Electrical Vibrations of Yeast Cell Membrane
... Fröhlich postulated electrically polar longitudinal vibrations in biological systems [1–4]. The vibrations generate endogenous electromagnetic field. The electromagnetic field is generated in a broad frequency spectrum. The oscillations in megahertz [5], gigahertz [6, 7], far infra red [8], visible ...
... Fröhlich postulated electrically polar longitudinal vibrations in biological systems [1–4]. The vibrations generate endogenous electromagnetic field. The electromagnetic field is generated in a broad frequency spectrum. The oscillations in megahertz [5], gigahertz [6, 7], far infra red [8], visible ...
2014 Advanced Placement Biology Summer Work
... questions answered. Since you covered cell structure so extensively last year, I will not formally lecture on Chapter 4, but I am happy to address specific questions and provide any clarification that you might need during the first 2 days of class. Assignment 1: Obtain the following required materi ...
... questions answered. Since you covered cell structure so extensively last year, I will not formally lecture on Chapter 4, but I am happy to address specific questions and provide any clarification that you might need during the first 2 days of class. Assignment 1: Obtain the following required materi ...
File - wentworth science
... The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle This membrane is called the nuclear envelope. It has openings in it known as nuclear pores. It is usually the largest organelle in the cell The nucleus is considered the “control center” of the cell This is so because the nucleus contains the DNA The DNA is ...
... The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle This membrane is called the nuclear envelope. It has openings in it known as nuclear pores. It is usually the largest organelle in the cell The nucleus is considered the “control center” of the cell This is so because the nucleus contains the DNA The DNA is ...
Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... b.Some prokaryotes adhere to substrates using pili. c. Some pili are specialized for DNA transfer. This process is called conjugation; note for later in class. ...
... b.Some prokaryotes adhere to substrates using pili. c. Some pili are specialized for DNA transfer. This process is called conjugation; note for later in class. ...
M1 Chapter 2
... through the cytosol of most eukaryotic cells. Their main function is the conversion of the potential energy of food molecules into ATP Every type of cell has a different amount of mitochondria.. There are more mitochondria in cells that have to perform lots of work, for exampleyour leg muscle cells, ...
... through the cytosol of most eukaryotic cells. Their main function is the conversion of the potential energy of food molecules into ATP Every type of cell has a different amount of mitochondria.. There are more mitochondria in cells that have to perform lots of work, for exampleyour leg muscle cells, ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... barrier that encloses a cell. It separates the cell's contents f r o m the cell's environment. The cell membrane is the outermost structure i n cells that lack a cell wall. I n cells that have a cell wall, the cell membrane lies just inside the cell wall. The cell membrane contains proteins, lipids, ...
... barrier that encloses a cell. It separates the cell's contents f r o m the cell's environment. The cell membrane is the outermost structure i n cells that lack a cell wall. I n cells that have a cell wall, the cell membrane lies just inside the cell wall. The cell membrane contains proteins, lipids, ...
One Postdoctoral Position in Xenopus embryology at the Stem Cell
... at the Stem Cell Center at Lund University, Sweden Located just across the bridge from Copenhagen airport, Lund University is Scandinavia’s largest institution for education and research. The Lund Stem Cell Center is a strong international research center with a focus on stem cell and developmental ...
... at the Stem Cell Center at Lund University, Sweden Located just across the bridge from Copenhagen airport, Lund University is Scandinavia’s largest institution for education and research. The Lund Stem Cell Center is a strong international research center with a focus on stem cell and developmental ...
1. Describe the structural organization of the genome.
... a cell • Organized into functional units called chromosomes (supercoiled DNA-protein complexes of chromatin) • The DNA exists in different phases at different stages in the cell cycle ...
... a cell • Organized into functional units called chromosomes (supercoiled DNA-protein complexes of chromatin) • The DNA exists in different phases at different stages in the cell cycle ...
Anti-Hsp70 antibody [EP1007Y] (HRP)
... In cooperation with other chaperones, Hsp70s stabilize preexistent proteins against aggregation and mediate the folding of newly translated polypeptides in the cytosol as well as within organelles. These chaperones participate in all these processes through their ability to recognize nonnative confo ...
... In cooperation with other chaperones, Hsp70s stabilize preexistent proteins against aggregation and mediate the folding of newly translated polypeptides in the cytosol as well as within organelles. These chaperones participate in all these processes through their ability to recognize nonnative confo ...
here
... Keywors: Catharanthus roseus,… Introduction: Catharanthus roseus is known to produce numerous alkaloids with high pharmaceutical importance such as vinblastine and vincristine which have antineoplastic activity. Since1998, it was demonstrated (1) that elicitation of grapevine cell cultures with cycl ...
