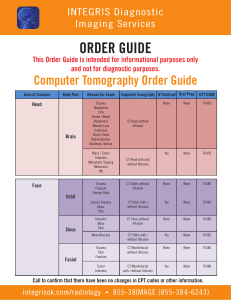
3D MPRAGE improves classification of cortical lesions
... inversion recovery (PSIR), has been used for detection and classification of cortical lesions. This study shows that high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition with gradient echo (MPRAGE) improves the classification of cortical lesions by allowing more accurate a ...
... inversion recovery (PSIR), has been used for detection and classification of cortical lesions. This study shows that high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition with gradient echo (MPRAGE) improves the classification of cortical lesions by allowing more accurate a ...
Computed tomography in the evaluation for transcatheter aortic
... to minimize cardiac output and prevent migration of the valve during deployment. The self-expanding CoreValve (Medtronic) is typically deployed without pacing. The stent-valve is anchored within the annulus and, depending on stent design, additional stability is provided by the displaced calcified l ...
... to minimize cardiac output and prevent migration of the valve during deployment. The self-expanding CoreValve (Medtronic) is typically deployed without pacing. The stent-valve is anchored within the annulus and, depending on stent design, additional stability is provided by the displaced calcified l ...
Two−dimensional longitudinal strain for the assessment of the left
... of limitations adherent to conventional methods. Due to its objectiveness, the important factor of intra-observer variability is eliminated, and this results in good reproducibility of the method, as reported by a number of authors [8, 9]. The quantitative nature of strain may allow for evaluation o ...
... of limitations adherent to conventional methods. Due to its objectiveness, the important factor of intra-observer variability is eliminated, and this results in good reproducibility of the method, as reported by a number of authors [8, 9]. The quantitative nature of strain may allow for evaluation o ...
ACR-AIUM-SPR-SRU Practice Parameter for the Performance of an
... analysis should be conducted with a carrier frequency of 3.0 MHz or greater. Lower frequencies are occasionally appropriate in patients with a large body habitus or densely calcified vessels. Examination using lower-frequency transducers can also be useful when the vessels are not adequately imaged ...
... analysis should be conducted with a carrier frequency of 3.0 MHz or greater. Lower frequencies are occasionally appropriate in patients with a large body habitus or densely calcified vessels. Examination using lower-frequency transducers can also be useful when the vessels are not adequately imaged ...
Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Patients With Myocardial
... imaging evidence of MI involve not only established modalities such as echocardiography and radionuclide imaging, but also the newer modalities, cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) and cardiac computed tomography. In particular, delayed enhancement (DE)-CMR appears to offer advantages in detecti ...
... imaging evidence of MI involve not only established modalities such as echocardiography and radionuclide imaging, but also the newer modalities, cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) and cardiac computed tomography. In particular, delayed enhancement (DE)-CMR appears to offer advantages in detecti ...
Interventional Radiology and Endovascular Repair of Abdominal
... CT: – High sensitivity (100%) – Better than US at defining aorta size, length, involvement of visceral vessels, leakage – 3 dimensional imaging – Needs technician – Higher cost – longer study time – exposure to contrast and ionizing radiation ...
... CT: – High sensitivity (100%) – Better than US at defining aorta size, length, involvement of visceral vessels, leakage – 3 dimensional imaging – Needs technician – Higher cost – longer study time – exposure to contrast and ionizing radiation ...
Magnetic Resonance Curriculum
... magnetic resonance (MR) technology. This document represents a collaborative effort involving representatives from the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT), the Association of Educators in Imaging and Radiologic Sciences (AEIRS) and the Section for Magnetic Resonance Technologists (SM ...
... magnetic resonance (MR) technology. This document represents a collaborative effort involving representatives from the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT), the Association of Educators in Imaging and Radiologic Sciences (AEIRS) and the Section for Magnetic Resonance Technologists (SM ...
Magnetic Resonance Curriculum
... magnetic resonance (MR) technology. This document represents a collaborative effort involving representatives from the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT), the Association of Educators in Imaging and Radiologic Sciences (AEIRS) and the Section for Magnetic Resonance Technologists (SM ...
