Grant MacEwan College - Faculty Web Pages
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... Many schemes make use of carbonyl substitution reactions. These reaction are one the few general methods for making C-C bonds. ...
... Many schemes make use of carbonyl substitution reactions. These reaction are one the few general methods for making C-C bonds. ...
... shaken and let stand for 5 min, then centrifuged (13000 rpm/3 min), and transferred to an HPLC vial, stored in refrigeration, for the HPLC analysis. General procedure for the enzymatic hydrolysis of (rac)-Nacetylmethionine, enzyme extract. 19-20 mg of each KAP was suspended in 1.0 mL of phosphate bu ...
Document
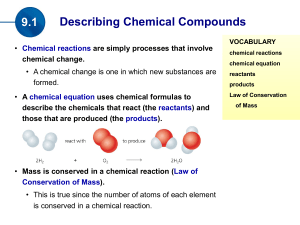
... Reactant 1 + Reactant 2 Product 1 + Product 2 (the number of reactants and products will vary) ...
... Reactant 1 + Reactant 2 Product 1 + Product 2 (the number of reactants and products will vary) ...
Indian Journal of Chemistry
... in the activation barrier (δmΔG≠) is measured. Solvent effects on reactivity trends for base hydrolysis of these compounds have been analysed into initial state and transition state components which are determined from transfer chemical potentials and kinetic data. It is observed that the substituen ...
... in the activation barrier (δmΔG≠) is measured. Solvent effects on reactivity trends for base hydrolysis of these compounds have been analysed into initial state and transition state components which are determined from transfer chemical potentials and kinetic data. It is observed that the substituen ...
Protecting Groups Introduction to Carbonyl
... Reagents; Oxidation and Reduction Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is ...
... Reagents; Oxidation and Reduction Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is ...
Unit 3 - Salina USD 305
... ◦ Begin Worksheet #2 ◦ Wrap Up – Reaction Sort Homework (Write in Planner): ◦ Worksheet #2 (Optional) ...
... ◦ Begin Worksheet #2 ◦ Wrap Up – Reaction Sort Homework (Write in Planner): ◦ Worksheet #2 (Optional) ...
Reaction of Organometallic Reagents with Aldehydes and Ketones.
... and organomagnesium (RMgX) reagents contain very polar carbon— metal bonds and are therefore very reactive reagents. • Organomagnesium reagents are called Grignard reagents. • Organocopper reagents (R2CuLi), also called organocuprates, have a less polar carbon—metal bond and are therefore less react ...
... and organomagnesium (RMgX) reagents contain very polar carbon— metal bonds and are therefore very reactive reagents. • Organomagnesium reagents are called Grignard reagents. • Organocopper reagents (R2CuLi), also called organocuprates, have a less polar carbon—metal bond and are therefore less react ...
File
... Be able to use the n +1 rule to deduce the spin– spin splitting patterns of adjacent, non-equivalent protons, limited to doublet, triplet and quartet formation in simple aliphatic compounds Know that gas-liquid chromatography can be used to separate mixtures of volatile liquids ...
... Be able to use the n +1 rule to deduce the spin– spin splitting patterns of adjacent, non-equivalent protons, limited to doublet, triplet and quartet formation in simple aliphatic compounds Know that gas-liquid chromatography can be used to separate mixtures of volatile liquids ...
organic revision nots
... with water in all proportions. 9. There are two – NH2 group in semi carbazide however only one is involved in the formation of semi carbazones. 10. It is necessary to control the pH during the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with ammonia derivatives. 11. o-hydroxybenzaldehyde is a liquid at room t ...
... with water in all proportions. 9. There are two – NH2 group in semi carbazide however only one is involved in the formation of semi carbazones. 10. It is necessary to control the pH during the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with ammonia derivatives. 11. o-hydroxybenzaldehyde is a liquid at room t ...
Full research publication
... methyl (2Z) - [3- (2-oxopentyl) quinoxalin-2 (1H) -ylidene] etanoat. On the basis of IR and 1H NMR spectroscopy and mass spectroscopy the structure of the synthesized compounds was found out. Its radical binding activity in the reaction with DPPH (DPPH) was studied, which was at the level of the sta ...
... methyl (2Z) - [3- (2-oxopentyl) quinoxalin-2 (1H) -ylidene] etanoat. On the basis of IR and 1H NMR spectroscopy and mass spectroscopy the structure of the synthesized compounds was found out. Its radical binding activity in the reaction with DPPH (DPPH) was studied, which was at the level of the sta ...
