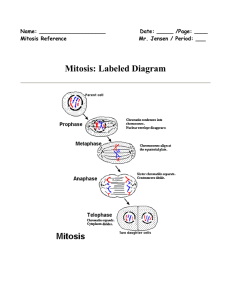
Mitosis (cell division) division is new generations of cells arising
... -Cell growth occurs. -Eventually plasma membrane pinches inward forming two new cells. -Referred to as Binary Cell Division (binary fission). *Cell division in Eukaryotes: -Involves two processes: Nuclear division (division of nuclear DNA) and Cytokinesis (physical division of cell.). -Two types of ...
... -Cell growth occurs. -Eventually plasma membrane pinches inward forming two new cells. -Referred to as Binary Cell Division (binary fission). *Cell division in Eukaryotes: -Involves two processes: Nuclear division (division of nuclear DNA) and Cytokinesis (physical division of cell.). -Two types of ...
What are cells? How many types are there? How Cells Are Put
... Why don’t we see 90 foot high elephants. It would be better for them. They would need ears as big as sail ship sails to cool themselves based on their lack of surface area… ...
... Why don’t we see 90 foot high elephants. It would be better for them. They would need ears as big as sail ship sails to cool themselves based on their lack of surface area… ...
THE Cell Story - aclassyspaceatmas
... When Sally was on her way she saw little dots called ribosomes which are packets of protein that help the plant grow. ...
... When Sally was on her way she saw little dots called ribosomes which are packets of protein that help the plant grow. ...
Anatomy of a Cell
... phospholipid molecules. These proteins consist of 3 main groups: integral proteins, outer-surface proteins and innersurface proteins. They play distinctive roles in cellular activities. • Integral proteins: firmly embedded in the membrane, transport substance across the cytoplasmic membrane in 3 mai ...
... phospholipid molecules. These proteins consist of 3 main groups: integral proteins, outer-surface proteins and innersurface proteins. They play distinctive roles in cellular activities. • Integral proteins: firmly embedded in the membrane, transport substance across the cytoplasmic membrane in 3 mai ...
LIPIDS IN MEMBRANES –
... cellular function, i.e. the membrane proteins which float laterally within the membrane. However, a large variety of lipids of different structure were found to reside in plasma membranes, much more than one would expect for just performing the functions of frame giving / compartmentation. Biophysic ...
... cellular function, i.e. the membrane proteins which float laterally within the membrane. However, a large variety of lipids of different structure were found to reside in plasma membranes, much more than one would expect for just performing the functions of frame giving / compartmentation. Biophysic ...
Cell Organelles Animal Cells
... Cytoplasm- clear thick jelly like substance between the Cell Membrane Function- allows materials to move within the cell ...
... Cytoplasm- clear thick jelly like substance between the Cell Membrane Function- allows materials to move within the cell ...
CHAPTER 4 – The Cell In Action
... cells to where water molecules are less concentrated in the salty solution; thus, the cells will shrink. The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell. Diffusion is when any kind of particles move from a crowded area to a less crowded area. The movemen ...
... cells to where water molecules are less concentrated in the salty solution; thus, the cells will shrink. The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell. Diffusion is when any kind of particles move from a crowded area to a less crowded area. The movemen ...
Lectures 6 & 7: Powerpoint
... isolate the cell’s contents from the external environment Regulate the exchange of substances between the inside and outside of the cell Communicate with other cells ...
... isolate the cell’s contents from the external environment Regulate the exchange of substances between the inside and outside of the cell Communicate with other cells ...
厦门大学细胞生物学课程试卷
... A: Lipid rafts are membrane microdomains that are enriched in cholesterol and glycosphingolipids. They have been implicated in processes as diverse as signal transduction, endocytosis and cholesterol trafficking. (2) Proteasome (4) A: Large protein complex in the cytosol with proteolytic activity th ...
... A: Lipid rafts are membrane microdomains that are enriched in cholesterol and glycosphingolipids. They have been implicated in processes as diverse as signal transduction, endocytosis and cholesterol trafficking. (2) Proteasome (4) A: Large protein complex in the cytosol with proteolytic activity th ...
Cell Extraction and Lysis Extraction kits - protein
... the membrane fraction before SDS-PAGE/Western analysis of COX4. A negligible amount of protein was found in all debris fractions. Abbreviations: AchE = acetylcholinesterase, COX4 = cytochrome oxidase subunit 4, hsp90 = heat shock protein 90, M = solubilised membrane protein fraction and H = hydrophi ...
