ISOMERISM - A general survey
... • the two different forms are known as OPTICAL ISOMERS or ENANTIOMERS and occur when molecules have a CHIRAL centre. • to find such a centre, look for an ASYMMETRIC CARBON ATOM ... one with four different atoms, or arranged tetrahedrally around it. ...
... • the two different forms are known as OPTICAL ISOMERS or ENANTIOMERS and occur when molecules have a CHIRAL centre. • to find such a centre, look for an ASYMMETRIC CARBON ATOM ... one with four different atoms, or arranged tetrahedrally around it. ...
Notes 07 Organometallic Compounds with notes
... R2CuLi + R’-X R-R’ + RCu + LiX Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Substitution. Creation of new C-C bonds. 1 alkyl iodides are best, otherwise an elimination reaction can occur. The R’ group in the halide can be aryl or vinyl. The R group of the cuprate can be aryl or vinyl. Although the mechanism looks ...
... R2CuLi + R’-X R-R’ + RCu + LiX Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Substitution. Creation of new C-C bonds. 1 alkyl iodides are best, otherwise an elimination reaction can occur. The R’ group in the halide can be aryl or vinyl. The R group of the cuprate can be aryl or vinyl. Although the mechanism looks ...
Hydrothermal Reactions from Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate to Phenol
... that the yield of phenol dramatically increases. This experiment confirms our mechanisms and may also provide industrial possibilities. Our study on the hydrothermal reactions from sodium hydrogen carbonate to phenol makes it possible to form prebiotic organic molecules based on carbonate under mild ...
... that the yield of phenol dramatically increases. This experiment confirms our mechanisms and may also provide industrial possibilities. Our study on the hydrothermal reactions from sodium hydrogen carbonate to phenol makes it possible to form prebiotic organic molecules based on carbonate under mild ...
Acyl Anions Derived from Enol Ethers
... The normal disconnection pattern of a carboxylic acid with a Grignard reagent and carbon dioxide as SEs (path a) and a disconnection leading to a carboxyl synthon with an "unnatural" negative charge (path b). Cyanide ion can act as an SE of a negatively charged carboxyl synthon. Its reaction with R ...
... The normal disconnection pattern of a carboxylic acid with a Grignard reagent and carbon dioxide as SEs (path a) and a disconnection leading to a carboxyl synthon with an "unnatural" negative charge (path b). Cyanide ion can act as an SE of a negatively charged carboxyl synthon. Its reaction with R ...
practice test
... Outline a chemical test that you could do to determine which compound you have. Be sure to include the reaction conditions, what you would expect to observe qualitatively from each of the two possible compounds and the structural formulas and names of any reactants and products.(6 marks) ...
... Outline a chemical test that you could do to determine which compound you have. Be sure to include the reaction conditions, what you would expect to observe qualitatively from each of the two possible compounds and the structural formulas and names of any reactants and products.(6 marks) ...
Organometallic Compounds: Alkyllithium Reagent
... not possible to prepare a Grignard reagent from an organic group that contains an acidic hydrogen (any hydrogen more acidic than the hydrogen atoms of an alkane or alkene). ...
... not possible to prepare a Grignard reagent from an organic group that contains an acidic hydrogen (any hydrogen more acidic than the hydrogen atoms of an alkane or alkene). ...
Lewis base-assisted Lewis acid-catalyzed selective
... of 1‐phenylethanol—the byproduct in the propylene oxide synthesis from ethylbenzene hydroperoxide [2]. Therefore, this reaction has been extensively studied [3–8]. Organic chemists often use 1‐arylethanol as a substrate to synthesize 1‐aryleth‐ ylene, which is a useful synthon ...
... of 1‐phenylethanol—the byproduct in the propylene oxide synthesis from ethylbenzene hydroperoxide [2]. Therefore, this reaction has been extensively studied [3–8]. Organic chemists often use 1‐arylethanol as a substrate to synthesize 1‐aryleth‐ ylene, which is a useful synthon ...
anna-chrobok-silesian-university-of-technology
... - Diels-Alder reaction, - oxidation of alcohols and ketones. IONIC LIQUIDS as homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts Recycling of ionic liquids prevents them from: - ending up in the aquatic environment, - release into the atmosphere (low volatility). ...
... - Diels-Alder reaction, - oxidation of alcohols and ketones. IONIC LIQUIDS as homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts Recycling of ionic liquids prevents them from: - ending up in the aquatic environment, - release into the atmosphere (low volatility). ...
... Green Technology has been mentioned in the past few years due to the environmental problems are still increasing as a result of the environmental care products demand increased. The biological processes have thus been developed for any manufacturing steps. Alkyl glycosides are classified as a non-io ...
Exam 2 review sheet
... reactions of carboxylic acids: to acyl chlorides, to acid anhydrides, to esters/lactones (mechanism for Fischer esterification); to amides: direct addition of carboxylic acid plus amine is usually unproductive; relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives: acid chloride > anhydride > ester > a ...
... reactions of carboxylic acids: to acyl chlorides, to acid anhydrides, to esters/lactones (mechanism for Fischer esterification); to amides: direct addition of carboxylic acid plus amine is usually unproductive; relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives: acid chloride > anhydride > ester > a ...
