l-Carnitine - Pure Encapsulations
... utilization by acting as a carrier of fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized and converted to energy. l-Carnitine also facilitates the removal of short and medium chain fatty acids from the mitochondria that accumulate during normal metabolic processes. In studies, l-carnitine ha ...
... utilization by acting as a carrier of fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized and converted to energy. l-Carnitine also facilitates the removal of short and medium chain fatty acids from the mitochondria that accumulate during normal metabolic processes. In studies, l-carnitine ha ...
Slide 1
... • Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. • Gaps (symbol “-”) are inserted between the residues so that residues with identical or ...
... • Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. • Gaps (symbol “-”) are inserted between the residues so that residues with identical or ...
Glycolysis Quiz
... 7. Enzymes involved in the oxidation reduction of a substance can not operate without NAD+. What is NAD+ known as? (a) co-enzyme (b) co-factor (c) amino acid (d) protein ...
... 7. Enzymes involved in the oxidation reduction of a substance can not operate without NAD+. What is NAD+ known as? (a) co-enzyme (b) co-factor (c) amino acid (d) protein ...
Wellness- lesson 03- Proteins
... When invaders or antigens like allergens, viruses, toxins, and bacteria attack our bodies, we fight back with protein-made antibodies. Once an antigen is detected, protein gets to work building more antibodies that attach to the invading substance and destroy it! Although the process works well, it ...
... When invaders or antigens like allergens, viruses, toxins, and bacteria attack our bodies, we fight back with protein-made antibodies. Once an antigen is detected, protein gets to work building more antibodies that attach to the invading substance and destroy it! Although the process works well, it ...
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency
... deficiency is also known as "favism," since G6PD deficient individuals are also sometimes allergic to fava beans. G6PD deficiency is an allelic abnormality which is inherited in an X-linked recessive fashion ...
... deficiency is also known as "favism," since G6PD deficient individuals are also sometimes allergic to fava beans. G6PD deficiency is an allelic abnormality which is inherited in an X-linked recessive fashion ...
A unique amino acid substitution, T126I, in human
... with an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is one of the major causes of human death. HBV is a double-stranded DNA virus with a very compact genome of only about 3200 bp. It encodes four proteins: S, P, C and X. Some regions of the genome encode two proteins using dif ...
... with an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is one of the major causes of human death. HBV is a double-stranded DNA virus with a very compact genome of only about 3200 bp. It encodes four proteins: S, P, C and X. Some regions of the genome encode two proteins using dif ...
primary structure
... 3.9 Phospholipids and steroids are important lipids with a variety of functions Phospholipids are structurally similar to fats and are an important component of all cells – For example, they are a major part of cell membranes, in which they cluster into a bilayer of phospholipids – The hydrophili ...
... 3.9 Phospholipids and steroids are important lipids with a variety of functions Phospholipids are structurally similar to fats and are an important component of all cells – For example, they are a major part of cell membranes, in which they cluster into a bilayer of phospholipids – The hydrophili ...
3 Resident, Department of Paediatrics, Krishna Institute of Medical
... includes Liver transplant. It may be an effective treatment. It will not reverse brain damage but it may arrest brain damage. However, considering dietary therapy is low risk and long term complications of liver transplant both have equally good outcome. CONCLUSION Intermittent MSUD is potentially a ...
... includes Liver transplant. It may be an effective treatment. It will not reverse brain damage but it may arrest brain damage. However, considering dietary therapy is low risk and long term complications of liver transplant both have equally good outcome. CONCLUSION Intermittent MSUD is potentially a ...
DNA Replication
... b) Transfer of the activated amino acid to its specific tRNA: In this step the amino acid residue of AA – AMP complex is transferred to a tRNA specific for that amino acid, resulting an AA – tRNA complex with liberation of AMP. AA – AMP + tRNA → AA – tRNA + AMP ...
... b) Transfer of the activated amino acid to its specific tRNA: In this step the amino acid residue of AA – AMP complex is transferred to a tRNA specific for that amino acid, resulting an AA – tRNA complex with liberation of AMP. AA – AMP + tRNA → AA – tRNA + AMP ...
Tutorial: Metabolic Signaling in the b-Cell
... Cycle Acetyl group has 2 carbons Oxaloacetate has 4 carbons Citrate has 6 carbons As the cycle progresses, first one carbon is lost and then another Cycle ends where it began, except that 4 NADH, one FADH2, and one GTP molecule have been made The coenzymes NADH and FADH2 are electron carriers that a ...
... Cycle Acetyl group has 2 carbons Oxaloacetate has 4 carbons Citrate has 6 carbons As the cycle progresses, first one carbon is lost and then another Cycle ends where it began, except that 4 NADH, one FADH2, and one GTP molecule have been made The coenzymes NADH and FADH2 are electron carriers that a ...
Citric Acid (or Krebs) Cycle - BYU
... In step 11, we learned that as high energy electrons passed down the chain of protein acceptors, energy was used to move H+ ions into the intermembranous space. This generates a proton gradient. This means that there will be a higher concentration of protons in the intermembranous space than there i ...
... In step 11, we learned that as high energy electrons passed down the chain of protein acceptors, energy was used to move H+ ions into the intermembranous space. This generates a proton gradient. This means that there will be a higher concentration of protons in the intermembranous space than there i ...
The Enzymes of Ammonia Assimilation and their
... The activities of GS, NADP-GOGAT and NADP-GDH in extracts of members of the ‘herbicola’, ‘carotovora’ and ‘amylovora’ clusters, grown with different sources of nitrogen, are shown in Table 1. NAD-GOGAT, NAD-GDH and corresponding amidotransferases and dehydrogenases (both NAD- and NADP-linked) able t ...