... magnetic resonance (MR) technology. This document represents a collaborative effort involving representatives from the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT), the Association of Educators in Imaging and Radiologic Sciences (AEIRS) and the Section for Magnetic Resonance Technologists (SM ...
diffusion_bas
... The Diffusion Tensor, D Diffusion is not equal in all directions (anisotropic). Use this to probe brain structure! Represent the diffusion pattern at each point in the brain using an ellipsoid. ...
... The Diffusion Tensor, D Diffusion is not equal in all directions (anisotropic). Use this to probe brain structure! Represent the diffusion pattern at each point in the brain using an ellipsoid. ...
Craniocervical Junction Injury
... lateral masses. There is an associated occipital condyle fracture and fracture through the C1 anterior arch. ...
... lateral masses. There is an associated occipital condyle fracture and fracture through the C1 anterior arch. ...
Full Text - Journal of Emergency Medicine Case Reports
... through the nephrostomy catheter showed immense extravasation of contrast from the UPJ (Figure 2). He was managed conservatively with bed rest and frequent serum haemoglobin monitoring. On follow-up, there was no deterioration of vital signs and hemoglobin value. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) sc ...
... through the nephrostomy catheter showed immense extravasation of contrast from the UPJ (Figure 2). He was managed conservatively with bed rest and frequent serum haemoglobin monitoring. On follow-up, there was no deterioration of vital signs and hemoglobin value. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) sc ...
Catharina Sundgren Estimation of patient setup errors in
... from several different angles. This will result in the irradiation of more healthy tissue, but the dose delivered to it will be lower. Usually, the beam angles are selected beforehand, based on experience. A prostate patient for instance is generally treated with 5 beams whereas a head-and-neck pati ...
... from several different angles. This will result in the irradiation of more healthy tissue, but the dose delivered to it will be lower. Usually, the beam angles are selected beforehand, based on experience. A prostate patient for instance is generally treated with 5 beams whereas a head-and-neck pati ...
Monte Carlo simulations in emission tomography and GATE: An
... and it has been shown that their use reduce the computational time by a factor between 2 and up to more than 10 [18], without jeopardizing the accuracy of the simulated data. The main issue related to the use of such techniques is that they strongly alter the statistical properties of simulated data ...
... and it has been shown that their use reduce the computational time by a factor between 2 and up to more than 10 [18], without jeopardizing the accuracy of the simulated data. The main issue related to the use of such techniques is that they strongly alter the statistical properties of simulated data ...
guidelines for the use of radiographs in clinicalorthodontics
... “Perhaps the AAO might be inspired to publish a more meaningful set of radiographic guidelines after the exceptional example set by their British colleagues.” 7 “I was impressed with the sensible approach taken, based on published science… I do believe the BOS points us in a direction that could res ...
... “Perhaps the AAO might be inspired to publish a more meaningful set of radiographic guidelines after the exceptional example set by their British colleagues.” 7 “I was impressed with the sensible approach taken, based on published science… I do believe the BOS points us in a direction that could res ...
SOMATOM Definition AS
... Every CT examination poses individual and specific requirements to achieve the optimum clinical outcome. These vary from institution to institution, from user to user, from patient to patient, The challenge is to find and apply the ideal settings for every individual examination, but at the same tim ...
... Every CT examination poses individual and specific requirements to achieve the optimum clinical outcome. These vary from institution to institution, from user to user, from patient to patient, The challenge is to find and apply the ideal settings for every individual examination, but at the same tim ...
September - BIDMC Radiology Alumni
... damage to other brain areas leaves a kind of vacuum that the enlarged ventricles fill. The fluid-filled ventricles can make the head size seem normal earlier in pregnancy, Dr. Levine said. But as scans of one pregnancy taken at 36 weeks gestation show, the fluid can be so prominent that the scan sho ...
... damage to other brain areas leaves a kind of vacuum that the enlarged ventricles fill. The fluid-filled ventricles can make the head size seem normal earlier in pregnancy, Dr. Levine said. But as scans of one pregnancy taken at 36 weeks gestation show, the fluid can be so prominent that the scan sho ...
