Adjusting kV to Improve Image Quality or Reduce Radiation Dose
... • 100 kV can be practically implemented already in most patients – Task-specific technique charts will include kV and mAs selection to perform most dose-efficient exam – 140 kV imaging may be most dose-efficient for large pts ...
... • 100 kV can be practically implemented already in most patients – Task-specific technique charts will include kV and mAs selection to perform most dose-efficient exam – 140 kV imaging may be most dose-efficient for large pts ...
New Efficient Detector for Radiation Therapy Imaging using Gas Electron Multipliers Ostling
... the dose might have to be reduced in order not to harm healthy tissues that are located inside the target volume. However, using intensity modulated radiation therapy, IMRT, for a given internal margin the tumor cure can successively be improved [8], not least by adaptive approaches [9]. For decades ...
... the dose might have to be reduced in order not to harm healthy tissues that are located inside the target volume. However, using intensity modulated radiation therapy, IMRT, for a given internal margin the tumor cure can successively be improved [8], not least by adaptive approaches [9]. For decades ...
Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography
... 40 ml is most common; 20 ml is used in some applications and by some institutions. The injection rate is typically 2 to 4 ml/second. Vessel contrast in CE-MRA is critically dependent on the timing of the contrast bolus (Fig. 15-2), the bolus geometry, and the choice of sequence parameters (Fig. 15-3 ...
... 40 ml is most common; 20 ml is used in some applications and by some institutions. The injection rate is typically 2 to 4 ml/second. Vessel contrast in CE-MRA is critically dependent on the timing of the contrast bolus (Fig. 15-2), the bolus geometry, and the choice of sequence parameters (Fig. 15-3 ...
Measurement of Pituitary Gland Height with MR Imaging
... From sagittal magnetic resonance (MR) images with 10 mm slice thickness, the mean vertical height of the pituitary gland in 42 normal patients was found to be 5.4 ± 0.9 mm. Computed tomographic (CT) scans in the coronal plane showed the same. Measurements of pituitary size in 13 patients with tumors ...
... From sagittal magnetic resonance (MR) images with 10 mm slice thickness, the mean vertical height of the pituitary gland in 42 normal patients was found to be 5.4 ± 0.9 mm. Computed tomographic (CT) scans in the coronal plane showed the same. Measurements of pituitary size in 13 patients with tumors ...
SADMFR guidelines for the use of cone-beam computed
... chosen if a high resolution is really needed (da Silveira et al. ...
... chosen if a high resolution is really needed (da Silveira et al. ...
Patch based Reconstruction Of Under-sampled Data
... the particular balance chosen between undersampling artifacts, signal to noise ratio (SNR), volume coverage, spatial resolution and temporal fidelity. TRACER (13), a nonlinear parallel imaging reconstruction (14) of golden ratio ordered variable density spiral acquisition, allows the reconstruction ...
... the particular balance chosen between undersampling artifacts, signal to noise ratio (SNR), volume coverage, spatial resolution and temporal fidelity. TRACER (13), a nonlinear parallel imaging reconstruction (14) of golden ratio ordered variable density spiral acquisition, allows the reconstruction ...
Left atrial volume quantification using cardiac MRI in atrial fibrillation
... CMR protocol, which takes approximately 40 min in total. LAV methods that use the routine acquired planes are more time efficient during both image acquisition and image analysis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to compare the Simpson’s method with three different CMR-based methods to measu ...
... CMR protocol, which takes approximately 40 min in total. LAV methods that use the routine acquired planes are more time efficient during both image acquisition and image analysis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to compare the Simpson’s method with three different CMR-based methods to measu ...
Advances in Environmental Biology Systems
... Today, diagnostic imaging is consisting of various branches. The information of imaging is divided into anatomical and function groups. In some systems as CT, MRI imaging based on anatomical techniques, the tumor is detected when the tissue is physiologically changed but in some systems including PE ...
... Today, diagnostic imaging is consisting of various branches. The information of imaging is divided into anatomical and function groups. In some systems as CT, MRI imaging based on anatomical techniques, the tumor is detected when the tissue is physiologically changed but in some systems including PE ...
Using Cone Beam CT in Clinical Practice
... CBCT provides excellent images of dense objects such as teeth and bone while MDCT yields excellent images of the entire range of objects seen in the human body from low density fluids to soft tissues all the way to highly dense, calcified tissues.19-22 At first glance, this lack of soft tissue detai ...
