OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
... The scale runs from 0 to 14 with 0 being highest in acidity and 14 lowest. When the pH is in the range of 0 -7, a solution is said to be acidic; if the pH is around 7, the solution is neutral; and if the pH is in the range of 7-14, the solution is basic. Amino acid side chains contain groups, such a ...
... The scale runs from 0 to 14 with 0 being highest in acidity and 14 lowest. When the pH is in the range of 0 -7, a solution is said to be acidic; if the pH is around 7, the solution is neutral; and if the pH is in the range of 7-14, the solution is basic. Amino acid side chains contain groups, such a ...
Energy Metabolism - Rajarata University of Sri Lanka
... illustrated by the speed with which aerobic cells, tissues, and organisms die if deprived of oxygen! An even more striking example is given by the elite marathon runner who, it has been calculated, uses a colossal 60kg of ATP during a race12. Moreover, an increase in the steady state level of ATP co ...
... illustrated by the speed with which aerobic cells, tissues, and organisms die if deprived of oxygen! An even more striking example is given by the elite marathon runner who, it has been calculated, uses a colossal 60kg of ATP during a race12. Moreover, an increase in the steady state level of ATP co ...
pH and pOH (cont.)
... • The concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions determine whether an aqueous solution is acidic, basic, or neutral. • An Arrhenius acid must contain an ionizable hydrogen atom. An Arrhennius base must contain an ionizable hydroxide group. • A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a hydrogen ion donor. A B ...
... • The concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions determine whether an aqueous solution is acidic, basic, or neutral. • An Arrhenius acid must contain an ionizable hydrogen atom. An Arrhennius base must contain an ionizable hydroxide group. • A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a hydrogen ion donor. A B ...
File
... It is asymmetric—both H atoms are on one side. It requires a lot heat to evaporate it. It is an excellent solvent for many substances. It determines the interactions between many biological solutes. ...
... It is asymmetric—both H atoms are on one side. It requires a lot heat to evaporate it. It is an excellent solvent for many substances. It determines the interactions between many biological solutes. ...
transition metal complexes of amino acid and peptide derivatives
... formation processes has already been widely studied. However the presence of carboxylate groups in the side chain modifies the charge of the ligands and the complexes. We have investigated the copper(II) and nickel(II) complexes of di-, tri- and tetra-peptides containing one, two or more aspartic an ...
... formation processes has already been widely studied. However the presence of carboxylate groups in the side chain modifies the charge of the ligands and the complexes. We have investigated the copper(II) and nickel(II) complexes of di-, tri- and tetra-peptides containing one, two or more aspartic an ...
Seminario Glúcidos 3 y lípidos 1. Comente los mecanismos de
... up in distilled water, sufficient KC1 was added to the test flasks to provide a fmal concentration of about 0.05 M. Throughout these fractionations, it was found essential that low temperatures be maintained in order to preserve enzyme activity. We have found that the Sorvall angle centrifuges are e ...
... up in distilled water, sufficient KC1 was added to the test flasks to provide a fmal concentration of about 0.05 M. Throughout these fractionations, it was found essential that low temperatures be maintained in order to preserve enzyme activity. We have found that the Sorvall angle centrifuges are e ...
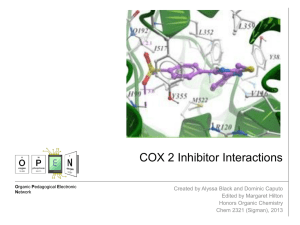
COX 2 Inhibitor Interactions - Center for Selective C–H
... Aspirin can act as a COX-2 inhibitor, yet it is not as selective as most COX-2 inhibitors. Thus, it will also react with COX-1 enzymes, causing undesired side effects. When aspirin interacts with the COX-2 active site, it permanently acetylates a residue in the active site, according to the followin ...
... Aspirin can act as a COX-2 inhibitor, yet it is not as selective as most COX-2 inhibitors. Thus, it will also react with COX-1 enzymes, causing undesired side effects. When aspirin interacts with the COX-2 active site, it permanently acetylates a residue in the active site, according to the followin ...
Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme/Active Site
... reaction by stabilizing the transition state intermediate. This is accomplished by lowering the energy barrier or activation energy- the energy that is required to promote the formation of transition state intermediate. The three dimensional cleft is formed by the groups that come from different par ...
... reaction by stabilizing the transition state intermediate. This is accomplished by lowering the energy barrier or activation energy- the energy that is required to promote the formation of transition state intermediate. The three dimensional cleft is formed by the groups that come from different par ...
Fatty acid
... Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • Lipids are hydrophobic because … • The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids • Fats are constructed from two types ...
... Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • Lipids are hydrophobic because … • The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids • Fats are constructed from two types ...
Improving the Content of Essential Amino Acids in
... potential to increase the contents of Trp and Met in a seed-specific manner have already been proven successful in basic research studies. Another advantage of genetically engineered traits is that they can be transformed into multiple plant species and genotypes and function synergistically with ma ...