... The activities of GS, NADP-GOGAT and NADP-GDH in extracts of members of the ‘herbicola’, ‘carotovora’ and ‘amylovora’ clusters, grown with different sources of nitrogen, are shown in Table 1. NAD-GOGAT, NAD-GDH and corresponding amidotransferases and dehydrogenases (both NAD- and NADP-linked) able t ...
Slide 1
... • Inositol is required for the synthesis of phosphatidyl Inositol which is a constituent of cell membrane. • It act as a lipotropic factor ( along with choline) and prevents the accumulation of fat in liver. ...
... • Inositol is required for the synthesis of phosphatidyl Inositol which is a constituent of cell membrane. • It act as a lipotropic factor ( along with choline) and prevents the accumulation of fat in liver. ...
Chapter 2: Biochemistry Problems
... covalently bonded to an oxygen or nitrogen (–OH or –NH) and a “hydrogen acceptor”: a lone pair of electrons on an oxygen or nitrogen atom (O: or N:). • Hydrophobic interactions: These occur when several or many hydrophobic atoms or groups clump together to avoid contact with water. Hydrophilic group ...
... covalently bonded to an oxygen or nitrogen (–OH or –NH) and a “hydrogen acceptor”: a lone pair of electrons on an oxygen or nitrogen atom (O: or N:). • Hydrophobic interactions: These occur when several or many hydrophobic atoms or groups clump together to avoid contact with water. Hydrophilic group ...
Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Royal Jelly
... Important proteins form 90% of the total amount of proteins with molecular mass of 49-87 kDa proteins and attributed to a gene family. Minor proteins contained in RJ are made from proteins and peptides with different functions, including antimicrobial and antifungal properties [23]. Protein fraction ...
... Important proteins form 90% of the total amount of proteins with molecular mass of 49-87 kDa proteins and attributed to a gene family. Minor proteins contained in RJ are made from proteins and peptides with different functions, including antimicrobial and antifungal properties [23]. Protein fraction ...
Cloning and expression of maize-leaf pyruvate, Pi dikinase
... relatively large number of PPDK-possessing bacterial species, in addition to rice and Arabidopsis. For ascertaining the identity of this gene as RP, we needed to show in vitro that the recombinantly produced protein had the unique catalytic properties of maize leaf RP. That is, Thr456-specific, ADP-d ...
... relatively large number of PPDK-possessing bacterial species, in addition to rice and Arabidopsis. For ascertaining the identity of this gene as RP, we needed to show in vitro that the recombinantly produced protein had the unique catalytic properties of maize leaf RP. That is, Thr456-specific, ADP-d ...
Glycolysis I
... indulge in regeneration of glucose from more oxidized starting materials • This process carries an energetic penalty; energy must be spent to bypass the three reactions of glycolysis that are irreversible. ...
... indulge in regeneration of glucose from more oxidized starting materials • This process carries an energetic penalty; energy must be spent to bypass the three reactions of glycolysis that are irreversible. ...
Modular Architecture of Metabolic Pathways Revealed by
... Metabolism is the most basic aspect of life. It represents a chemical system generating all necessary chemical substances in living cells through chemical reactions. It also represents a genetic system in the sense that chemical reactions are catalyzed by genome-encoded enzymes. The dual aspect of m ...
... Metabolism is the most basic aspect of life. It represents a chemical system generating all necessary chemical substances in living cells through chemical reactions. It also represents a genetic system in the sense that chemical reactions are catalyzed by genome-encoded enzymes. The dual aspect of m ...
poster - Computer Science and Engineering
... Phospho.ELM Data Set – a resource containing 1805 proteins from different species covering 1372 Tyr, 3175 Ser and 767 Thr experimentally verified phosphorylation sites manually curated from the literature. We constructed separate data sets for kinase families that are well represented in terms of th ...
... Phospho.ELM Data Set – a resource containing 1805 proteins from different species covering 1372 Tyr, 3175 Ser and 767 Thr experimentally verified phosphorylation sites manually curated from the literature. We constructed separate data sets for kinase families that are well represented in terms of th ...
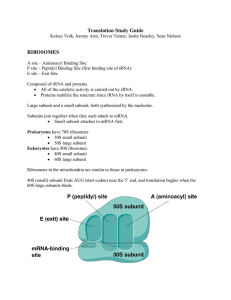
handout
... AUG start codon. 2. Next, the tRNA and small sub-unit complex bind to translation initiation factors and attach to the 5’ cap of the mature mRNA. 3. Next, the entire complex scans in the 3’ direction until it finds the AUG start codon of the mRNA 4. Lastly, the 60S large sub-unit binds to the comple ...
... AUG start codon. 2. Next, the tRNA and small sub-unit complex bind to translation initiation factors and attach to the 5’ cap of the mature mRNA. 3. Next, the entire complex scans in the 3’ direction until it finds the AUG start codon of the mRNA 4. Lastly, the 60S large sub-unit binds to the comple ...
Enzymatic Synthesis of Arginine Phosphate with Coupled ATP
... work with limited amounts (100-400 U) of the relatively expensive6enzyme and to let the reaction proceed over several days. Arginine kinase was immobilized in a polyacrylamide gel (PAN 1000) using a procedure described previously (12), and using ADP, Mg2+, Arg, and NOT7 to protect the active site. I ...
... work with limited amounts (100-400 U) of the relatively expensive6enzyme and to let the reaction proceed over several days. Arginine kinase was immobilized in a polyacrylamide gel (PAN 1000) using a procedure described previously (12), and using ADP, Mg2+, Arg, and NOT7 to protect the active site. I ...