... CBCT provides excellent images of dense objects such as teeth and bone while MDCT yields excellent images of the entire range of objects seen in the human body from low density fluids to soft tissues all the way to highly dense, calcified tissues.19-22 At first glance, this lack of soft tissue detai ...
The management of imaging dose during image-guided
... Data for the dose delivered by the various radiographic imaging modalities being used during radiation therapy are presently scattered widely through the literature, making it ...
... Data for the dose delivered by the various radiographic imaging modalities being used during radiation therapy are presently scattered widely through the literature, making it ...
The management of imaging dose during image-guided
... Data for the dose delivered by the various radiographic imaging modalities being used during radiation therapy are presently scattered widely through the literature, making it ...
... Data for the dose delivered by the various radiographic imaging modalities being used during radiation therapy are presently scattered widely through the literature, making it ...
Approach to Solid Liver Masses in the Cirrhotic Patient
... wash-out. The diagnostic accuracy of MRI and computed tomography (CT), sensitivity, and specificity in the diagnosis of liver mass is shown in Table 3 [19]. Fine needle aspiration and core biopsy Fine needle aspiration and core biopsy (FNAB) is safe, accurate and cost effective. Its specificity appr ...
... wash-out. The diagnostic accuracy of MRI and computed tomography (CT), sensitivity, and specificity in the diagnosis of liver mass is shown in Table 3 [19]. Fine needle aspiration and core biopsy Fine needle aspiration and core biopsy (FNAB) is safe, accurate and cost effective. Its specificity appr ...
Novalis Brochure - Behestan Darman
... are image-guided systems and software that provide highly accurate real-time information used for surgical navigation and radiosurgical planning and delivery. BrainLAB systems and software are leveraged to provide clinicians with an information portal to more effectively access and interpret diagnos ...
... are image-guided systems and software that provide highly accurate real-time information used for surgical navigation and radiosurgical planning and delivery. BrainLAB systems and software are leveraged to provide clinicians with an information portal to more effectively access and interpret diagnos ...
quantitative nuclear medicine imaging: concepts
... three dimensional imaging, supported by SPECT, PET and hybrid equipment. Methods of iterative reconstruction have been developed to allow for more consistent compensation for physical effects and imaging system limitations. On these grounds, quantitative imaging is now a broad field of work for the ...
... three dimensional imaging, supported by SPECT, PET and hybrid equipment. Methods of iterative reconstruction have been developed to allow for more consistent compensation for physical effects and imaging system limitations. On these grounds, quantitative imaging is now a broad field of work for the ...
- Wiley Online Library
... a relatively small region of interest (ROI) in a reconstructed 3D image. Thus, region-of-interest imaging technique is considered a reasonable dose reduction method in which the ROI is only illuminated during a scan by use of a filter that blocks the beam outside the ROI. Through this method, all th ...
... a relatively small region of interest (ROI) in a reconstructed 3D image. Thus, region-of-interest imaging technique is considered a reasonable dose reduction method in which the ROI is only illuminated during a scan by use of a filter that blocks the beam outside the ROI. Through this method, all th ...
Breast Imaging For Screening And Diagnosing Cancer
... elastography, scintimammography, electrical impedance scanning and computer-aided detection for MRI, automated breast ultrasound and ultrasound for breast cancer screening and the diagnosis of breast cancer. The National Cancer Institute estimates that about 40 percent of women undergoing screening ...
... elastography, scintimammography, electrical impedance scanning and computer-aided detection for MRI, automated breast ultrasound and ultrasound for breast cancer screening and the diagnosis of breast cancer. The National Cancer Institute estimates that about 40 percent of women undergoing screening ...
Transmission and emission x-ray microscopy: operation modes
... limitations on the specimen thickness (<100 nm) and state (dry or frozen hydrated specimen slices). In comparison, x-ray microscopes can image not only thicker specimens in their natural environment (e.g. whole cells) but the unique interactions of x-rays with matter allow control of the specimen ch ...
... limitations on the specimen thickness (<100 nm) and state (dry or frozen hydrated specimen slices). In comparison, x-ray microscopes can image not only thicker specimens in their natural environment (e.g. whole cells) but the unique interactions of x-rays with matter allow control of the specimen ch ...
R E V I E W Physics,
... absorbs the X-rays and generates a light scintillation that is then detected by an array of photodiodes. Indirect systems suffer from resolution degradation caused by light spread in the scintillator and poor quantum efficiency with thin scintillators. Direct digital detectors utilize a direct-conve ...
... absorbs the X-rays and generates a light scintillation that is then detected by an array of photodiodes. Indirect systems suffer from resolution degradation caused by light spread in the scintillator and poor quantum efficiency with thin scintillators. Direct digital detectors utilize a direct-conve ...
File Ref.No.38933/GA - IV - J2/2013/CU UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT
... The Board of Studies in Radiation Physics, vide paper read as (3), resolved to approve the Revised Syllabus of MSc programme in Radiation Physics under CCSS (PG) in the University Teaching Department, with effect from 2013 admissions. The Dean Faculty of Science recommended to implement the resoluti ...
... The Board of Studies in Radiation Physics, vide paper read as (3), resolved to approve the Revised Syllabus of MSc programme in Radiation Physics under CCSS (PG) in the University Teaching Department, with effect from 2013 admissions. The Dean Faculty of Science recommended to implement the resoluti ...
Chapter 1 - ImageProcessingPlace
... the late 1960s and early 1970s to be used in medical imaging, remote Earth resources observations, and astronomy. The invention in the early 1970s of computerized axial tomography (CAT), also called computerized tomography (CT) for short, is one of the most important events in the application of ima ...
... the late 1960s and early 1970s to be used in medical imaging, remote Earth resources observations, and astronomy. The invention in the early 1970s of computerized axial tomography (CAT), also called computerized tomography (CT) for short, is one of the most important events in the application of ima ...
Breast Imaging for Screening and Diagnosing Cancer
... when added to contrast-enhanced MRI. There is insufficient evidence to assess whether the use of CAD systems would maintain or increase the sensitivity, specificity, and recall rates of MRI of the breast. Prospective, well-designed and executed studies are needed to determine whether or not the use ...
... when added to contrast-enhanced MRI. There is insufficient evidence to assess whether the use of CAD systems would maintain or increase the sensitivity, specificity, and recall rates of MRI of the breast. Prospective, well-designed and executed studies are needed to determine whether or not the use ...
Magnetic resonance imaging of cholesteatoma: an update
... surgery. Based on this investigation, no second look surgery was performed. Clinical micro-otoscopical follow-up 26 months after the primary surgery showed no suspicious signs of residual or recurrent disease. a: Axial HRCT image at the level of the lateral semicircular canal on the right side. The ...
... surgery. Based on this investigation, no second look surgery was performed. Clinical micro-otoscopical follow-up 26 months after the primary surgery showed no suspicious signs of residual or recurrent disease. a: Axial HRCT image at the level of the lateral semicircular canal on the right side. The ...
to the Curriculum Guide 2008 in Word format
... This curriculum document establishes national, standardized educational guidelines for MR, including clinical and didactic components. The curriculum is suitable for all programs in this discipline, including limited fellowships, certificate programs and collegiate-based education programs. The curr ...
... This curriculum document establishes national, standardized educational guidelines for MR, including clinical and didactic components. The curriculum is suitable for all programs in this discipline, including limited fellowships, certificate programs and collegiate-based education programs. The curr ...
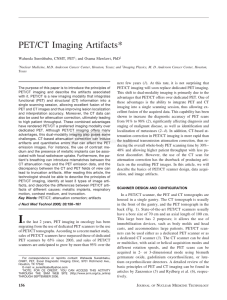
CT Dose Summit 2011
... patients and referring physicians know, don’t know, are afraid of, and expect from us • Communicate with referring colleagues and with patients—that is how we educate others about radiation safety and dose ...
... patients and referring physicians know, don’t know, are afraid of, and expect from us • Communicate with referring colleagues and with patients—that is how we educate others about radiation safety and dose ...
PET/CT Imaging Artifacts - Society of Nuclear Medicine
... single scanning session, allowing excellent fusion of the PET and CT images and thus improving lesion localization and interpretation accuracy. Moreover, the CT data can also be used for attenuation correction, ultimately leading to high patient throughput. These combined advantages have rendered PE ...
... single scanning session, allowing excellent fusion of the PET and CT images and thus improving lesion localization and interpretation accuracy. Moreover, the CT data can also be used for attenuation correction, ultimately leading to high patient throughput. These combined advantages have rendered PE ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.