Catalysis by main-group metal - Université Paris-Sud
... alcohols through borrowing hydrogen catalysis (or hydrogen auto transfer),2 has been recognized as one of the most practical methods for the industrial production of substituted alkyl amines. The broad availability of alcohols, combined with the fact that water is the only by-product of such reactio ...
... alcohols through borrowing hydrogen catalysis (or hydrogen auto transfer),2 has been recognized as one of the most practical methods for the industrial production of substituted alkyl amines. The broad availability of alcohols, combined with the fact that water is the only by-product of such reactio ...
Triruthenium and triosmium carbonyl clusters containing chiral
... bond of levamisolium salts could take place over complexes of low-valent metals different from palladium. We now report that the treatment of levamisolium salts with some triruthenium and triosmium carbonyl cluster complexes leads, through processes that involve an S–C(sp2 ) bond cleavage as a key r ...
... bond of levamisolium salts could take place over complexes of low-valent metals different from palladium. We now report that the treatment of levamisolium salts with some triruthenium and triosmium carbonyl cluster complexes leads, through processes that involve an S–C(sp2 ) bond cleavage as a key r ...
Chapter 12- Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds, Redox Reactions
... Reactions of alkyl lithiums and Grignard reagents • A) Reactions with compounds that contain acidic hydrogens • Alkyl lithiums and grignard reagents are very strong bases • They will react with any compound that has a hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom such as oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur ...
... Reactions of alkyl lithiums and Grignard reagents • A) Reactions with compounds that contain acidic hydrogens • Alkyl lithiums and grignard reagents are very strong bases • They will react with any compound that has a hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom such as oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur ...
CHEM 242 Organic Chemistry II-Bender
... Course Content: Organic Chemistry I will cover chapters 13 – 20, 22, and 23. Special emphasis will be placed on aromatic compounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, phenols, spectroscopy, structure and reactivity, biomolecules and multi-step synthesis. Laboratory is included and chapter ...
... Course Content: Organic Chemistry I will cover chapters 13 – 20, 22, and 23. Special emphasis will be placed on aromatic compounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, phenols, spectroscopy, structure and reactivity, biomolecules and multi-step synthesis. Laboratory is included and chapter ...
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts are never changed. • For example when the number of atoms of the reactant element(s) are the same as the number of atoms of the product element(s), the equation is balanced. ...
... coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts are never changed. • For example when the number of atoms of the reactant element(s) are the same as the number of atoms of the product element(s), the equation is balanced. ...
alcohols ws 1 - Chesterhouse School
... (d) Lactic acid is chiral. Draw displayed formulae of the two optical isomers of lactic acid clearly showing their three-dimensional structures. Indicate with an asterisk (*) the chiral carbon atom in each. ...
... (d) Lactic acid is chiral. Draw displayed formulae of the two optical isomers of lactic acid clearly showing their three-dimensional structures. Indicate with an asterisk (*) the chiral carbon atom in each. ...
Date - Chaminade University`s syllabus repository
... Theories of covalent bonding: Lewis Model; Orbital Hybridization Model; Molecular ...
... Theories of covalent bonding: Lewis Model; Orbital Hybridization Model; Molecular ...
Chapter 7 Hydrosilylation of Carbon
... to the participation of π-benzylic palladium intermediates [1, 2]. It is known that bisphosphine-palladium complexes are catalytically much less active than monophosphine-palladium complexes and hence asymmetric synthesis has been attempted by use of chiral monodentate phosphine ligands. In the first ...
... to the participation of π-benzylic palladium intermediates [1, 2]. It is known that bisphosphine-palladium complexes are catalytically much less active than monophosphine-palladium complexes and hence asymmetric synthesis has been attempted by use of chiral monodentate phosphine ligands. In the first ...
+ H 2 O(l )
... 2) Balance all elements except “H” and “O”. 3) Balance the “O’s” by adding water, H2O. 4) Balance the “H’s” by adding hydrogen ions, H+. 5) Balance the charges by adding electrons. If necessary, multiply one or both half reactions by an integer to equalize the number of electrons transferred in the ...
... 2) Balance all elements except “H” and “O”. 3) Balance the “O’s” by adding water, H2O. 4) Balance the “H’s” by adding hydrogen ions, H+. 5) Balance the charges by adding electrons. If necessary, multiply one or both half reactions by an integer to equalize the number of electrons transferred in the ...
Enantioselective synthesis

Enantioselective synthesis, also called chiral synthesis or asymmetric synthesis, is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer.Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity.