10.5 Carbonyl Compounds (a) describe: (i) the
... (i) the formation of aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols respectively using Cr2O72-/H+ (ii) the reduction of aldehydes and ketones e.g. using NaBH4 (b) describe the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of hydrogen cyanide with aldehydes and ketones (c) describe the use ...
... (i) the formation of aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols respectively using Cr2O72-/H+ (ii) the reduction of aldehydes and ketones e.g. using NaBH4 (b) describe the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of hydrogen cyanide with aldehydes and ketones (c) describe the use ...
CH 23 HW
... 4. Why metallic behavior (prevalence of ionic bonding and basic oxides) of transition elements decreases as oxidation state increases; how valence-state electronegativity explains transition metal atoms in oxoanions (§23.1) 5. Why many transition metal compounds are colored and paramagnetic (§23.1) ...
... 4. Why metallic behavior (prevalence of ionic bonding and basic oxides) of transition elements decreases as oxidation state increases; how valence-state electronegativity explains transition metal atoms in oxoanions (§23.1) 5. Why many transition metal compounds are colored and paramagnetic (§23.1) ...
Document
... The results of an ESI-MS study of the metal cation complexation properties of an unusual molecular box, 4, are reported along with the corresponding results obtained for another bis(diazacrown) host, 2, that serves as a model compound for comparison. Both host systems bind selectively to Li+ and Na+ ...
... The results of an ESI-MS study of the metal cation complexation properties of an unusual molecular box, 4, are reported along with the corresponding results obtained for another bis(diazacrown) host, 2, that serves as a model compound for comparison. Both host systems bind selectively to Li+ and Na+ ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
... Even though Sc and Zn are place in the first row transition element series, they are not truly transitional element; they do some limited proprieties similar to that of transitional elements such as high melting and boiling point, Sc has melting point of 2748k, Zinc behave atypically due it having ...
... Even though Sc and Zn are place in the first row transition element series, they are not truly transitional element; they do some limited proprieties similar to that of transitional elements such as high melting and boiling point, Sc has melting point of 2748k, Zinc behave atypically due it having ...
6. d and f-Block Elements and Coordination Chemistry
... to move to soluble coordination compounds is a deliberate one. The study of the transition metals in solids have been dominated by solid-state physicists, and is closely tied to important technical advances, such as the development of the first Ruby lasers. Chemists have been more involved in studyi ...
... to move to soluble coordination compounds is a deliberate one. The study of the transition metals in solids have been dominated by solid-state physicists, and is closely tied to important technical advances, such as the development of the first Ruby lasers. Chemists have been more involved in studyi ...
AP Reaction Rules
... Complex Ion Formation: a substrate gets surrounded by ligands Substrate is electron-deficient (Lewis acid) – like BF3 or transition metal Ligands are electron rich (Lewis base) – like NH3 or negative polyatomic ion Typically there is an excess of ligands (“excess”, large volume of “concentrated”) Ty ...
... Complex Ion Formation: a substrate gets surrounded by ligands Substrate is electron-deficient (Lewis acid) – like BF3 or transition metal Ligands are electron rich (Lewis base) – like NH3 or negative polyatomic ion Typically there is an excess of ligands (“excess”, large volume of “concentrated”) Ty ...
Isomerism of coordination compounds
... Isomerism of coordination compounds Structural isomerism Ionization isomerism When ligands are exchanged in a complex by the counter-ion, it is called ionization isomerism. e.g. [Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Br2 and [Pt(NH3)4Br2]Cl Linkage isomerism A ligand connects with the central metal atom through different ato ...
... Isomerism of coordination compounds Structural isomerism Ionization isomerism When ligands are exchanged in a complex by the counter-ion, it is called ionization isomerism. e.g. [Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Br2 and [Pt(NH3)4Br2]Cl Linkage isomerism A ligand connects with the central metal atom through different ato ...
one of the tasks (coordination chemistry)
... • The higher the oxidation state of a metal, the more stable the complexes it forms with a given ligand. The ligand-metal bond strength is higher for higher oxidation states of the metal. Sets of examples that illustrate the proposition are 16 and 17; 25 and 26; 27 and 28. • For a given metal ion, t ...
