochemical reactions, transporting molecules, and they form the basis of structures such as skin, hair, and tendon. The shape of protein is specified by its amino acid sequence. There are 20 different ...
... Proteins are main building blocks of our Life. They are responsible for catalyzing and regulating biochemical reactions, transporting molecules, and they form the basis of structures such as skin, hair, and tendon. The shape of protein is specified by its amino acid sequence. There are 20 different ...
Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers
... • Every chemical reaction between molecules involves bond breaking and bond forming • The initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called the free energy of activation, or activation energy (EA) • Activation energy is often supplied in the form of heat from the surroundings ...
... • Every chemical reaction between molecules involves bond breaking and bond forming • The initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called the free energy of activation, or activation energy (EA) • Activation energy is often supplied in the form of heat from the surroundings ...
Preparation of pyruvate for the citric acid cycle Recap 1. We have
... We have worked our way through glycolysis We now have 2 molecules of pyruvate We have produced 2 ATPs and 2 NADHs ...
... We have worked our way through glycolysis We now have 2 molecules of pyruvate We have produced 2 ATPs and 2 NADHs ...
Foundations of Biology
... A single transcription factor (or group of transcription factors) may regulate expression of a group of genes (i.e., heat shock proteins) A single gene may be regulated by a number of independent transcription factors (i.e., metallothionein) Eukaryotic regulation does not seem to involve repression ...
... A single transcription factor (or group of transcription factors) may regulate expression of a group of genes (i.e., heat shock proteins) A single gene may be regulated by a number of independent transcription factors (i.e., metallothionein) Eukaryotic regulation does not seem to involve repression ...
Protein Modifications and Proteomics
... i) N-linked glycosylation- It takes place in the ER and continues in the golgi body. Here the carbohydrate moiety is attached to the amide group of the asparagine residue when it is present in the sequence NXS/T where, N is asparagine, X is any amino acid other than proline, S/T stands for serine/th ...
... i) N-linked glycosylation- It takes place in the ER and continues in the golgi body. Here the carbohydrate moiety is attached to the amide group of the asparagine residue when it is present in the sequence NXS/T where, N is asparagine, X is any amino acid other than proline, S/T stands for serine/th ...
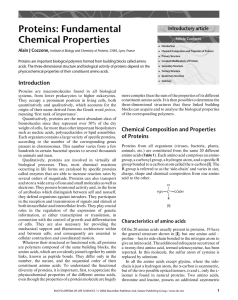
Proteins: Fundamental Chemical Properties
... biomolecules since they represent over 50% of the dry weight of cells, far more than other important biopolymers such as nucleic acids, polysaccharides or lipid assemblies. Each organism contains a large variety of specific proteins, according to the number of the corresponding genes present in chrom ...
... biomolecules since they represent over 50% of the dry weight of cells, far more than other important biopolymers such as nucleic acids, polysaccharides or lipid assemblies. Each organism contains a large variety of specific proteins, according to the number of the corresponding genes present in chrom ...
Activity-based probes that target diverse cysteine protease families
... residue (Fig. 1a) were radio-iodinated and tested against several purified and recombinant cysteine proteases of the CD clan, as members of this clan are known to have high specificity for cleavage at a single defined P1 amino acid residue (Fig. 1b)14. This group included the human caspase-3, which ...
... residue (Fig. 1a) were radio-iodinated and tested against several purified and recombinant cysteine proteases of the CD clan, as members of this clan are known to have high specificity for cleavage at a single defined P1 amino acid residue (Fig. 1b)14. This group included the human caspase-3, which ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... level by controlling synthesis of key enzymes Enzyme _____________– enzymes are made only when suitable substrates are present ...
... level by controlling synthesis of key enzymes Enzyme _____________– enzymes are made only when suitable substrates are present ...
Document
... b. Phosphofructokinase, which catalyzes the formation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, is inhibited by high levels of ATP, and activated by high levels of ADP and AMP. c. High levels of ATP or acetyl CoA inhibit pyruvate kinase, which stops the formation of pyruvate in reaction 10. ...
... b. Phosphofructokinase, which catalyzes the formation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, is inhibited by high levels of ATP, and activated by high levels of ADP and AMP. c. High levels of ATP or acetyl CoA inhibit pyruvate kinase, which stops the formation of pyruvate in reaction 10. ...
b-oxidation - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... chain fatty acids • Odd chain fatty acids are less common • Formed by some bacteria in the stomachs of rumaniants and the human colon. • b-oxidation occurs pretty much as w/ even chain fatty acids until the final thiolase cleavage which results in a 3 carbon acyl-CoA (propionyl-CoA) • Special set of ...
... chain fatty acids • Odd chain fatty acids are less common • Formed by some bacteria in the stomachs of rumaniants and the human colon. • b-oxidation occurs pretty much as w/ even chain fatty acids until the final thiolase cleavage which results in a 3 carbon acyl-CoA (propionyl-CoA) • Special set of ...
Peptides and proteins Chapter 36:
... acids is termed a protein. However, interleukins, cytokines, and interferon are also sometimes referred to as peptides, even though they possess a much higher molecular weight (Figure 36.2). Sometimes the distinction between the two categories relies more on the function of the molecule rather than ...
