Metabolic Engineering for Production of Complex Lipids in Tobacco
... esterified to a glycerol backbone at the sn-1, sn-2 and sn-3 positions (Figure 3c). The fatty acids in a TAG molecule can differ, but are naturally a mixture of two or three different fatty acids. Most natural fats are composed of a mixture of simple and mixed triacylglycerols. In most organisms, TA ...
... esterified to a glycerol backbone at the sn-1, sn-2 and sn-3 positions (Figure 3c). The fatty acids in a TAG molecule can differ, but are naturally a mixture of two or three different fatty acids. Most natural fats are composed of a mixture of simple and mixed triacylglycerols. In most organisms, TA ...
Engineering Cytosolic Acetyl-CoA Metabolism in Saccharomyces
... pyruvate formate lyase and its activating enzyme from Escherichia coli were expressed with two different cofactors, ferredoxin or flavodoxin, and their reductase, respectively, and it was found that the co-expression of either of these cofactors had a positive effect on growth under aerobic conditio ...
... pyruvate formate lyase and its activating enzyme from Escherichia coli were expressed with two different cofactors, ferredoxin or flavodoxin, and their reductase, respectively, and it was found that the co-expression of either of these cofactors had a positive effect on growth under aerobic conditio ...
Unit 6 Vitamins Defining a vitamin Essential
... Rare; Listlessness, fatigue, headache, sleep disturbance, nausea, abdominal distress; Alcoholics at risk Usually in combination with other deficiencies Vitamin B5: _____________________ Exists in free and protein-bound (biocytin) forms; biocytin must be cleaved from protein by biotinidase before bei ...
... Rare; Listlessness, fatigue, headache, sleep disturbance, nausea, abdominal distress; Alcoholics at risk Usually in combination with other deficiencies Vitamin B5: _____________________ Exists in free and protein-bound (biocytin) forms; biocytin must be cleaved from protein by biotinidase before bei ...
Decreased Complete Oxidation Capacity of Fatty Acid in the Liver of
... a consequence, fatty acids may be accumulated in hepatic cells (Jonas et al., 1978), and the fatty acid complete oxidation process decreased (Murondoti, 2004). Therefore, liver fatty acid complete oxidation may be a key factor involved in decreasing BHBA and providing more ATP to prevent ketosis, bu ...
... a consequence, fatty acids may be accumulated in hepatic cells (Jonas et al., 1978), and the fatty acid complete oxidation process decreased (Murondoti, 2004). Therefore, liver fatty acid complete oxidation may be a key factor involved in decreasing BHBA and providing more ATP to prevent ketosis, bu ...
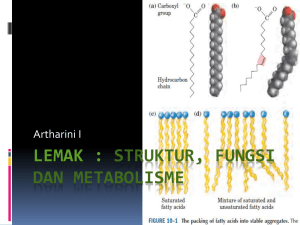
LEMAK : Struktur, Fungsi dan Metabolisme
... Besides the payout of ATP that comes from fatty acid oxidation, another benefit is the generation of H2O that occurs when O2 is reduced by the final reaction in the electron transport system, as well as, the formation of H2O in oxidative phosphorylation. 2 NADH + 2 H+ + O2 --> 2 H2O 2 FADH2 + O2 --> ...
... Besides the payout of ATP that comes from fatty acid oxidation, another benefit is the generation of H2O that occurs when O2 is reduced by the final reaction in the electron transport system, as well as, the formation of H2O in oxidative phosphorylation. 2 NADH + 2 H+ + O2 --> 2 H2O 2 FADH2 + O2 --> ...
C H A P
... We have mentioned before (see General Introduction 3.4 and 4, and Chapter 3) that lipase inhibitors have a high pharmacological interest because they could help in the therapy of diseases in which lipases play an important role such as obesity or infective diseases produced by lipolytic microorganis ...
... We have mentioned before (see General Introduction 3.4 and 4, and Chapter 3) that lipase inhibitors have a high pharmacological interest because they could help in the therapy of diseases in which lipases play an important role such as obesity or infective diseases produced by lipolytic microorganis ...
Bin Presentation(sulfonic)3 - Indiana University Bloomington
... between 38100% of maximal in these engineered cells that over-express the glucagon receptor. We found that homocysteic acid can function as a substitute for Glu9 in glucagon structurefunction relationships, although the correlation is not simple with a number of unexpected findings. Substitution of ...
... between 38100% of maximal in these engineered cells that over-express the glucagon receptor. We found that homocysteic acid can function as a substitute for Glu9 in glucagon structurefunction relationships, although the correlation is not simple with a number of unexpected findings. Substitution of ...