... Keywors: Catharanthus roseus,… Introduction: Catharanthus roseus is known to produce numerous alkaloids with high pharmaceutical importance such as vinblastine and vincristine which have antineoplastic activity. Since1998, it was demonstrated (1) that elicitation of grapevine cell cultures with cycl ...
Tools for visualizing and quantifying neuronal cell health
... activity, which is required to activate its fluorescence, as well as cell membrane integrity, which is required for its intracellular retention (Figures 1B and 1E). In general, Calcein AM can be directly applied to cells and incubated for 10–30 minutes with good results. To minimize potential backgr ...
... activity, which is required to activate its fluorescence, as well as cell membrane integrity, which is required for its intracellular retention (Figures 1B and 1E). In general, Calcein AM can be directly applied to cells and incubated for 10–30 minutes with good results. To minimize potential backgr ...
cell wall
... Vacuoles are small sacs are filled with food and water. They are used by cells as storage tanks. All plant cells have vacuoles, but not all animal cells do. The primary place where plants store water is within its vacuoles. When a plants vacuoles are filled with water, they become plump, giving the ...
... Vacuoles are small sacs are filled with food and water. They are used by cells as storage tanks. All plant cells have vacuoles, but not all animal cells do. The primary place where plants store water is within its vacuoles. When a plants vacuoles are filled with water, they become plump, giving the ...
HO HB Exam Study Guide Semester I
... proteins, dipeptide bonding (to make an amino acid chain) characteristics of nucleic acids, (DNA and RNA), monomer of a nucleic acid structural and empirical formulas amino acid chain - know how to join two amino acids Study all terms for chapter 3 Know the Chart of organic compounds Know the ...
... proteins, dipeptide bonding (to make an amino acid chain) characteristics of nucleic acids, (DNA and RNA), monomer of a nucleic acid structural and empirical formulas amino acid chain - know how to join two amino acids Study all terms for chapter 3 Know the Chart of organic compounds Know the ...
Gram Staining and Cell Wall Structure
... having. Bacterial cell walls do NOT contain cellulose like plant cell walls do. Bacterial cell walls are made mostly of a chemical called peptidogly (made of polypeptides bonded to modified sugars), but the amount and location of the peptidoglycan are different in the two possible types of cell wall ...
... having. Bacterial cell walls do NOT contain cellulose like plant cell walls do. Bacterial cell walls are made mostly of a chemical called peptidogly (made of polypeptides bonded to modified sugars), but the amount and location of the peptidoglycan are different in the two possible types of cell wall ...
CHAPTER 7 A TOUR OF THE CELL
... A centrifuge spins test tubes holding mixtures of disrupted cells at various speeds. The resulting forces cause a fraction of the cell components to settle to the bottom of the tube, forming a pellet. ○ At lower speeds, the pellet consists of larger components; higher speeds yield a pellet with smal ...
... A centrifuge spins test tubes holding mixtures of disrupted cells at various speeds. The resulting forces cause a fraction of the cell components to settle to the bottom of the tube, forming a pellet. ○ At lower speeds, the pellet consists of larger components; higher speeds yield a pellet with smal ...
A1983QP60500001
... The work cited was a first attempt to describe the structure of the primary cell wall as an entity. Researchers had looked at fractions and individual components of primary cell walls but had not considered the aggregate of those components. The formation of a team of three graduate students—Talmadg ...
... The work cited was a first attempt to describe the structure of the primary cell wall as an entity. Researchers had looked at fractions and individual components of primary cell walls but had not considered the aggregate of those components. The formation of a team of three graduate students—Talmadg ...
CYTOSKELETON (MICROTUBULES, FILAMENTS: THICK, THIN
... – Intermediate filaments are built from a diverse class of subunits from a family of proteins called keratins. • Intermediate filaments are more permanent fixtures of the cytoskeleton than are the other two classes. ...
... – Intermediate filaments are built from a diverse class of subunits from a family of proteins called keratins. • Intermediate filaments are more permanent fixtures of the cytoskeleton than are the other two classes. ...
Novel agents for the in-situ detection of cysteine oxidation states
... Cysteine (Cys-SH) readily undergoes oxidation by reactive oxygen species (ROS) to form sulfenic (Cys-OH), sulfinic (Cys-SO2H) and sulfonic (Cys-SO3H) acids. Thiol modifications of cysteine have been implicated as modulators of cellular processes and represent significant biological modifications tha ...
