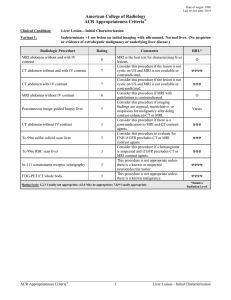
Nuclear Medicine Phantom Instructions
... resolution of your camera detector(s). The resolution images will be acquired with the fourquadrant bar phantom that you should already own and use on a regular basis. A camera accredited for General Nuclear Medicine will have to be reaccredited if it is to be used later for SPECT. SPECT and Planar ...
... resolution of your camera detector(s). The resolution images will be acquired with the fourquadrant bar phantom that you should already own and use on a regular basis. A camera accredited for General Nuclear Medicine will have to be reaccredited if it is to be used later for SPECT. SPECT and Planar ...
CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION EQUIPMENT PERFORMANCE AAPM REPORT NO. 70 Report of Task Group #17
... facilities dealing with different clinical imaging issues outside the realm of normal radiology imaging systems, many medical physicists have only limited experience evaluating the performance of this equipment. The patient and scattered radiation doses in these rooms are among the highest delivered ...
... facilities dealing with different clinical imaging issues outside the realm of normal radiology imaging systems, many medical physicists have only limited experience evaluating the performance of this equipment. The patient and scattered radiation doses in these rooms are among the highest delivered ...
radiation protection in diagnostic radiology
... • Digital radiography requires training to benefit from the advantages of this technology. • Image quality and diagnostic information are closely related to patient dose. • The transmission, archiving and retrieval of images can influence the workflow • A quality control program is essential in digi ...
... • Digital radiography requires training to benefit from the advantages of this technology. • Image quality and diagnostic information are closely related to patient dose. • The transmission, archiving and retrieval of images can influence the workflow • A quality control program is essential in digi ...
Improvements in Segmentation Using Scatter and Photopeak
... the masking process was confirmed by the results from a low count phantom. In a case study, automatic extraction by SSPAC had a 44% success rate for low count (stress condition) myocardial single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) images, but reached a success rate of 99% with the addition ...
... the masking process was confirmed by the results from a low count phantom. In a case study, automatic extraction by SSPAC had a 44% success rate for low count (stress condition) myocardial single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) images, but reached a success rate of 99% with the addition ...
Document
... great significance for patient care. Also, SPECT imaging allows the determination of whether clinical ischemia is caused by restenosis at the site of angioplasty or by progression of disease in other coronary arteries.8 Therefore, it is beneficial for patients who are being prepared for revasculariz ...
... great significance for patient care. Also, SPECT imaging allows the determination of whether clinical ischemia is caused by restenosis at the site of angioplasty or by progression of disease in other coronary arteries.8 Therefore, it is beneficial for patients who are being prepared for revasculariz ...
communicating radiation risks in paediatric imaging
... Advancing imaging technology has opened new horizons for clinical diagnostics and has greatly improved patient care. As a result, the use of medical imaging has increased rapidly worldwide during the past several decades and the spectrum of its applications in paediatric health care has expanded. Pa ...
... Advancing imaging technology has opened new horizons for clinical diagnostics and has greatly improved patient care. As a result, the use of medical imaging has increased rapidly worldwide during the past several decades and the spectrum of its applications in paediatric health care has expanded. Pa ...
Application Training Brochure
... give users system, application and technology training that combines theoretical principles with handson exercises in a one-day to five-day course format. You can extend your skills and gain new knowledge by working on course content closely with your peers. Offering many of our courses in collabora ...
... give users system, application and technology training that combines theoretical principles with handson exercises in a one-day to five-day course format. You can extend your skills and gain new knowledge by working on course content closely with your peers. Offering many of our courses in collabora ...
MD Expo
... accreditation for deemed status purposes: The hospital maintains either a written inventory of all medical equipment or a written inventory of selected equipment categorized by physical risk associated with use (including all life-support equipment) and equipment incident history. The hospital evalu ...