Effects of tRNA modification on translational accuracy depend on
... and E. coli -galactosidase (7). The reporters genes are carried on a low copy bacterial plasmid, pJC27 (30), and expressed from a regulated Ptac promoter (31). Codons encoding four active site amino acids were targeted for mutagenesis: Lys 529 (K529) of Fluc and either glutamic acid 537 (E537), asp ...
... and E. coli -galactosidase (7). The reporters genes are carried on a low copy bacterial plasmid, pJC27 (30), and expressed from a regulated Ptac promoter (31). Codons encoding four active site amino acids were targeted for mutagenesis: Lys 529 (K529) of Fluc and either glutamic acid 537 (E537), asp ...
BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Problem Unit Two
... inhibitor (i.e., a bacterial toxin, a chemical, etc.), the overproduction of an enzyme, or the introduction of a foreign enzyme (i.e., viral infection). Enzymes are popular therapeutic targets. Pharmaceuticals are frequently enzyme inhibitors. Enzyme assays are important in diagnosis. A diminution o ...
... inhibitor (i.e., a bacterial toxin, a chemical, etc.), the overproduction of an enzyme, or the introduction of a foreign enzyme (i.e., viral infection). Enzymes are popular therapeutic targets. Pharmaceuticals are frequently enzyme inhibitors. Enzyme assays are important in diagnosis. A diminution o ...
Lecture 5 - Fermentation and CHO feeder
... Glycogen is primarily stored in the liver and is used to maintain blood glucose levels between meals But … neither G1P nor G6P can be transported out of liver cells Require separate pathway (below) to convert G6P to glucose for transport ...
... Glycogen is primarily stored in the liver and is used to maintain blood glucose levels between meals But … neither G1P nor G6P can be transported out of liver cells Require separate pathway (below) to convert G6P to glucose for transport ...
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Metabolic engineering of for production
... acids at the low pH values where these compounds occur predominantly in their undissociated form. Production at these lower pH values with more acid-tolerant microorganisms, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, would reduce the cost for pH titrants and ensuing byproduct formation (e.g. gypsum). In addi ...
... acids at the low pH values where these compounds occur predominantly in their undissociated form. Production at these lower pH values with more acid-tolerant microorganisms, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, would reduce the cost for pH titrants and ensuing byproduct formation (e.g. gypsum). In addi ...
Molecular Cloning of Dog Mast Cell Tryptase and a Related Protease
... protease. Using R N A from dog mastocytoma cells, we constructed a c D N A library in XgtlO. Screening of the library with an oligonucleotide probe based on the N-terminal sequence of tryptase purified from the same cell source allowed us to isolate and sequence overlapping clones coding for dog mas ...
... protease. Using R N A from dog mastocytoma cells, we constructed a c D N A library in XgtlO. Screening of the library with an oligonucleotide probe based on the N-terminal sequence of tryptase purified from the same cell source allowed us to isolate and sequence overlapping clones coding for dog mas ...
topological changes in the cyp3a4 active site probed with
... plays a significant role in the metabolism of a wide variety of drugs (Guengerich, 1999; Nebert and Russell, 2002). Because of its pharmacological significance and the potential for drug-drug interactions, CYP3A4 has been the subject of a large number of studies focused on elucidating the relationsh ...
... plays a significant role in the metabolism of a wide variety of drugs (Guengerich, 1999; Nebert and Russell, 2002). Because of its pharmacological significance and the potential for drug-drug interactions, CYP3A4 has been the subject of a large number of studies focused on elucidating the relationsh ...
The Bacterial Heterotrimeric Amidotransferase GatCAB
... Gln-tRNAGln (when n=2) (Adapted from [8]). ...
... Gln-tRNAGln (when n=2) (Adapted from [8]). ...
The Three-Dimensional Structure of Aspergillus niger Pectin Lyase
... amino acid sequence. PLB shares 46 to 65% amino acid sequence identity with other A. niger pectin lyases. Unlike the Pels, pectin lyases do not require Ca21 for enzymatic activity; nevertheless, Ca21 and Na1 are known to stimulate enzymatic activity near the pH optimum of 8.5 (Kester and Visser, 199 ...
... amino acid sequence. PLB shares 46 to 65% amino acid sequence identity with other A. niger pectin lyases. Unlike the Pels, pectin lyases do not require Ca21 for enzymatic activity; nevertheless, Ca21 and Na1 are known to stimulate enzymatic activity near the pH optimum of 8.5 (Kester and Visser, 199 ...
Chapter 8: Energy generation:glycolysis
... Oxygen is used up during the reaction, so in chemical terms the process is an oxidation. Glucose oxidation is a highly exergonic reaction, yielding 2870 kJ of energy for every mole of glucose that is broken down. In biochemical terms, this is a substantial amount of energy; a typical endergonic enzy ...