... Cysteine (Cys-SH) readily undergoes oxidation by reactive oxygen species (ROS) to form sulfenic (Cys-OH), sulfinic (Cys-SO2H) and sulfonic (Cys-SO3H) acids. Thiol modifications of cysteine have been implicated as modulators of cellular processes and represent significant biological modifications tha ...
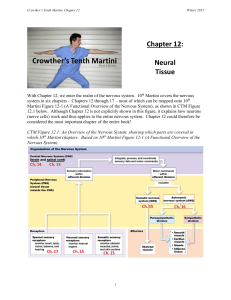
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... macromolecules like proteins and nucleic acids. A fascinating central fact of biology is that cells, including neurons, almost never have the same electrical charge inside and outside their cell membrane. The inside of the cell is generally slightly negative when compared to the outside. We can visu ...
... macromolecules like proteins and nucleic acids. A fascinating central fact of biology is that cells, including neurons, almost never have the same electrical charge inside and outside their cell membrane. The inside of the cell is generally slightly negative when compared to the outside. We can visu ...
Abstract - BMB Reports
... In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), cell cycle regulation is deeply connected to pluripotency. Especially, core transcription factors (CTFs) which are essential to maintain the pluripotency transcription programs should be reset during M/G1 transition. However, it remains unknown about how CTFs are gove ...
... In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), cell cycle regulation is deeply connected to pluripotency. Especially, core transcription factors (CTFs) which are essential to maintain the pluripotency transcription programs should be reset during M/G1 transition. However, it remains unknown about how CTFs are gove ...
Lecture 5 Cytoplasm, organelles Pinar Tulay_4
... • Synthesis of both membrane-bound (organelle and plasma membrane proteins) and soluble proteins (organelle and secreted proteins) • Most proteins that enter the endomembrane system, enter the ER co-tranlationally: as translation is occurring • Most proteins of other membrane bound organelles (mitoc ...
... • Synthesis of both membrane-bound (organelle and plasma membrane proteins) and soluble proteins (organelle and secreted proteins) • Most proteins that enter the endomembrane system, enter the ER co-tranlationally: as translation is occurring • Most proteins of other membrane bound organelles (mitoc ...
Section 19-1 Bacteria
... a. The rod-shaped are called b. The spherical-shaped are called c. The corkscrew-shaped are called 17. A method of telling two different types of eubacteria apart by using dyes is called 18. What colors are Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria under the microscope when treated with Gram stain? 1 ...
... a. The rod-shaped are called b. The spherical-shaped are called c. The corkscrew-shaped are called 17. A method of telling two different types of eubacteria apart by using dyes is called 18. What colors are Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria under the microscope when treated with Gram stain? 1 ...
Chapter 6 lecture outline
... A centrifuge spins test tubes holding mixtures of disrupted cells at various speeds. The resulting forces cause a fraction of the cell components to settle to the bottom of the tube, forming a pellet. ○ At lower speeds, the pellet consists of larger components; higher speeds yield a pellet with smal ...
... A centrifuge spins test tubes holding mixtures of disrupted cells at various speeds. The resulting forces cause a fraction of the cell components to settle to the bottom of the tube, forming a pellet. ○ At lower speeds, the pellet consists of larger components; higher speeds yield a pellet with smal ...
PAST PAPER Q part 1
... Which of the following are the most abundant molecules located in the plasma membrane? A. Glycoproteins B. Phospholipids C. Carrier proteins D. Cholesterol Question 7 Membranes are not usually permeable to protein and polysaccharide macromolecules. Which of the following is the best explanation as t ...
... Which of the following are the most abundant molecules located in the plasma membrane? A. Glycoproteins B. Phospholipids C. Carrier proteins D. Cholesterol Question 7 Membranes are not usually permeable to protein and polysaccharide macromolecules. Which of the following is the best explanation as t ...
Cell division and mitosis
... DNA “Overload” – there is a limit to the number of proteins a DNA molecule can code for at one time. As the cell gets bigger, it needs more proteins, but, it may have to wait if there’s already too many proteins being made Exchange of Materials – there is a limit to the amount of materials a cell ca ...
... DNA “Overload” – there is a limit to the number of proteins a DNA molecule can code for at one time. As the cell gets bigger, it needs more proteins, but, it may have to wait if there’s already too many proteins being made Exchange of Materials – there is a limit to the amount of materials a cell ca ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.







![Anti-Hsp70 antibody [EP1007Y] (HRP)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017843849_1-ac97f6d6c05a961c3b80cb959c0fee29-300x300.png)