Acceptance Testing and Quality Control of Dental Imaging
... radiography in general, can be found in references 1–3. There is approximately a factor of two difference in the speed, or sensitivity, of D-speed compared with E-, E/F-, or F-speed films; as a result, the E-, E/F-, or F-speed film requires only approximately half of the radiation of the D-speed fil ...
... radiography in general, can be found in references 1–3. There is approximately a factor of two difference in the speed, or sensitivity, of D-speed compared with E-, E/F-, or F-speed films; as a result, the E-, E/F-, or F-speed film requires only approximately half of the radiation of the D-speed fil ...
Medical Physics Personnel for Medical Imaging Requirements
... made available in all the medical institutions that use ionising radiation for medical purposes, whatever their status, provides information on the medical physics tasks to be carried out and their quantification. It contains recommendations concerning the involvement of medical physicists (with or ...
... made available in all the medical institutions that use ionising radiation for medical purposes, whatever their status, provides information on the medical physics tasks to be carried out and their quantification. It contains recommendations concerning the involvement of medical physicists (with or ...
AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of the Musculoskeletal
... The biceps tendon should be examined with the forearm in supination and resting on the thigh or with the arm in slight external rotation. The tendon is examined in a transverse plane (short axis), where it emerges from under the acromion, to the musculotendinous junction distally. Longitudinal view ...
... The biceps tendon should be examined with the forearm in supination and resting on the thigh or with the arm in slight external rotation. The tendon is examined in a transverse plane (short axis), where it emerges from under the acromion, to the musculotendinous junction distally. Longitudinal view ...
Mri And Ct Of The Female Pelvis
... a pelvic mri scan specifically ... depending on if you’re male or female. a pelvic mri scan is a useful ... for inspecting your pelvic area, such as a ct ... ...
... a pelvic mri scan specifically ... depending on if you’re male or female. a pelvic mri scan is a useful ... for inspecting your pelvic area, such as a ct ... ...
The Mini C-arm Adds Quality and Efficiency to the Pediatric
... kept with the patient information and corresponding radiation emitted and time of radiation exposure. The log book is examined by radiation physics on an annual basis. Using these data, a radiation physicist (S.H.K.) calculated the amount of skin exposure for each fracture evaluated. This study exam ...
... kept with the patient information and corresponding radiation emitted and time of radiation exposure. The log book is examined by radiation physics on an annual basis. Using these data, a radiation physicist (S.H.K.) calculated the amount of skin exposure for each fracture evaluated. This study exam ...
clinical studies - Neurochirurgisch Centrum Amsterdam
... Computed tomographic (CT) myelography and routine twodimensional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques still lack resolution in infants, whereas other techniques are technically too demanding (2, 4, 5, 7, 11, 18, 21, 24). A new, fully flow-compensated, three-dimensional (3D) MRI technique with ...
... Computed tomographic (CT) myelography and routine twodimensional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques still lack resolution in infants, whereas other techniques are technically too demanding (2, 4, 5, 7, 11, 18, 21, 24). A new, fully flow-compensated, three-dimensional (3D) MRI technique with ...
AAPM-RSNA Physics Tutorial for Residents: Typical Patient
... X rays ionize atoms and molecules in human tissues through the deposition of energy. This ionization is the first step in a series of events that may lead to a biologic effect. Absorbed dose is a measure of energy deposited per unit mass and provides a means to gauge the potential for biologic effec ...
... X rays ionize atoms and molecules in human tissues through the deposition of energy. This ionization is the first step in a series of events that may lead to a biologic effect. Absorbed dose is a measure of energy deposited per unit mass and provides a means to gauge the potential for biologic effec ...
6 The Simulation Process in the Determination and Definition of the
... than bony anatomy, is available for design of treatment portals. Shortly after the introduction of clinical CT scanners in early 1970s, it was realized that this imaging modality has much to offer in a radiation oncology setting. The CT images provide information not only about target volumes but ab ...
... than bony anatomy, is available for design of treatment portals. Shortly after the introduction of clinical CT scanners in early 1970s, it was realized that this imaging modality has much to offer in a radiation oncology setting. The CT images provide information not only about target volumes but ab ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.