Cell Motility - Cochran`s Half Acre
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
Cell structures & Functions
... • Location: Surrounding the cell • Function: Controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell – “Selectively permeable” ...
... • Location: Surrounding the cell • Function: Controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell – “Selectively permeable” ...
Cell Organelles Book - Birmingham City Schools
... Made of protein tubes called ____________________ Microtubules arranged (9 + 2 arrangement) Function in _____________________, in moving fluids, or in small particles across the cell surface ___________are shorter and more numerous on cells ____________are longer and fewer (usually 1-3) on ...
... Made of protein tubes called ____________________ Microtubules arranged (9 + 2 arrangement) Function in _____________________, in moving fluids, or in small particles across the cell surface ___________are shorter and more numerous on cells ____________are longer and fewer (usually 1-3) on ...
HONORS BIO TRANSPORT TEST NAME (2 points each) MULTIPLE
... The substance that is dissolved to make a solution is called the ________________ A. dissolver B. solvent C. solute D. vesicle ...
... The substance that is dissolved to make a solution is called the ________________ A. dissolver B. solvent C. solute D. vesicle ...
ppt.
... Symport carrier proteins provide the cell with a means of two-way diffusion. Sodium-Na+ Active Transport ...
... Symport carrier proteins provide the cell with a means of two-way diffusion. Sodium-Na+ Active Transport ...
SBI4U - Membrane Transport
... • the movement of materials into and out of the cell is critical to a cell’s survival and functioning ...
... • the movement of materials into and out of the cell is critical to a cell’s survival and functioning ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists Produces a usable form of energy for the cell ...
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists Produces a usable form of energy for the cell ...
Cells Alive Tutorial 08-09
... page, or hit your back button) For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? ...
... page, or hit your back button) For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... c. To carry DNA d. To digest cellulose. 2. What is the purpose of a cell membrane? a. To make lipids b. To make phospholipids c. To protect the cell d. To support the cell wall 3. What is the genetic material inside a cell’s nucleus? a. Protein b. Lipids c. Chromosomes (DNA) d. Nucleolus 4. What do ...
... c. To carry DNA d. To digest cellulose. 2. What is the purpose of a cell membrane? a. To make lipids b. To make phospholipids c. To protect the cell d. To support the cell wall 3. What is the genetic material inside a cell’s nucleus? a. Protein b. Lipids c. Chromosomes (DNA) d. Nucleolus 4. What do ...
Chapter 07
... neighboring cells are fused. They prevent leakage of extracellular fluid. Desmosomes (anchoring junctions, animals only): These are rivets that fasten cells together into strong sheets. Gap Junctions: These provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells which are large enough for salt ions, sug ...
... neighboring cells are fused. They prevent leakage of extracellular fluid. Desmosomes (anchoring junctions, animals only): These are rivets that fasten cells together into strong sheets. Gap Junctions: These provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells which are large enough for salt ions, sug ...
Presentation
... – The cell membrane has two major functions. • forms a boundary between inside and outside of the cell • controls passage of materials in and out of cell ...
... – The cell membrane has two major functions. • forms a boundary between inside and outside of the cell • controls passage of materials in and out of cell ...
Specialised Cells
... Task: learning about specialised cells: Use the worksheet to draw a diagram of each type of cell, labelling the key features. Add detail to explain the function of each feature: a) sperm cells – acrosome, haploid nucleus, mitochondria and tail b) egg cells – nutrients in the cytoplasm, haploid nucl ...
... Task: learning about specialised cells: Use the worksheet to draw a diagram of each type of cell, labelling the key features. Add detail to explain the function of each feature: a) sperm cells – acrosome, haploid nucleus, mitochondria and tail b) egg cells – nutrients in the cytoplasm, haploid nucl ...
The Cell Review
... eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells = no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles • Eukaryotic cells = nucleus; have membrane bound organelles ...
... eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells = no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles • Eukaryotic cells = nucleus; have membrane bound organelles ...
Ecology
... organisms made up of cells that have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane e, multiple chromosomes, and a mitotic cycle; eukaryotes include animals., plant and fungi but not bacteria or ...
... organisms made up of cells that have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane e, multiple chromosomes, and a mitotic cycle; eukaryotes include animals., plant and fungi but not bacteria or ...
Slide ()
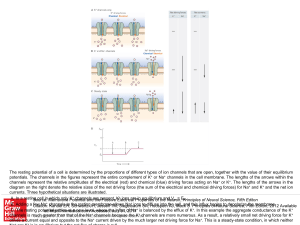
... Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available C. The resting potential settles at a new level, where the influx Na+ is balanced by the efflux of K+. In this example the aggregate conductance of the K+ at: http://mhm ...
... Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available C. The resting potential settles at a new level, where the influx Na+ is balanced by the efflux of K+. In this example the aggregate conductance of the K+ at: http://mhm ...
The Cell Review
... eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells = no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles • Eukaryotic cells = nucleus; have membrane bound organelles ...
... eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells = no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles • Eukaryotic cells = nucleus; have membrane bound organelles ...
MADANIA (High School) Grade 10-Biology
... on Earth. A main purpose of a cell is to organize. Cells hold a variety of pieces and each cell has a different set of functions. There are two kinds of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. All cells have several basic features in common: They are bounded by a plasma membrane They contain a semifl ...
... on Earth. A main purpose of a cell is to organize. Cells hold a variety of pieces and each cell has a different set of functions. There are two kinds of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. All cells have several basic features in common: They are bounded by a plasma membrane They contain a semifl ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint
... • Prokaryotic cells lack membrane enclosed structures. • Eukaryotic cells possess membrane enclosed structures. ...
... • Prokaryotic cells lack membrane enclosed structures. • Eukaryotic cells possess membrane enclosed structures. ...
Tour Of The Cell
... • The volume enclosed by the plasma membrane of plant cells is often much larger than the corresponding volume in animal cells, because plant cells contain a large vacuole that reduces the volume of the cytoplasm. ...
... • The volume enclosed by the plasma membrane of plant cells is often much larger than the corresponding volume in animal cells, because plant cells contain a large vacuole that reduces the volume of the cytoplasm. ...
File: Chap03, Chapter 3: Structure and Function of the Cell
... When a sperm cell comes into contact with an egg cell, there is a change in the electrical charge across the plasma membrane and various channel proteins close. These channels would be called A) open-gated channels. B) voltage-gated channels. ...
... When a sperm cell comes into contact with an egg cell, there is a change in the electrical charge across the plasma membrane and various channel proteins close. These channels would be called A) open-gated channels. B) voltage-gated channels. ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.