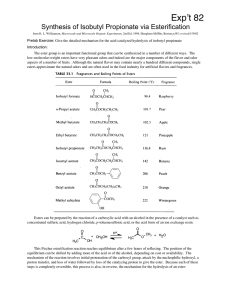
Synthesis of Isobutyl Propionate via Esterification
... we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester ...
... we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester ...
Reactions and Balancing
... Some helpful hints for balancing equations: Take one element at a time, working left to right except for H and O. Metals, then nonmetals are a good way, too. Save H for next to last, and O until last. IF everything balances except for O, and there is no way to balance O with a whole number, doub ...
... Some helpful hints for balancing equations: Take one element at a time, working left to right except for H and O. Metals, then nonmetals are a good way, too. Save H for next to last, and O until last. IF everything balances except for O, and there is no way to balance O with a whole number, doub ...
Synthesis of hetero cyclic compounds pyrazole and pyridiazine from
... Iraqi National Journal of Chemistry 2015; 15 (4) carbonyl group at (1738cm-1)to(1646 cm-1) and appearance band at(3369cm-1) stretching band of NH. The 1H NMR (DMSO_d6) of compound [2] : 6.5(d, 4H , CH ...
... Iraqi National Journal of Chemistry 2015; 15 (4) carbonyl group at (1738cm-1)to(1646 cm-1) and appearance band at(3369cm-1) stretching band of NH. The 1H NMR (DMSO_d6) of compound [2] : 6.5(d, 4H , CH ...
Full Text - Iraqi National Journal of Chemistry
... Iraqi National Journal of Chemistry 2015; 15 (4) carbonyl group at (1738cm-1)to(1646 cm-1) and appearance band at(3369cm-1) stretching band of NH. The 1H NMR (DMSO_d6) of compound [2] : 6.5(d, 4H , CH ...
... Iraqi National Journal of Chemistry 2015; 15 (4) carbonyl group at (1738cm-1)to(1646 cm-1) and appearance band at(3369cm-1) stretching band of NH. The 1H NMR (DMSO_d6) of compound [2] : 6.5(d, 4H , CH ...
Study Guide for Exam 2-‐ Aldehydes and Ketones
... forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to ...
... forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to ...
Example - Request a Spot account
... 1. identity of each reactant & product involved in the reaction 2. phase of each reactant and product involved in the reaction (i.e. solid (s), liquid (l) or gas (g)) 3. relative quantity of each reactant and product involved in the reaction (the coefficients!) 4. relative molar quantity of each rea ...
... 1. identity of each reactant & product involved in the reaction 2. phase of each reactant and product involved in the reaction (i.e. solid (s), liquid (l) or gas (g)) 3. relative quantity of each reactant and product involved in the reaction (the coefficients!) 4. relative molar quantity of each rea ...
Reductive etherification of substituted cyclohexanones with
... having bulky substituents at the 4-position, using secondary alcohols as reductants. The zeolite appears to be active for both acid-catalysed conversion of the ketones to (hemi)acetals and consecutive Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley (MPV)-type hydride transfer to yield ethers. Until now two catalysts were ...
... having bulky substituents at the 4-position, using secondary alcohols as reductants. The zeolite appears to be active for both acid-catalysed conversion of the ketones to (hemi)acetals and consecutive Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley (MPV)-type hydride transfer to yield ethers. Until now two catalysts were ...
Designing Organic Synthesis - Department of Chemistry, IIT Bombay
... History Simple targets were considered in early days Theses simple targets were synthesized by often starting with compounds which are closely related to products These became impractical when the targets became more complex To tackle this, higher level of intellectual planning and skill are requir ...
... History Simple targets were considered in early days Theses simple targets were synthesized by often starting with compounds which are closely related to products These became impractical when the targets became more complex To tackle this, higher level of intellectual planning and skill are requir ...
Chapter 12 –Part 2 Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds with
... l An ether solvent is used because it forms a complex with the ...
... l An ether solvent is used because it forms a complex with the ...
Jordan University of Science and Technology
... This course deals primarily with the basic principles of organic chemistry in order to understand the structures and reactivity of organic molecules This course also deals mainly with the constitution and properties of the different classes of organic compounds, with considerable attention to stereo ...
... This course deals primarily with the basic principles of organic chemistry in order to understand the structures and reactivity of organic molecules This course also deals mainly with the constitution and properties of the different classes of organic compounds, with considerable attention to stereo ...
Contents - Personal WWW Pages
... Tolman’s rules were developed in the early 1970s, based on the observation that the majority of well characterised transition metal organometallic complexes have either 16 or 18 valence electrons (although there are now plenty of exceptions, especially in the early transition elements) and this obse ...
... Tolman’s rules were developed in the early 1970s, based on the observation that the majority of well characterised transition metal organometallic complexes have either 16 or 18 valence electrons (although there are now plenty of exceptions, especially in the early transition elements) and this obse ...
Enantioselective synthesis

Enantioselective synthesis, also called chiral synthesis or asymmetric synthesis, is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer.Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity.