Cell Membrane
... to make sure the cell stays intact in this environment. What would happen if a cell dissolved in water, like sugar does? Obviously, the cell could not survive in such an environment. So something must protect the cell and allow it to survive in its water-based environment. All cells have a barrier a ...
... to make sure the cell stays intact in this environment. What would happen if a cell dissolved in water, like sugar does? Obviously, the cell could not survive in such an environment. So something must protect the cell and allow it to survive in its water-based environment. All cells have a barrier a ...
7.2 Cell Structure
... For Questions 19–22, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ...
... For Questions 19–22, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Endomembrane System • Golgi Apparatus o Compartment of flattened membrane sacs o Proteins and lipids from the ER (transported by vesicles) are sorted, packaged, and tagged so that they end up in the right place ...
... Endomembrane System • Golgi Apparatus o Compartment of flattened membrane sacs o Proteins and lipids from the ER (transported by vesicles) are sorted, packaged, and tagged so that they end up in the right place ...
Types of Passive Transport
... 1. Requires no energy 2. Molecules move from high to low concentration 3. Molecules move with the concentration gradient. “Go with the flow” Low ...
... 1. Requires no energy 2. Molecules move from high to low concentration 3. Molecules move with the concentration gradient. “Go with the flow” Low ...
Cells - Quia
... 30 Process defined as the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane (7) ...
... 30 Process defined as the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane (7) ...
Cytology 20 Questions - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 12) Which of the following statements about internal membranes in eukaryotic cells is false? A) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes form membranous compartments called organelles. B) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes provide an additional area for many metabolic processes to occur. C) In e ...
... 12) Which of the following statements about internal membranes in eukaryotic cells is false? A) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes form membranous compartments called organelles. B) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes provide an additional area for many metabolic processes to occur. C) In e ...
Cell Structure and Function - Goshen Central School District
... Cilia and flagella are extensions of the plasma membrane Cilia and flagella are composed of microtubules in a “9+2” arrangement formed by centrioles which become membrane-anchored structures called basal bodies Cilia are short (10-25 µm) and numerous while flagella are long (50-75 µm) but few in any ...
... Cilia and flagella are extensions of the plasma membrane Cilia and flagella are composed of microtubules in a “9+2” arrangement formed by centrioles which become membrane-anchored structures called basal bodies Cilia are short (10-25 µm) and numerous while flagella are long (50-75 µm) but few in any ...
Exploring the inner geography of the plasma membrane
... where a cell perceives signals from its environment and neighbouring cells. It is also the site that has to organize the carbohydrate-rich surface of a cell, may it be the glycocalyx of animal cells or the cell wall of plant and fungal cells. This task requires intricate topological patterning of th ...
... where a cell perceives signals from its environment and neighbouring cells. It is also the site that has to organize the carbohydrate-rich surface of a cell, may it be the glycocalyx of animal cells or the cell wall of plant and fungal cells. This task requires intricate topological patterning of th ...
Types of Transport
... • bind to a specific type of diffusing molecule. • have a highly specific hydrophilic region to which the solute molecule binds. • binding cause the protein to undergo a change in shape that moves the solute across the bilayer and release it on the other side ...
... • bind to a specific type of diffusing molecule. • have a highly specific hydrophilic region to which the solute molecule binds. • binding cause the protein to undergo a change in shape that moves the solute across the bilayer and release it on the other side ...
Lecture 6 eukaryote
... • Phagocytosis: use of cell surface protrusions to surround and engulf particles • Clathrin-dependent: clathrin protein-coated pits have external receptors that specifically bind macromolecules • Caveolae-dependent endocytosis: form caveolae (cholesterol & membrane protein) invagination from plasma ...
... • Phagocytosis: use of cell surface protrusions to surround and engulf particles • Clathrin-dependent: clathrin protein-coated pits have external receptors that specifically bind macromolecules • Caveolae-dependent endocytosis: form caveolae (cholesterol & membrane protein) invagination from plasma ...
IMMS 1 Revision
... Mitochondria - cell ‘battery’, oxidative phosphorylation, mtDNA, double membrane (inner highly folded) ● Outer membrane - lipid synthesis and fatty acid metabolism ● Inner membrane* - Respiratory (electron transport) chain ATP production ● Matrix - Tricarboxylic acid (Krebs’) cycle ...
... Mitochondria - cell ‘battery’, oxidative phosphorylation, mtDNA, double membrane (inner highly folded) ● Outer membrane - lipid synthesis and fatty acid metabolism ● Inner membrane* - Respiratory (electron transport) chain ATP production ● Matrix - Tricarboxylic acid (Krebs’) cycle ...