... the membrane fraction before SDS-PAGE/Western analysis of COX4. A negligible amount of protein was found in all debris fractions. Abbreviations: AchE = acetylcholinesterase, COX4 = cytochrome oxidase subunit 4, hsp90 = heat shock protein 90, M = solubilised membrane protein fraction and H = hydrophi ...
transport across the membrane
... • are both forms of Active Transport and require ATP energy - energy required because they are changing the shape of the cell membrane. It requires a great deal of energy to fuse a vacuole with the cell membrane or create a vacuole from the cell membrane. The vacuoles are made from a phospholipid bi ...
... • are both forms of Active Transport and require ATP energy - energy required because they are changing the shape of the cell membrane. It requires a great deal of energy to fuse a vacuole with the cell membrane or create a vacuole from the cell membrane. The vacuoles are made from a phospholipid bi ...
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
... “mosaic” of proteins and phospholipids that are constantly moving and changing ...
... “mosaic” of proteins and phospholipids that are constantly moving and changing ...
Layout 4
... cells, and animal and plant cells ● Examine the structure and role of the cell membrane, and explains diffusion and osmosis ...
... cells, and animal and plant cells ● Examine the structure and role of the cell membrane, and explains diffusion and osmosis ...
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 5
... 3. ______ The energy needed to power the sodium-potassium pump is provided by the a. binding of ATP to the pump. c. removal of a phosphate group from ATP. b. transport of ATP by the pump. d. formation of ATP. 4. ______Pinocytosis involves the transport of a. large particles out of a cell. c. whole c ...
... 3. ______ The energy needed to power the sodium-potassium pump is provided by the a. binding of ATP to the pump. c. removal of a phosphate group from ATP. b. transport of ATP by the pump. d. formation of ATP. 4. ______Pinocytosis involves the transport of a. large particles out of a cell. c. whole c ...
Aida.Membranes
... 14. Define and contrast the following terms: membrane potential, electrochemical gradient, electrogenic pump and proton pump. Membrane potential- difference in electrical potential and fluidity of the interior and exterior of a cell. Electrochemical gradient- an ions concentration gradient Electroge ...
... 14. Define and contrast the following terms: membrane potential, electrochemical gradient, electrogenic pump and proton pump. Membrane potential- difference in electrical potential and fluidity of the interior and exterior of a cell. Electrochemical gradient- an ions concentration gradient Electroge ...
HRW BIO CRF Ch 04_p01-44
... endocytosis. During endocytosis, the cell membrane forms a pouch around a substance outside the cell. The pouch then closes up and pinches off from the membrane to form a vesicle. Vesicles formed by endocytosis may fuse with lysosomes or other organelles. The movement of a substance by a vesicle to ...
... endocytosis. During endocytosis, the cell membrane forms a pouch around a substance outside the cell. The pouch then closes up and pinches off from the membrane to form a vesicle. Vesicles formed by endocytosis may fuse with lysosomes or other organelles. The movement of a substance by a vesicle to ...
B1: Cell Structure
... 1. What does the cell theory state? – All living things are made up of cells – The cell is also the functional unit of life – All living cells come from pre-existing cells ...
... 1. What does the cell theory state? – All living things are made up of cells – The cell is also the functional unit of life – All living cells come from pre-existing cells ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
1.1-BIO-HOM-HomeostasisIntro.CellMembrane
... What is the cell membrane mostly made of? • LIPIDS! What other molecule is found in the membrane? • PROTEIN! Hydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic: What part is hydrophilic? • The head! What part is hydrophobic? • The tail! What part lets stuff enter the cell? • The protein! ...
... What is the cell membrane mostly made of? • LIPIDS! What other molecule is found in the membrane? • PROTEIN! Hydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic: What part is hydrophilic? • The head! What part is hydrophobic? • The tail! What part lets stuff enter the cell? • The protein! ...
transport
... – From greater to lesser area of water • Particles can’t move because membrane won’t allow it! • When talking about cells… – consider membrane only soluble to water (unless told otherwise) – Concentration is relative to cytoplasm ...
... – From greater to lesser area of water • Particles can’t move because membrane won’t allow it! • When talking about cells… – consider membrane only soluble to water (unless told otherwise) – Concentration is relative to cytoplasm ...
Chapter_7PP - biologywithbengele
... two layers- tails facing each other to form the…. Demonstrate the function of the cell membrane and explain its role in maintaining homeostasis ...
... two layers- tails facing each other to form the…. Demonstrate the function of the cell membrane and explain its role in maintaining homeostasis ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.