cell-transport-g9
... region of their lower concentration (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane’ ...
... region of their lower concentration (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane’ ...
Chapt 5 - Workforce Solutions
... What is facilitated diffusion? Carrier proteins bind to the molecule that they transport across the membrane. Facilitated diffusion is movement of a molecule from high to low concentration with the help of a carrier protein. -is specific -is passive -saturates when all carriers are occupied ...
... What is facilitated diffusion? Carrier proteins bind to the molecule that they transport across the membrane. Facilitated diffusion is movement of a molecule from high to low concentration with the help of a carrier protein. -is specific -is passive -saturates when all carriers are occupied ...
Cells and Their Environment
... • Cells, tissues, organs, and organisms must maintain a balance. • Cells do so by controlling and regulating what gets into and out of the cell. ...
... • Cells, tissues, organs, and organisms must maintain a balance. • Cells do so by controlling and regulating what gets into and out of the cell. ...
Exam Outline - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Eukaryotic vs prokaryotic; unicellular vs multi cellular; plant vs animal ...
... Eukaryotic vs prokaryotic; unicellular vs multi cellular; plant vs animal ...
Cell Transport notes
... concentration of solutes in two fluids – isotonic fluids: equal solute concentration – hypotonic fluid: a fluid with fewer solute concentration – hypertonic fluid: a fluid with a high solute concentration. ...
... concentration of solutes in two fluids – isotonic fluids: equal solute concentration – hypotonic fluid: a fluid with fewer solute concentration – hypertonic fluid: a fluid with a high solute concentration. ...
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
... concentration to an area of high concentration. • Unlike diffusion, particles go against the concentration gradient. • It is analogous to rowing a boat upstream against the current (concentration gradient). ...
... concentration to an area of high concentration. • Unlike diffusion, particles go against the concentration gradient. • It is analogous to rowing a boat upstream against the current (concentration gradient). ...
cell drinking
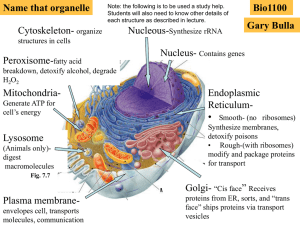
... • Ribosomes are on outside surfce of rough ER • Ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein ...
... • Ribosomes are on outside surfce of rough ER • Ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein ...
Created by Tiarra Moore Crawford Long Middle School Atlanta, GA
... Does a cell really need a semipermeable membrane? What if it didn't have one? ...
... Does a cell really need a semipermeable membrane? What if it didn't have one? ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Introduction to Cells
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
Transport worksheet
... 5. A red blood cell is placed in distilled water. Describe and explain the changes in the shape of the red blood cell. 6. If you took a fresh water amoeba (unicellular organism) and placed it in sea water, what changes would occur to the organism? 7. Two cells are attached by a common membrane. In c ...
... 5. A red blood cell is placed in distilled water. Describe and explain the changes in the shape of the red blood cell. 6. If you took a fresh water amoeba (unicellular organism) and placed it in sea water, what changes would occur to the organism? 7. Two cells are attached by a common membrane. In c ...
1. The transport method of neurotransmitters between nerve cells is
... b. Occurs in protozoans and algae but not in more complex organisms c. Involves the specific binding of molecules to receptors on the cell surface d. Is the nonspecific uptake of fluids by pinching inward of the plasma membrane e. Is movement of molecules against the concentration gradient through a ...
... b. Occurs in protozoans and algae but not in more complex organisms c. Involves the specific binding of molecules to receptors on the cell surface d. Is the nonspecific uptake of fluids by pinching inward of the plasma membrane e. Is movement of molecules against the concentration gradient through a ...
General Biology Notes 9 The Cell Membrane (pages 204, 205, 208
... 1. __________________ also are surrounded by membrane B. The cell membrane has several _________________… 1. It controls what ___________ and leaves the cell 2. It receives signals from and sends signals to surrounding cells or the surrounding _______________________ 3. Helps maintain the cell size ...
