Topic guide 1.2: Enzymes
... Applying heat energy to molecules increases their kinetic energy so there will be an increased number of collisions between enzyme and substrate molecules. This in turn will increase the rate of reaction and so the products will be formed more quickly. However, applying too much heat can cause enzym ...
... Applying heat energy to molecules increases their kinetic energy so there will be an increased number of collisions between enzyme and substrate molecules. This in turn will increase the rate of reaction and so the products will be formed more quickly. However, applying too much heat can cause enzym ...
pdf-download
... corresponding back reaction. One example is the racemic resolution of amino acids like methionine to the desired enantiopure L-compounds. Another class of enzymes that can be found regularly in commercialised processes are the so-called oxidoreductases, enzymes that perform oxidation or reduction re ...
... corresponding back reaction. One example is the racemic resolution of amino acids like methionine to the desired enantiopure L-compounds. Another class of enzymes that can be found regularly in commercialised processes are the so-called oxidoreductases, enzymes that perform oxidation or reduction re ...
Divergent Evolution of Function in the ROK Sugar
... ABSTRACT: The D-allose and N-acetyl-D-mannosamine kinases of Escherichia coli K-12 are divergent members of the functionally diverse ROK (repressor, open reading frame, kinase) superfamily. Previous work in our laboratory has demonstrated that AlsK and NanK possess weak phosphoryl transfer activity ...
... ABSTRACT: The D-allose and N-acetyl-D-mannosamine kinases of Escherichia coli K-12 are divergent members of the functionally diverse ROK (repressor, open reading frame, kinase) superfamily. Previous work in our laboratory has demonstrated that AlsK and NanK possess weak phosphoryl transfer activity ...
Final Respiration
... Efficiency of Glycolysis • Compare the kilocalories of glucose with the kilocalories in the ATP that is made. • The 2 ATP molecules made during glycolysis account for only 2% of the energy in glucose • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for ...
... Efficiency of Glycolysis • Compare the kilocalories of glucose with the kilocalories in the ATP that is made. • The 2 ATP molecules made during glycolysis account for only 2% of the energy in glucose • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for ...
cellrespdiagrams
... Efficiency of Glycolysis • Compare the kilocalories of glucose with the kilocalories in the ATP that is made. • The 2 ATP molecules made during glycolysis account for only 2% of the energy in glucose • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for ...
... Efficiency of Glycolysis • Compare the kilocalories of glucose with the kilocalories in the ATP that is made. • The 2 ATP molecules made during glycolysis account for only 2% of the energy in glucose • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for ...
REVIEWS
... carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur. This enables them to feed the central metabolic pathways — glycolysis, the pentose-phosphate pathway, the citric acid cycle and the 2‑oxoglutarate–glutamate–glutamine cycle — from which all of the precursors that are required for the synthesis of the cell’s ...
... carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur. This enables them to feed the central metabolic pathways — glycolysis, the pentose-phosphate pathway, the citric acid cycle and the 2‑oxoglutarate–glutamate–glutamine cycle — from which all of the precursors that are required for the synthesis of the cell’s ...
Final Respiration
... Efficiency of Glycolysis • Compare the kilocalories of glucose with the kilocalories in the ATP that is made. • The 2 ATP molecules made during glycolysis account for only 2% of the energy in glucose • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for ...
... Efficiency of Glycolysis • Compare the kilocalories of glucose with the kilocalories in the ATP that is made. • The 2 ATP molecules made during glycolysis account for only 2% of the energy in glucose • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for ...
pdf
... be charged with that amino acid. The amino acid is recognized on the basis of its side chain structure and chemistry. The correct tRNA is recognized as described above. Some of the Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases have proof reading capabilities. After the amino acid has been attached, some of these enzym ...
... be charged with that amino acid. The amino acid is recognized on the basis of its side chain structure and chemistry. The correct tRNA is recognized as described above. Some of the Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases have proof reading capabilities. After the amino acid has been attached, some of these enzym ...
macromolecules test 1
... Which one of the following statements correctly describes a process that occurs during protein synthesis? J. K. ...
... Which one of the following statements correctly describes a process that occurs during protein synthesis? J. K. ...
cell respiration notes ap - Wesleyan
... Regulated by phosphofructokinase ALLOSTERIC enzyme near beginning of pathway AMP turns pathway on (AMP is high when ATP is needed) ATP turns pathway off (don’t waste energy making ATP when not needed) ...
... Regulated by phosphofructokinase ALLOSTERIC enzyme near beginning of pathway AMP turns pathway on (AMP is high when ATP is needed) ATP turns pathway off (don’t waste energy making ATP when not needed) ...
PDF Full-text
... peptide analogues include: phosphonamidates (X = NH, the closest TS analogues), phosphonates (X = O, pseudodepsipeptides) and phosphinates (X = CH2). All these compounds appear particularly effective in regulating the activity of metalloproteases. Nevertheless, investigation of other proteases (e.g. ...
... peptide analogues include: phosphonamidates (X = NH, the closest TS analogues), phosphonates (X = O, pseudodepsipeptides) and phosphinates (X = CH2). All these compounds appear particularly effective in regulating the activity of metalloproteases. Nevertheless, investigation of other proteases (e.g. ...