... potential to increase the contents of Trp and Met in a seed-specific manner have already been proven successful in basic research studies. Another advantage of genetically engineered traits is that they can be transformed into multiple plant species and genotypes and function synergistically with ma ...
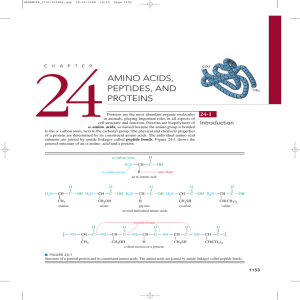
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely deficient in one or more of the essential amino acids are called incomplete proteins. If the protein in a person’s diet comes mostly from one incomplete source, the am ...
... those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely deficient in one or more of the essential amino acids are called incomplete proteins. If the protein in a person’s diet comes mostly from one incomplete source, the am ...
A new subfamily of fungal subtilases: structural and functional
... prokaryotic subtilases, many members of this superfamily have been identified in eukaryotes such as fungi, plants, insects and mammals. Pleurotus ostreatus and Phanerochaete chrysosporium are white-rot basidiomycetes, which belong to different subclasses of ligninolytic micro-organisms, producing di ...
... prokaryotic subtilases, many members of this superfamily have been identified in eukaryotes such as fungi, plants, insects and mammals. Pleurotus ostreatus and Phanerochaete chrysosporium are white-rot basidiomycetes, which belong to different subclasses of ligninolytic micro-organisms, producing di ...
T M 24,
... drive, and to a wide variety of other surfaces in the world around us. These coatings are also serving to protect the surfaces from a variety of environmental hazards, including moisture, UV damage, and biological growth (e.g. mold). What more can coatings do for us? Recent advances in materials and ...
... drive, and to a wide variety of other surfaces in the world around us. These coatings are also serving to protect the surfaces from a variety of environmental hazards, including moisture, UV damage, and biological growth (e.g. mold). What more can coatings do for us? Recent advances in materials and ...
Proteins
... • It is composed of α, β, and κ caseins which form a micelle, or a solubilized unit. ...
... • It is composed of α, β, and κ caseins which form a micelle, or a solubilized unit. ...
A fatty acid
... One fatty acid replaced by phosphate PO4 Molecule has Hydrophilic head, and long ...
... One fatty acid replaced by phosphate PO4 Molecule has Hydrophilic head, and long ...
Prediction of DNA-binding residues in proteins from amino acid
... The protein–DNA recognition mechanism is complicated and the interactions consist of a variety of atomic contacts involving hydrogen bonds, van der Waals contacts and electrostatic, watermediated bonds between amino acid residues and nucleotide bases. Such residues that recognize DNA can be identifi ...
... The protein–DNA recognition mechanism is complicated and the interactions consist of a variety of atomic contacts involving hydrogen bonds, van der Waals contacts and electrostatic, watermediated bonds between amino acid residues and nucleotide bases. Such residues that recognize DNA can be identifi ...
Cell Bio!!!!
... a) Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins always bind to the minor groove in the DNA double helix. b) The minor groove presents four different configurations of hydrogen-bond donor, hydrogen-bond acceptor, hydrogen atom and methyl group; whereas, the major groove presents two. c) Some gene regulator ...
... a) Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins always bind to the minor groove in the DNA double helix. b) The minor groove presents four different configurations of hydrogen-bond donor, hydrogen-bond acceptor, hydrogen atom and methyl group; whereas, the major groove presents two. c) Some gene regulator ...
Preview - International Institute of Naturopathy
... (with the exception of seafood, which contains saturated fatty acids as well as an equally large number of polyunsaturated fatty acids), whereas vegetable fats consist largely of unsaturated fatty acids (with the exception of coconut and palm oil, which consist almost exclusively of saturated fatty ...
... (with the exception of seafood, which contains saturated fatty acids as well as an equally large number of polyunsaturated fatty acids), whereas vegetable fats consist largely of unsaturated fatty acids (with the exception of coconut and palm oil, which consist almost exclusively of saturated fatty ...
Glycolysis
... ∆Go’ = -85 kJ/mol 9 of the ten metabolites of glycolysis are phosphorylated. Phosphorylated intermediates serve 3 ...
... ∆Go’ = -85 kJ/mol 9 of the ten metabolites of glycolysis are phosphorylated. Phosphorylated intermediates serve 3 ...
A novel zinc-dependent D-serine dehydratase
... of normal L-aminoacyl tRNAs and cause a delay of cell growth [12]. In S. cerevisiae cells, D-tyrosine was found to serve as a substrate of tyrosine tRNA synthase [13]. It is possible that the formation of D-aminoacyl tRNAs is one of the reasons for the toxicity of D-amino acids to S. cerevisiae cell ...
... of normal L-aminoacyl tRNAs and cause a delay of cell growth [12]. In S. cerevisiae cells, D-tyrosine was found to serve as a substrate of tyrosine tRNA synthase [13]. It is possible that the formation of D-aminoacyl tRNAs is one of the reasons for the toxicity of D-amino acids to S. cerevisiae cell ...