6 systems biology of cell organization
... The genome of every organism contains the information necessary to produce a system of RNA and protein molecules that provides the foundation for cell structure, function, and organization. An important paradigm in biology is that “structure determines function.” The information in most genes is use ...
... The genome of every organism contains the information necessary to produce a system of RNA and protein molecules that provides the foundation for cell structure, function, and organization. An important paradigm in biology is that “structure determines function.” The information in most genes is use ...
CL_review-RS - The OBO Foundry
... is transitioning from Oliver Hoffman to Alexander Diehl. As part of this transition, Dr. Diehl has actively engaged the immunology research community to flesh out the hematopoietic cell branch. The end result has been a major improvement in both the content and the structure of this branch. Similar ...
... is transitioning from Oliver Hoffman to Alexander Diehl. As part of this transition, Dr. Diehl has actively engaged the immunology research community to flesh out the hematopoietic cell branch. The end result has been a major improvement in both the content and the structure of this branch. Similar ...
Hijacking of eukaryotic functions by intracellular bacterial pathogens
... cell membrane ends with the complete inclusion of the invading bacteria. Minor mobilization of cytoskeletal proteins is needed for this type of pathogen-mediated phagocytosis, which is initiated by specific contacts between bacterial ligands (adhesins) and host cell surface receptors (Fig. 1). Unlik ...
... cell membrane ends with the complete inclusion of the invading bacteria. Minor mobilization of cytoskeletal proteins is needed for this type of pathogen-mediated phagocytosis, which is initiated by specific contacts between bacterial ligands (adhesins) and host cell surface receptors (Fig. 1). Unlik ...
Major Histocompatibilty Complex (MHC) and T Cell Receptors
... polymorphism for a species, an individual has maximum of six different class I MHC products and only slightly more class II MHC products. A peptide must associate with a given MHC of that individual, otherwise no immune response can occur. That is one level of control. ...
... polymorphism for a species, an individual has maximum of six different class I MHC products and only slightly more class II MHC products. A peptide must associate with a given MHC of that individual, otherwise no immune response can occur. That is one level of control. ...
3.2 Cell Organelles
... • Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest material. • Centrioles are tubes found in the centrosomes – made of microtubules. – Centrioles help divide DNA. – Centrioles form cilia and flagella. ...
... • Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest material. • Centrioles are tubes found in the centrosomes – made of microtubules. – Centrioles help divide DNA. – Centrioles form cilia and flagella. ...
presentation Prof Khwaja
... What can we learn from the identification of specific molecular abnormalities in malignant disease? ...
... What can we learn from the identification of specific molecular abnormalities in malignant disease? ...
FM Dyes Label Sterol-Rich Plasma Membrane
... dynamics in their periphery (3D environment) and between them (Fig. 2A–C). Tiny structures appeared to detach from or to fuse with the immobile FM patches, while others appeared or disappeared from the focal plane, suggesting movement from or into deeper regions of the cytoplasm. These dynamic FM-st ...
... dynamics in their periphery (3D environment) and between them (Fig. 2A–C). Tiny structures appeared to detach from or to fuse with the immobile FM patches, while others appeared or disappeared from the focal plane, suggesting movement from or into deeper regions of the cytoplasm. These dynamic FM-st ...
Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function HUMAN SKIN HUMAN
... endosymbiont theory, a symbiotic mutual rela–tionship involved one prokaryotic cell living inside of another. The endosymbiont theory is discussed in greater detail in Chapter 14. Imagine how organisms would be different if the eukaryotic form had not evolved. Because eukaryotic cells are larger and ...
... endosymbiont theory, a symbiotic mutual rela–tionship involved one prokaryotic cell living inside of another. The endosymbiont theory is discussed in greater detail in Chapter 14. Imagine how organisms would be different if the eukaryotic form had not evolved. Because eukaryotic cells are larger and ...
Lineage-specific proteins essential for endocytosis in trypanosomes
... emergence of a true eukaryotic cell, the lineage rapidly diversified into multiple kingdoms or supergroups, represented for example by plants, animals, fungi, amoeba and many protist lineages. The ~1.5 billion year period since this radiation is vast, and while core metabolic and gene expression pat ...
... emergence of a true eukaryotic cell, the lineage rapidly diversified into multiple kingdoms or supergroups, represented for example by plants, animals, fungi, amoeba and many protist lineages. The ~1.5 billion year period since this radiation is vast, and while core metabolic and gene expression pat ...
3.2 Cell Organelles Cells have an internal structure.
... Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts. • A cell wall provides rigid support. • Chloroplasts convert solar energy to chemical energy. ...
... Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts. • A cell wall provides rigid support. • Chloroplasts convert solar energy to chemical energy. ...
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma:- a clinico
... 3. T cell and NK cell lymphoproliferative disorders – Haem 01 4. Therapy of peripheral T / NK neoplasm’s – Haem 06 5. Aggressive Peripheral T cell lymphomas – Haem 05 6. Auto hematopoietic SCT in peripheral T cell lymphoma using uniform high dose regimen – Smith et al – BMT 2007 7. Clinical characte ...
... 3. T cell and NK cell lymphoproliferative disorders – Haem 01 4. Therapy of peripheral T / NK neoplasm’s – Haem 06 5. Aggressive Peripheral T cell lymphomas – Haem 05 6. Auto hematopoietic SCT in peripheral T cell lymphoma using uniform high dose regimen – Smith et al – BMT 2007 7. Clinical characte ...