... acids is termed a protein. However, interleukins, cytokines, and interferon are also sometimes referred to as peptides, even though they possess a much higher molecular weight (Figure 36.2). Sometimes the distinction between the two categories relies more on the function of the molecule rather than ...
Brain Needs in Different Metabolic states
... or fatty acids because they are more reduced (greater hydrogen/carbon ratio) than pyruvate and do not uncouple the mitochondrial proton gradient as occurs with fatty acid metabolism. In contrast to glucose, ketone bodies by-pass cytoplasmic glycolysis and directly enter the mitochondria where they a ...
... or fatty acids because they are more reduced (greater hydrogen/carbon ratio) than pyruvate and do not uncouple the mitochondrial proton gradient as occurs with fatty acid metabolism. In contrast to glucose, ketone bodies by-pass cytoplasmic glycolysis and directly enter the mitochondria where they a ...
No Slide Title
... secondary structure but has a mild preference for the helix. It is isosteric with glutamic acid. ...
... secondary structure but has a mild preference for the helix. It is isosteric with glutamic acid. ...
Protein Metabolism
... Rate-limiting step: carbomyl-p-synthetase I, activated by N-acetyl-glu (synthesized greatly after ingestion of a protein-rich meal: AcetylCoA + Glu ...
... Rate-limiting step: carbomyl-p-synthetase I, activated by N-acetyl-glu (synthesized greatly after ingestion of a protein-rich meal: AcetylCoA + Glu ...
19-6-SA-V1-S1__mcq_a..
... 35. These are multiple forms of the given enzyme that occurs within the same animal species. 43. Suffix __________ should be used only for single enzymes 51. All __________ are made up of protein but all proteins are not made up of _______________. 1. Absolute group _________. Ex.: Trypsin and pepsi ...
... 35. These are multiple forms of the given enzyme that occurs within the same animal species. 43. Suffix __________ should be used only for single enzymes 51. All __________ are made up of protein but all proteins are not made up of _______________. 1. Absolute group _________. Ex.: Trypsin and pepsi ...
Chapter 19 - Evangel University
... • During germination, plants use the acetyl-CoA produced in fatty acid oxidation to produce oxaloacetate and other intermediates for carbohydrate synthesis • Once plants begin photosynthesis and can fix CO2, glyoxysomes disappear ...
... • During germination, plants use the acetyl-CoA produced in fatty acid oxidation to produce oxaloacetate and other intermediates for carbohydrate synthesis • Once plants begin photosynthesis and can fix CO2, glyoxysomes disappear ...
pdf
... a. Approximately 20 enzymes, one per amino acid. b. Must recognize several cognate tRNAs, i.e. that accept the same amino acid but recognize a different codon in the mRNA (a consequence of the degeneracy in the genetic code). c. Must not recognize the incorrect tRNA - i.e. these enzymes require prec ...
... a. Approximately 20 enzymes, one per amino acid. b. Must recognize several cognate tRNAs, i.e. that accept the same amino acid but recognize a different codon in the mRNA (a consequence of the degeneracy in the genetic code). c. Must not recognize the incorrect tRNA - i.e. these enzymes require prec ...
Allosteric enzymes
... In allosteric regulation, the activity of an enzyme is regulated by reversible binding (non-covelent) of an effectors molecule to a site on the enzyme other than the active site, known as the allosteric enzyme. Allosteric effectors can be either positive or negative. Negative effectors decrease the ...
... In allosteric regulation, the activity of an enzyme is regulated by reversible binding (non-covelent) of an effectors molecule to a site on the enzyme other than the active site, known as the allosteric enzyme. Allosteric effectors can be either positive or negative. Negative effectors decrease the ...
Cellular Respiration Stations Worksheet Station 1: Overview Why is
... 3. True or false? If false, make it so that the answer is true: Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria. 4. Is oxygen needed in order for glycolysis to occur? 5. Fill in the blanks below with regards to the steps of glycolysis: Step 1: Glucose is phosphorylated with _____________ phosphates; these pho ...
... 3. True or false? If false, make it so that the answer is true: Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria. 4. Is oxygen needed in order for glycolysis to occur? 5. Fill in the blanks below with regards to the steps of glycolysis: Step 1: Glucose is phosphorylated with _____________ phosphates; these pho ...
Macromolecules
... The hydrocarbons of fat molecules provide energy for our bodies Copyright Cmassengale ...
... The hydrocarbons of fat molecules provide energy for our bodies Copyright Cmassengale ...
Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid Cycle
... product of step three, and a succinyl group is the product of step four. CoA binds the succinyl group to form succinyl CoA. The enzyme that catalyzes step four is regulated by feedback inhibition of ATP, succinyl CoA, and NADH. Step 5. In step ve, a phosphate group is substituted for coenzyme A, an ...
... product of step three, and a succinyl group is the product of step four. CoA binds the succinyl group to form succinyl CoA. The enzyme that catalyzes step four is regulated by feedback inhibition of ATP, succinyl CoA, and NADH. Step 5. In step ve, a phosphate group is substituted for coenzyme A, an ...