... accreditation for deemed status purposes: The hospital maintains either a written inventory of all medical equipment or a written inventory of selected equipment categorized by physical risk associated with use (including all life-support equipment) and equipment incident history. The hospital evalu ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... ible light. The light is then detected by a Si photodiode. The resulting electrical current is amplified and converted into a digital signal. Key requirements for a suitable detector material are good detection efficiency, i.e., high atomic number, and very short afterglow time to enable the fast ga ...
... ible light. The light is then detected by a Si photodiode. The resulting electrical current is amplified and converted into a digital signal. Key requirements for a suitable detector material are good detection efficiency, i.e., high atomic number, and very short afterglow time to enable the fast ga ...
Anterior-segment imaging for assessment of
... include connective tissues, cytoplasmic organelles, cell nuclei and melanin granules [19] . However, owing to the fact that the speed of light is so much faster than that of sound, the time delay between the emission of a light pulse and detection of a reflection is too brief to measure directly. He ...
... include connective tissues, cytoplasmic organelles, cell nuclei and melanin granules [19] . However, owing to the fact that the speed of light is so much faster than that of sound, the time delay between the emission of a light pulse and detection of a reflection is too brief to measure directly. He ...
Design and Preliminary Accuracy Studies of an MRI
... new cases of prostate cancer and 27,050 deaths caused by prostate cancer in the United States. The current standard of care for verifying the existence of prostate cancer is transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) guided biopsy. TRUS provides limited diagnostic accuracy and image resolution. In [2] the author ...
... new cases of prostate cancer and 27,050 deaths caused by prostate cancer in the United States. The current standard of care for verifying the existence of prostate cancer is transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) guided biopsy. TRUS provides limited diagnostic accuracy and image resolution. In [2] the author ...
Full-Text PDF
... Methods used for motion correction in MRI include navigator pulses, optical tracking devices and post-processing software methods as well as some preliminary evaluation of techniques which use wireless data. The non-wireless based methods have some advantages but also suffer from increased acquisiti ...
... Methods used for motion correction in MRI include navigator pulses, optical tracking devices and post-processing software methods as well as some preliminary evaluation of techniques which use wireless data. The non-wireless based methods have some advantages but also suffer from increased acquisiti ...
MEDICAL PHYSICS INTERNATIONAL
... discussed above, as well as the reaction of the human visual perception system to those factors. High noise may obscure the low contrast object in the noise and make it difficult for a human to perceive it. Poor spatial resolution may blur the object and blend it in with the background and poor unif ...
... discussed above, as well as the reaction of the human visual perception system to those factors. High noise may obscure the low contrast object in the noise and make it difficult for a human to perceive it. Poor spatial resolution may blur the object and blend it in with the background and poor unif ...
CT Scan Parameters and Radiation Dose
... an impetus for performing these studies with the least possible radiation dose [1]. It is now believed that as many as 0.4% of all malignancies in the United States can be traced back to radiation from CT studies performed between 1991 and 1996 and that radiation from CT studies currently being perf ...
... an impetus for performing these studies with the least possible radiation dose [1]. It is now believed that as many as 0.4% of all malignancies in the United States can be traced back to radiation from CT studies performed between 1991 and 1996 and that radiation from CT studies currently being perf ...
MR Angiography of the Portal Venous System
... For patients with limited breath-holding capabilities who could not suspend breathing during the portal venous phase, axial 2D gradient echo ...
... For patients with limited breath-holding capabilities who could not suspend breathing during the portal venous phase, axial 2D gradient echo ...
Computed tomography
... array" absorbs the penetrated X-rays, measures the Xray amount, and transmits the data to a computer system. A sophisticated computer system, in turn, calculates and analyzes data from each detector in each level, and finally reconstructs multiple, twodimensional, cross-sectional images. ...
... array" absorbs the penetrated X-rays, measures the Xray amount, and transmits the data to a computer system. A sophisticated computer system, in turn, calculates and analyzes data from each detector in each level, and finally reconstructs multiple, twodimensional, cross-sectional images. ...
Free Full Text - Hellenic Society of Nuclear Medicine
... contrast on AC PET images, Inhomogeneity of data transmission may lead to a noisy background and decreasing the signal to noise ratio [19]. Furthermore, the absolute background for lesions on NAC PET images is variable, showing higher uptake at the lesion’s edge and slightly lower uptake towards the ...