... Oxygen is used up during the reaction, so in chemical terms the process is an oxidation. Glucose oxidation is a highly exergonic reaction, yielding 2870 kJ of energy for every mole of glucose that is broken down. In biochemical terms, this is a substantial amount of energy; a typical endergonic enzy ...
Fermentation metabolism and its evolution in algae
... (AdhE). While this reaction consumes reducing equivalents, it does not result in the generation of ATP (Wolfe, 2005). By coordinating the amount of ethanol and acetate (and other organic acids) synthesized and excreted into the medium, bacteria can efficiently balance their energy requirement with th ...
... (AdhE). While this reaction consumes reducing equivalents, it does not result in the generation of ATP (Wolfe, 2005). By coordinating the amount of ethanol and acetate (and other organic acids) synthesized and excreted into the medium, bacteria can efficiently balance their energy requirement with th ...
Chapter 27 Amino acid
... One way in which amino acids differ is in respect to their acid-base properties. This is the basis for certain experimental methods for ...
... One way in which amino acids differ is in respect to their acid-base properties. This is the basis for certain experimental methods for ...
Branched-chain amino acid restriction in Zucker
... Current evidence suggests that the obesity-related rise in circulating BCAA is the product of multiple metabolic perturbations related to their synthesis and catabolism, rather than being driven by increased intake of these essential amino acids [4,9]. One potential contributing factor has emerged ...
... Current evidence suggests that the obesity-related rise in circulating BCAA is the product of multiple metabolic perturbations related to their synthesis and catabolism, rather than being driven by increased intake of these essential amino acids [4,9]. One potential contributing factor has emerged ...
Glycerol is a major substrate for glucose, glycogen, and
... 1971). Similarly, tissue glycogen begins to accumulate by embryonic day (e) 6 (via the uronic acid pathway), peaking on e12, declining 50% by e13, and then increasing >4-fold by e20 (Hazelwood, 1971). Even though several substrates can serve as precursors for glucose and glycogen synthesis (Langslow ...
... 1971). Similarly, tissue glycogen begins to accumulate by embryonic day (e) 6 (via the uronic acid pathway), peaking on e12, declining 50% by e13, and then increasing >4-fold by e20 (Hazelwood, 1971). Even though several substrates can serve as precursors for glucose and glycogen synthesis (Langslow ...
phosphorylation. synthesis via the mechanism of substrate level
... growth on pyruvate, the reverse reactions catalyzed by phosphate acetyltransferase and acetate kinase might convert acetyl-CoA to acetate and phosphorylate ADP under conditions in which the conversion of acetyl-CoA to methane is ...
... growth on pyruvate, the reverse reactions catalyzed by phosphate acetyltransferase and acetate kinase might convert acetyl-CoA to acetate and phosphorylate ADP under conditions in which the conversion of acetyl-CoA to methane is ...
Profile TildeCRF: a new tool for protein homology detection
... A trellis diagram representing a simple grammatical analyzer . . . . An attempt to use the states of a size 2 profile model in a taggingbased trellis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.3 Consequences for chosing each of the possible states for the first column of the tr ...
... A trellis diagram representing a simple grammatical analyzer . . . . An attempt to use the states of a size 2 profile model in a taggingbased trellis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.3 Consequences for chosing each of the possible states for the first column of the tr ...
The role of sphingolipid metabolism in cutaneous
... generate mainly palmitoyl-CoA [27], which can be ω-hydroxylated and also elongated. As suggested by inhibitor studies, FAs and possibly also ceramides containing ULC-FAs can undergo ω-hydroxylation most likely catalyzed by a P-450-type 4 isoform (CYP4F) [28], a prerequisite for the formation of ω-OH ...
... generate mainly palmitoyl-CoA [27], which can be ω-hydroxylated and also elongated. As suggested by inhibitor studies, FAs and possibly also ceramides containing ULC-FAs can undergo ω-hydroxylation most likely catalyzed by a P-450-type 4 isoform (CYP4F) [28], a prerequisite for the formation of ω-OH ...
Cellular Respiration - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Glucose is a high-energy molecule, and its breakdown products, CO2 and H2O, are low-energy molecules. Therefore, as the equation shows, energy is released. This is the energy that will be used to produce ATP molecules. The cell carries out cellular respiration in order to build up ATP molecules. The ...
... Glucose is a high-energy molecule, and its breakdown products, CO2 and H2O, are low-energy molecules. Therefore, as the equation shows, energy is released. This is the energy that will be used to produce ATP molecules. The cell carries out cellular respiration in order to build up ATP molecules. The ...