Cell Size, Cell Cycle, and Uncontrolled Cell Division
... Before we go over each of the phases, let’s talk about DNA... - During interphase, it is in chromatin form (Depictions often look like Ramen) - During mitosis, it condenses into X shape called chromosomes - Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in their body (somatic) cells ...
... Before we go over each of the phases, let’s talk about DNA... - During interphase, it is in chromatin form (Depictions often look like Ramen) - During mitosis, it condenses into X shape called chromosomes - Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in their body (somatic) cells ...
Substances enter and leave cells through the cell membrane
... material and be able to interpret experimental results in terms of membrane pore and particle size: the pore size is large enough to allow water molecules through but restricts the movement of solute molecules. ...
... material and be able to interpret experimental results in terms of membrane pore and particle size: the pore size is large enough to allow water molecules through but restricts the movement of solute molecules. ...
Synaptic Potentials
... potential depends on the summation (the additive effect) of all the incoming signals. Each active synapse can result in a local potential (either an EPSP or an IPSP). The net effect of all the local potentials on the trigger zone determines whether or not there is an action potential in the postsyna ...
... potential depends on the summation (the additive effect) of all the incoming signals. Each active synapse can result in a local potential (either an EPSP or an IPSP). The net effect of all the local potentials on the trigger zone determines whether or not there is an action potential in the postsyna ...
Make Vocabulary Flash Cards
... Diffusion – The process of matter spreading out evenly from its source. An example of ...
... Diffusion – The process of matter spreading out evenly from its source. An example of ...
File
... Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. Any rough working should be done in this booklet. ...
... Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. Any rough working should be done in this booklet. ...
Cells - quigleysciencestandards
... the opposite process of photosynthesis in which living organisms take in oxygen and sugars in order to give off carbon dioxide, water, & energy There can be one or many mitochondria in a cell Found in plant & animal cells ...
... the opposite process of photosynthesis in which living organisms take in oxygen and sugars in order to give off carbon dioxide, water, & energy There can be one or many mitochondria in a cell Found in plant & animal cells ...
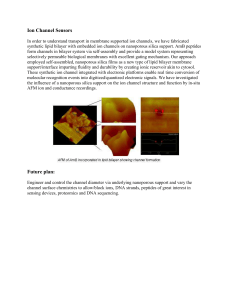
Ion Channel Sensors
... Ion Channel Sensors In order to understand transport in membrane supported ion channels, we have fabricated synthetic lipid bilayer with embedded ion channels on nanoporous silica support. AmB peptides form channels in bilayer system via self-assembly and provide a model system representing selectiv ...
... Ion Channel Sensors In order to understand transport in membrane supported ion channels, we have fabricated synthetic lipid bilayer with embedded ion channels on nanoporous silica support. AmB peptides form channels in bilayer system via self-assembly and provide a model system representing selectiv ...
Membrane TXPT2
... Animal cells need Na outside and K inside The ATP changes the shape of the protein… Basic Ion Pump ...
... Animal cells need Na outside and K inside The ATP changes the shape of the protein… Basic Ion Pump ...
Lecture #3 Date
... pass. Gap junctions are necessary for communication between cells in many types of tissues, including heart muscle and animal embryos. ...
... pass. Gap junctions are necessary for communication between cells in many types of tissues, including heart muscle and animal embryos. ...
Parts of Plant and Animal Cells By
... • A endoplasmic reticulum is an eukaryotic organelle that forms an interconnected network of tubules(small tubes), vesicles(bubble of liquid), and cisternae(a flattened membrane disk) within cells. ...
... • A endoplasmic reticulum is an eukaryotic organelle that forms an interconnected network of tubules(small tubes), vesicles(bubble of liquid), and cisternae(a flattened membrane disk) within cells. ...
Research Interests: Sickle cell disease is a blood disorder that is
... contains a γ chain in place of its β counterpart, it does not contain the valine mutation and will not incorporate into polymers. Unfortunately the lack of specificity of this treatment leads to numerous undesirable side effects. As an alternative method of treating sickle cell disease I would like ...
... contains a γ chain in place of its β counterpart, it does not contain the valine mutation and will not incorporate into polymers. Unfortunately the lack of specificity of this treatment leads to numerous undesirable side effects. As an alternative method of treating sickle cell disease I would like ...
WHAT DO YOU KNOW ABOUT CELLS?
... 3. Bob is studying for his English test and is getting tired. He needs a source of quick energy. What would be the BEST thing for him to eat? a. A piece of ham b. A bowl of pasta c. Butter d. A bowl of yogurt 4. When you eat food, the food needs to be broken down into smaller pieces. What kind of ma ...
... 3. Bob is studying for his English test and is getting tired. He needs a source of quick energy. What would be the BEST thing for him to eat? a. A piece of ham b. A bowl of pasta c. Butter d. A bowl of yogurt 4. When you eat food, the food needs to be broken down into smaller pieces. What kind of ma ...