Document
... Cell – smallest unit that can live and reproduce on its own or as part of a multicelled organism. It has an outer membrane, DNA, and other components called organelles. Tissue – cells form tissues. It is an organized group of similar cells that perform the same task. For example, muscle is a tissue ...
... Cell – smallest unit that can live and reproduce on its own or as part of a multicelled organism. It has an outer membrane, DNA, and other components called organelles. Tissue – cells form tissues. It is an organized group of similar cells that perform the same task. For example, muscle is a tissue ...
Modern cell theory
... surface of the cell which separates the cell from the environment. The cytoplasm is the aqueous content within the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane : It is like any other membrane in the cell but it plays a very important function. It forms the border of a cell, so it is also called the cell membra ...
... surface of the cell which separates the cell from the environment. The cytoplasm is the aqueous content within the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane : It is like any other membrane in the cell but it plays a very important function. It forms the border of a cell, so it is also called the cell membra ...
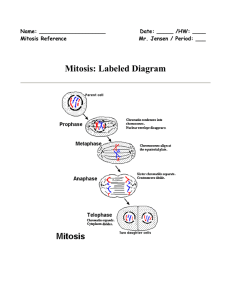
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Crossword Puzzle: Cells
... 15. double layer surrounding the nucleus 17. energy molecule made inside the mitochondria 18. short hair-like structures made of microtubules that help move cells 19. a constant internal environment maintained by cells 20. made of similar cells working together to do a job such as muscle 22. long wh ...
... 15. double layer surrounding the nucleus 17. energy molecule made inside the mitochondria 18. short hair-like structures made of microtubules that help move cells 19. a constant internal environment maintained by cells 20. made of similar cells working together to do a job such as muscle 22. long wh ...
Systems Microbiology 1
... a. Draw the general structure of gram negative and gram positive bacterial cell walls. b. What gives these cell walls their structural integrity, how, and why is that important. Structural integrity of bacterial cell walls is provided by peptidoglycan crosslinking, which is important for stability a ...
... a. Draw the general structure of gram negative and gram positive bacterial cell walls. b. What gives these cell walls their structural integrity, how, and why is that important. Structural integrity of bacterial cell walls is provided by peptidoglycan crosslinking, which is important for stability a ...
Cells and Their Environment
... 1. Endocytosis- active transport that moves large particles into cell membrane • 2 types• Phagocytosis- cell eating • Pinocytosis-cell drinking ...
... 1. Endocytosis- active transport that moves large particles into cell membrane • 2 types• Phagocytosis- cell eating • Pinocytosis-cell drinking ...
Osmosis and diffusion webquest
... (“Cell biology animations”) and select “osmosis” under “cell transport”. a. In the basic animation, describe the movement of the water molecules across the membrane. Consider the volume of fluid on each side. ...
... (“Cell biology animations”) and select “osmosis” under “cell transport”. a. In the basic animation, describe the movement of the water molecules across the membrane. Consider the volume of fluid on each side. ...
Word bonk: focilitoted, diffusion , glucose, proteins, osmosis thot olso
... Word bonk: focilitoted, diffusion , glucose, proteins, osmosis ...
... Word bonk: focilitoted, diffusion , glucose, proteins, osmosis ...
Chapter 4 - Tolland High School
... cell membrane only allows specific substances to pass through it ...
... cell membrane only allows specific substances to pass through it ...
Chapter 4
... area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration caused by the random motion of particles of the substance is called diffusion. ...
... area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration caused by the random motion of particles of the substance is called diffusion. ...
Nanoscale localisation of a Candida albicans peptide
... Infection Biology (HKI), Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena Germany How to localize a protein on a cell membrane? Cell membranes incorporate many proteins of different size. In order to directly differentiate between different proteins, the molecule of interest is usually specifically labeled. Howeve ...
... Infection Biology (HKI), Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena Germany How to localize a protein on a cell membrane? Cell membranes incorporate many proteins of different size. In order to directly differentiate between different proteins, the molecule of interest is usually specifically labeled. Howeve ...
Pre – AP Biology
... ONLY found in Eukaryotes ONLY because they have the organelle.) – These make proteins that will leave the cell to be used elsewhere. (Most are for communication between cells, such as antibodies for fighting infection.) ...
... ONLY found in Eukaryotes ONLY because they have the organelle.) – These make proteins that will leave the cell to be used elsewhere. (Most are for communication between cells, such as antibodies for fighting infection.) ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.