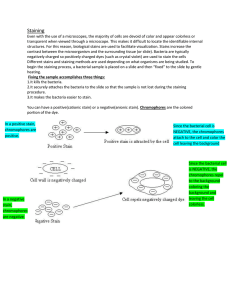
Gram Stain
... Even with the use of a microscopes, the majority of cells are devoid of color and appear colorless or transparent when viewed through a microscope. This makes it difficult to locate the identifiable internal structures. For this reason, biological stains are used to facilitate visualization. Stains ...
... Even with the use of a microscopes, the majority of cells are devoid of color and appear colorless or transparent when viewed through a microscope. This makes it difficult to locate the identifiable internal structures. For this reason, biological stains are used to facilitate visualization. Stains ...
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
... • In the presence of a positive membrane potential, the rate of binding-site eversion from the matrix to the cytosolic side is more rapid for ATP than for ADP because ATP has one more negative charge. • The membrane potential is decreased by the exchange of ATP for ADP, which results in a net transf ...
... • In the presence of a positive membrane potential, the rate of binding-site eversion from the matrix to the cytosolic side is more rapid for ATP than for ADP because ATP has one more negative charge. • The membrane potential is decreased by the exchange of ATP for ADP, which results in a net transf ...
BACTERIA
... A hard, protective case that forms around the DNA of the bacteria cell during unfavorable growth conditions. Spores allow bacteria to survive harsh conditions. (extreme heat, lack of moisture, etc…) ...
... A hard, protective case that forms around the DNA of the bacteria cell during unfavorable growth conditions. Spores allow bacteria to survive harsh conditions. (extreme heat, lack of moisture, etc…) ...
TSM53 - The External, Middle, and Inner Ear
... o Superior prominence made by the lateral process of malleus o Internal folds on either side of the lateral process – anterior and posterior malleolar folds Superior to these folds the membrane is thin and non-fibrous – pars flaccida Inferior to the folds it is thick and tense – pars tensa o Int ...
... o Superior prominence made by the lateral process of malleus o Internal folds on either side of the lateral process – anterior and posterior malleolar folds Superior to these folds the membrane is thin and non-fibrous – pars flaccida Inferior to the folds it is thick and tense – pars tensa o Int ...
Pore-Forming Proteins and Adaptation of Living Organisms to
... cells, as well as various eukaryotic tissues. The cytolytic activity of melittin is underlain by its ability to form pores in membranes using an amphiphilic α-helix formed by two chain regions (residues 1-10 and 13-26). Depending on the type of preferable fatty acids of the membrane bilayer, on meli ...
... cells, as well as various eukaryotic tissues. The cytolytic activity of melittin is underlain by its ability to form pores in membranes using an amphiphilic α-helix formed by two chain regions (residues 1-10 and 13-26). Depending on the type of preferable fatty acids of the membrane bilayer, on meli ...
Columbus County Schools Science Curriculum Guide SUBJECT
... Cell Theory…: Standing on the Shoulders of Giants Put the following quote on the board and ask the students to think about the meaning of the quote. Sir Isaac Newton once said, “If I have seen further, it is because I was standing on the shoulders of giants.” Students should write down their own int ...
... Cell Theory…: Standing on the Shoulders of Giants Put the following quote on the board and ask the students to think about the meaning of the quote. Sir Isaac Newton once said, “If I have seen further, it is because I was standing on the shoulders of giants.” Students should write down their own int ...
to the complete text
... Sorting of membrane cargo into a COPII prebudding complex has been described for several proteins in yeast [19••] and mammals [20,21••] and is believed to be mediated via an interaction with the Sec23p complex [21••], although no direct binding of these components has been demonstrated. Thus, sortin ...
... Sorting of membrane cargo into a COPII prebudding complex has been described for several proteins in yeast [19••] and mammals [20,21••] and is believed to be mediated via an interaction with the Sec23p complex [21••], although no direct binding of these components has been demonstrated. Thus, sortin ...
cell communication powerpoint
... Steps of Cellular Communication 1. Reception: “detection” of signal by a receptor molecule on a target cell (or receptor molecule within cell, depending on type of signal). PRIMARY MESSENGER. Signal does not participate in the actual pathway. In most cases, doesn’t even get into the cell! 2. Transd ...
... Steps of Cellular Communication 1. Reception: “detection” of signal by a receptor molecule on a target cell (or receptor molecule within cell, depending on type of signal). PRIMARY MESSENGER. Signal does not participate in the actual pathway. In most cases, doesn’t even get into the cell! 2. Transd ...
Microbiology 6/e
... penetrate animal cells. Penetration -i) endocytosis ii) direct fusion of viral envelop with host cell membrane Endocytosis – the entire virus (including the envelope) is engulfted by the cell – enclosed in a vacuole or vesicle - Most naked viruses enter cell by endocytosis in which virions are captu ...
... penetrate animal cells. Penetration -i) endocytosis ii) direct fusion of viral envelop with host cell membrane Endocytosis – the entire virus (including the envelope) is engulfted by the cell – enclosed in a vacuole or vesicle - Most naked viruses enter cell by endocytosis in which virions are captu ...
Chapter 3-multiplication
... penetrate animal cells. Penetration -i) endocytosis ii) direct fusion of viral envelop with host cell membrane Endocytosis – the entire virus (including the envelope) is engulfted by the cell – enclosed in a vacuole or vesicle - Most naked viruses enter cell by endocytosis in which virions are captu ...
... penetrate animal cells. Penetration -i) endocytosis ii) direct fusion of viral envelop with host cell membrane Endocytosis – the entire virus (including the envelope) is engulfted by the cell – enclosed in a vacuole or vesicle - Most naked viruses enter cell by endocytosis in which virions are captu ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.