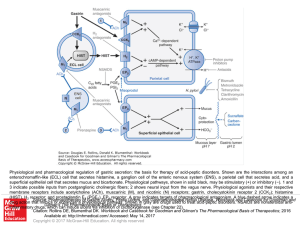
Slide ()
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
Chapter 4
... maintenance of the cell Vacuoles are membranous sacs that are found in a variety of cells and possess an assortment of functions – Examples are the central vacuole in plants with hydrolytic functions, pigment vacuoles in plants to provide color to flowers, and contractile vacuoles in some protists ...
... maintenance of the cell Vacuoles are membranous sacs that are found in a variety of cells and possess an assortment of functions – Examples are the central vacuole in plants with hydrolytic functions, pigment vacuoles in plants to provide color to flowers, and contractile vacuoles in some protists ...
Cell Structure - Industrial ISD
... Prokaryote- is a single-celled organism that LACKS a nucleus and other compartments They were the only organisms on Earth for 2 billion years. They are very simple and small. The familiar prokaryotes that cause infection and cause food to spoil are ...
... Prokaryote- is a single-celled organism that LACKS a nucleus and other compartments They were the only organisms on Earth for 2 billion years. They are very simple and small. The familiar prokaryotes that cause infection and cause food to spoil are ...
Biology_Goal_4a_Review
... 9. ________________Light energy is converted to chemical energy 10. ________________ Storage of materials; large structure in plants 11. ________________ Semi-fluid substance where most cellular reactions take place 12. ________________Powerhouse of the cell where ATP is produced 13. _______________ ...
... 9. ________________Light energy is converted to chemical energy 10. ________________ Storage of materials; large structure in plants 11. ________________ Semi-fluid substance where most cellular reactions take place 12. ________________Powerhouse of the cell where ATP is produced 13. _______________ ...
File
... rather than phospholipids and is external the cell membrane. Provides structural barrier for some substances to the internal environment. ...
... rather than phospholipids and is external the cell membrane. Provides structural barrier for some substances to the internal environment. ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 9e
... lined with polar amino acids. • Carrier proteins—membrane proteins that bind some substances and speed their diffusion through the bilayer. ...
... lined with polar amino acids. • Carrier proteins—membrane proteins that bind some substances and speed their diffusion through the bilayer. ...
Cell Organelles
... • A small grain-like structure in the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made (protein synthesis) • May be attached to ER or floating in the cytoplasm • small circular organelles ...
... • A small grain-like structure in the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made (protein synthesis) • May be attached to ER or floating in the cytoplasm • small circular organelles ...
Identify the structures labeled a–e in the diagram of the human
... Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. What did Wendell Stanley’s work suggest about the nature of viruses? Stanley's work seemed to indicate that the infectious agent in TMV was a protein, in spite of the fact that TMV was known to contain RNA ____________________________ ...
... Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. What did Wendell Stanley’s work suggest about the nature of viruses? Stanley's work seemed to indicate that the infectious agent in TMV was a protein, in spite of the fact that TMV was known to contain RNA ____________________________ ...
CELL ORGANELLES
... production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by a process known as cell respiration. ATP is a chemical compound that stores energy in the form of chemical bonds. Energy is derived from cell nutrients, mostly from glucose and fatty acids, and released whenever it is needed by the energy-requiring ...
... production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by a process known as cell respiration. ATP is a chemical compound that stores energy in the form of chemical bonds. Energy is derived from cell nutrients, mostly from glucose and fatty acids, and released whenever it is needed by the energy-requiring ...
THE CELL MEMBRANE Section 1: Cell Membrane Key Ideas How
... A target cell is bombarded by hundreds of signals. But it recognizes and responds only to the few signals that are important for its function. This response to some signals, but not to others, is made possible by receptor proteins, such as the ones in the cell’s membrane. A receptor protein binds sp ...
... A target cell is bombarded by hundreds of signals. But it recognizes and responds only to the few signals that are important for its function. This response to some signals, but not to others, is made possible by receptor proteins, such as the ones in the cell’s membrane. A receptor protein binds sp ...
Cell organelles
... Cell Wall - Outer covering of most cells that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape. Cytoplasm - A gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic molecules. Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane Surrounds the cell's cytoplasm ...
... Cell Wall - Outer covering of most cells that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape. Cytoplasm - A gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic molecules. Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane Surrounds the cell's cytoplasm ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... The observations and conclusions of many scientists helped to develop the current understanding of the cell Robert Hooke (1665) __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ _______________________________________ ...
... The observations and conclusions of many scientists helped to develop the current understanding of the cell Robert Hooke (1665) __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ _______________________________________ ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.