Amino Acid Composition in Fillets of Mirror Crossbreds Common
... (Ježek and Buchtová 2007). The factors considered include carp fillet shelf-life under various experimental packaging conditions (vacuum, modified atmosphere) and storage conditions with the objective to define physical and chemical indicators and their concrete numerical values that are decisive fo ...
... (Ježek and Buchtová 2007). The factors considered include carp fillet shelf-life under various experimental packaging conditions (vacuum, modified atmosphere) and storage conditions with the objective to define physical and chemical indicators and their concrete numerical values that are decisive fo ...
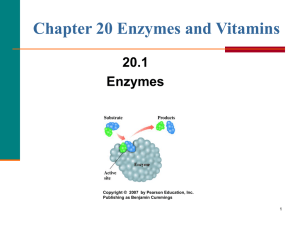
Enzymes
... Some enzymes require coenzymes • Some enzymes require a coenzyme (another compound) to be bound to them before they can catalyze reactions. • Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds. • Eg. of coenzymes: Vitamin B complex ...
... Some enzymes require coenzymes • Some enzymes require a coenzyme (another compound) to be bound to them before they can catalyze reactions. • Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds. • Eg. of coenzymes: Vitamin B complex ...
Module 6 – Microbial Metabolism
... group of electron carriers (usually to NAD+ and FAD). Then, the electrons are passed through a series of different electron carriers to molecules of O2 or other oxidized inorganic and organic molecules. This process occurs in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes and in the inner mitochondrial membrane ...
... group of electron carriers (usually to NAD+ and FAD). Then, the electrons are passed through a series of different electron carriers to molecules of O2 or other oxidized inorganic and organic molecules. This process occurs in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes and in the inner mitochondrial membrane ...
enhanced rate of ethanol elimination from blood after intravenous
... Abstract — Aims: To investigate the effect of an amino acid mixture given intravenously (i.v.) on the rate of ethanol elimination from blood compared with equicaloric glucose and Ringer’s acetate as control treatments. Methods: In a randomized cross-over study, six healthy men (mean age 23 years) fa ...
... Abstract — Aims: To investigate the effect of an amino acid mixture given intravenously (i.v.) on the rate of ethanol elimination from blood compared with equicaloric glucose and Ringer’s acetate as control treatments. Methods: In a randomized cross-over study, six healthy men (mean age 23 years) fa ...
Chapter 15 Acids and Bases
... the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make a molecule of H2O it is often helpful to think of H2O as H-OH the cation from the base combines with the anion from the acid to make a salt acid + base → salt + water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) H+(aq)+Cl-(aq)+Na+(aq)+ ...
... the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make a molecule of H2O it is often helpful to think of H2O as H-OH the cation from the base combines with the anion from the acid to make a salt acid + base → salt + water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) H+(aq)+Cl-(aq)+Na+(aq)+ ...
A novel assay method for an amino acid racemase reaction based
... The new assay method established in the present study for the measurement of the catalytic activity of ALR is based on the CD spectra of both enantiomers of Ala. The method is highly quantitative and provides visible data that reflect the exhaustive reaction of ALR. We conclude that the CD assay met ...
... The new assay method established in the present study for the measurement of the catalytic activity of ALR is based on the CD spectra of both enantiomers of Ala. The method is highly quantitative and provides visible data that reflect the exhaustive reaction of ALR. We conclude that the CD assay met ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... An enzyme in a pathway that controls the rate of the reaction. 2. PR Speeds up a reaction by combining with an enzyme in the pathway. 3. Z Removal of a peptide activates the enzyme. 4. FC Some product binds to the first enzyme to limit the synthesis of product. ...
... An enzyme in a pathway that controls the rate of the reaction. 2. PR Speeds up a reaction by combining with an enzyme in the pathway. 3. Z Removal of a peptide activates the enzyme. 4. FC Some product binds to the first enzyme to limit the synthesis of product. ...
Monosaccharides
... phosphoric acid esters (phosphates). For example, glucose phosphorylation takes place with the participation of ATP and enzyme glucokinase: ...
... phosphoric acid esters (phosphates). For example, glucose phosphorylation takes place with the participation of ATP and enzyme glucokinase: ...
Cell Respiration Notes Kelly
... Regulated by phosphofructokinase ALLOSTERIC enzyme near beginning of pathway AMP turns pathway on (AMP is high when ATP is needed) ATP turns pathway off (don’t waste energy making ATP when not needed) ...
... Regulated by phosphofructokinase ALLOSTERIC enzyme near beginning of pathway AMP turns pathway on (AMP is high when ATP is needed) ATP turns pathway off (don’t waste energy making ATP when not needed) ...
Cell Respiration Notes
... Regulated by phosphofructokinase ALLOSTERIC enzyme near beginning of pathway AMP turns pathway on (AMP is high when ATP is needed) ATP turns pathway off (don’t waste energy making ATP when not needed) ...
... Regulated by phosphofructokinase ALLOSTERIC enzyme near beginning of pathway AMP turns pathway on (AMP is high when ATP is needed) ATP turns pathway off (don’t waste energy making ATP when not needed) ...