... contrast on AC PET images, Inhomogeneity of data transmission may lead to a noisy background and decreasing the signal to noise ratio [19]. Furthermore, the absolute background for lesions on NAC PET images is variable, showing higher uptake at the lesion’s edge and slightly lower uptake towards the ...
MATLAB as a Tool in Nuclear Medicine Image Processing
... attached to a pharmaceutical (tracer) and the whole complex is then delivered to the patient intravenously or by swallowing or even by inhalation. The radiopharmaceutical follows its physiological pathway and it is concentrated on specific organs and tissues for short periods of time. Then, the pati ...
... attached to a pharmaceutical (tracer) and the whole complex is then delivered to the patient intravenously or by swallowing or even by inhalation. The radiopharmaceutical follows its physiological pathway and it is concentrated on specific organs and tissues for short periods of time. Then, the pati ...
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE
... was used as a diagnostic technique. With the advent of magnetic resonance imaging and other noninvasive techniques, knee arthroscopy is now used for the treatment of various knee pathologies. Indications for knee arthroscopy include the treatment of meniscal pathology, specified articular cartilage ...
... was used as a diagnostic technique. With the advent of magnetic resonance imaging and other noninvasive techniques, knee arthroscopy is now used for the treatment of various knee pathologies. Indications for knee arthroscopy include the treatment of meniscal pathology, specified articular cartilage ...
Cystic lesions of the pancreato-duodenal confluence. Who is who?
... A wide spectrum of anomalies can be encountered at radiologic evaluation of the pancreato-duodenal junction. The hystology of the anatomic structures and pathology of different anomalies favor a true cystic or a cystic-like component at radiologic evaluation. From January 2009 through May 2012 we ha ...
... A wide spectrum of anomalies can be encountered at radiologic evaluation of the pancreato-duodenal junction. The hystology of the anatomic structures and pathology of different anomalies favor a true cystic or a cystic-like component at radiologic evaluation. From January 2009 through May 2012 we ha ...
radiation protection in diagnostic radiology
... • The smallest film and cassette size compatible with the expected image must be used together with automatic collimation. Otherwise the patient would be over-irradiated, by receiving radiation over a larger volume. Irradiating a smaller volume also minimizes the amount of scattered radiation and im ...
... • The smallest film and cassette size compatible with the expected image must be used together with automatic collimation. Otherwise the patient would be over-irradiated, by receiving radiation over a larger volume. Irradiating a smaller volume also minimizes the amount of scattered radiation and im ...
PAGE 6 - The Scanner Magazine
... is being kept alive by Porsche, formerly a medium-sized enterprise looking into the abyss of insolvency before a courageous management engineered a successful turn-around. Just like Porsche’s Wendelin Wiedeking, forward-looking managers of hospitals and radiology practices have to seriously rethink ...
... is being kept alive by Porsche, formerly a medium-sized enterprise looking into the abyss of insolvency before a courageous management engineered a successful turn-around. Just like Porsche’s Wendelin Wiedeking, forward-looking managers of hospitals and radiology practices have to seriously rethink ...
Compensators for dose and scatter management in cone
... more precise treatment delivery, with numerous techniques developed to accomplish visualization of soft-tissue structures of interest with the patient in treatment position.1 A recently developed technology for soft-tissue visualization and image-guided radiation therapy is kV cone-beam CT 共CBCT兲.2 ...
... more precise treatment delivery, with numerous techniques developed to accomplish visualization of soft-tissue structures of interest with the patient in treatment position.1 A recently developed technology for soft-tissue visualization and image-guided radiation therapy is kV cone-beam CT 共CBCT兲.2 ...
LOGIQ E9 Shear Wave Elastography
... Motion due to respiration, arterial pressure, cardiac, or other muscle activity can be used to derive elasticity information in arteries, skeletal muscle, and myocardium. ...
... Motion due to respiration, arterial pressure, cardiac, or other muscle activity can be used to derive elasticity information in arteries, skeletal muscle, and myocardium. ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.