... 1. __________________ also are surrounded by membrane B. The cell membrane has several _________________… 1. It controls what ___________ and leaves the cell 2. It receives signals from and sends signals to surrounding cells or the surrounding _______________________ 3. Helps maintain the cell size ...
Year 8 Science
... Mitosis is the name given to the process of cell division that produces two identical cells. Mitosis consists of four phases. In the diagram below, indicate which phase of mitosis is represented by each of the letters: Prophase a) A ______________ The nucleus membrane breaks down. The chromosomes t ...
... Mitosis is the name given to the process of cell division that produces two identical cells. Mitosis consists of four phases. In the diagram below, indicate which phase of mitosis is represented by each of the letters: Prophase a) A ______________ The nucleus membrane breaks down. The chromosomes t ...
cells
... • Plants add several substances to the cell wall: – Suberin – waxy substance found on cell walls on the bottom of the leaf to retain water – Lignin – hard substance added to the cell walls of stems to make them woody ...
... • Plants add several substances to the cell wall: – Suberin – waxy substance found on cell walls on the bottom of the leaf to retain water – Lignin – hard substance added to the cell walls of stems to make them woody ...
LB145-lecture4
... What does animal cell have that plants don’t? A. A single plasma membrane surrounding it B. Mitochondria C. A true Nucleus D. The cell wall surrounding it E. None of the above ...
... What does animal cell have that plants don’t? A. A single plasma membrane surrounding it B. Mitochondria C. A true Nucleus D. The cell wall surrounding it E. None of the above ...
Cell Membranes The composition of nearly all cell
... known as diffusion. In any solution, solute particles move constantly. They collide with one another and tend to spread out randomly. As a result, the particles tend to move from an area of greater concentration to an area of lower concentration, a process known as diffusion (dih-FYOO-zhun). When th ...
... known as diffusion. In any solution, solute particles move constantly. They collide with one another and tend to spread out randomly. As a result, the particles tend to move from an area of greater concentration to an area of lower concentration, a process known as diffusion (dih-FYOO-zhun). When th ...
Cell specialisation
... 1 The diagrams above show some of the different types of cells found in your body. a Label the nucleus, cytoplasm and cell membrane in each cell. b Write a caption for each cell diagram to explain the function of the cell. c Write notes beside each cell to explain how it is adapted for its funct ...
... 1 The diagrams above show some of the different types of cells found in your body. a Label the nucleus, cytoplasm and cell membrane in each cell. b Write a caption for each cell diagram to explain the function of the cell. c Write notes beside each cell to explain how it is adapted for its funct ...
Honors Biology Unit 2 Study Guide: Biochemistry
... 13. List types of cells that would be expected to have cell walls and/or cell membranes 14. Describe what cell walls and cell membranes do 15. Diagram the structure of the cell wall and cell membrane 16. Explain and diagram the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure; include 4 major types of integ ...
... 13. List types of cells that would be expected to have cell walls and/or cell membranes 14. Describe what cell walls and cell membranes do 15. Diagram the structure of the cell wall and cell membrane 16. Explain and diagram the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure; include 4 major types of integ ...
Membrane Structure and Function - AP-Science-Experience-JMHS
... Describe how each of the following can affect membrane fluidity: a. decreasing temperature ...
... Describe how each of the following can affect membrane fluidity: a. decreasing temperature ...
Document
... reticulum. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is like an industrial conveyor belt which can transport substance; the smooth endoplasmic reticulum can produce steroid hormones. Golgi body:They are adjacent to the nucleus and formed by the stack of many flat sac membranes, acting as an industrial cutting ...
... reticulum. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is like an industrial conveyor belt which can transport substance; the smooth endoplasmic reticulum can produce steroid hormones. Golgi body:They are adjacent to the nucleus and formed by the stack of many flat sac membranes, acting as an industrial cutting ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.