... • The higher the oxidation state of a metal, the more stable the complexes it forms with a given ligand. The ligand-metal bond strength is higher for higher oxidation states of the metal. Sets of examples that illustrate the proposition are 16 and 17; 25 and 26; 27 and 28. • For a given metal ion, t ...
Document
... LFT – application of MO theory The valence orbitals on the metal and ligand are used to form SALCs Using empirical energy and overlap considerations – the relative energies of the MOs are estimated ...
... LFT – application of MO theory The valence orbitals on the metal and ligand are used to form SALCs Using empirical energy and overlap considerations – the relative energies of the MOs are estimated ...
Transition Metals
... • Geometrical isomerism (cis-trans): Atoms or groups of atoms can assume different positions around a rigid ring. Pt(NH3)2Cl2 • Optical isomerism: the isomers have opposite ...
... • Geometrical isomerism (cis-trans): Atoms or groups of atoms can assume different positions around a rigid ring. Pt(NH3)2Cl2 • Optical isomerism: the isomers have opposite ...
UJDIPa - The Vital Chemist
... If β – large ∆G = large and – Ve, therefore the formation of ML6n+ will be favoring than the M(H2O)6n+ and therefore M(H2O)6n+ is thermodynamically unstable, however, if β = small, ∆G = small and +ve, favouring formation of M(H2O)6n+. This is said to be thermodynamically stable. Note also that a com ...
... If β – large ∆G = large and – Ve, therefore the formation of ML6n+ will be favoring than the M(H2O)6n+ and therefore M(H2O)6n+ is thermodynamically unstable, however, if β = small, ∆G = small and +ve, favouring formation of M(H2O)6n+. This is said to be thermodynamically stable. Note also that a com ...
Determination of Transition Metals by Ion Chromatography
... eluent. Note that both ferrous and ferric ions can be determined. Since the ferrous ion is easily oxidized to ferric, oxygen must be removed from the eluent by degassing. To remove oxygen from the analytical column, pump a solution of 0.1 M sodium sulfite (12.6 g/L Na2SO3) through the column for 2 h ...
... eluent. Note that both ferrous and ferric ions can be determined. Since the ferrous ion is easily oxidized to ferric, oxygen must be removed from the eluent by degassing. To remove oxygen from the analytical column, pump a solution of 0.1 M sodium sulfite (12.6 g/L Na2SO3) through the column for 2 h ...
Polymerization of Olefins: An Outlook After 50
... Aluminum alkyls are reducing agents, and therefore a reduction Ti(IV) to Ti(III) inevitably takes place if the two components are brought together. ...
... Aluminum alkyls are reducing agents, and therefore a reduction Ti(IV) to Ti(III) inevitably takes place if the two components are brought together. ...
Chapter_23_Transition_Metal_Chemistry
... ethylenediamine. Because there are three chloride ions each with a -1 charge, the cation is [Cr(en)3]3+. The en ligands are neutral so the oxidation number of Cr must be +3. Because there are three en groups present and the name of the ligand already contains di (rule 4), the compound is called tris ...
... ethylenediamine. Because there are three chloride ions each with a -1 charge, the cation is [Cr(en)3]3+. The en ligands are neutral so the oxidation number of Cr must be +3. Because there are three en groups present and the name of the ligand already contains di (rule 4), the compound is called tris ...
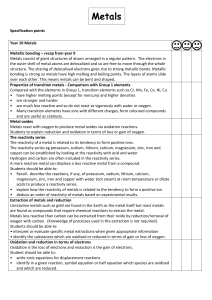
Metals s
... The reactivity series eg potassium, sodium, lithium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, iron and copper can be established by looking at the reactivity with acid and water Hydrogen and carbon are often included in the reactivity series. A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from a compound ...
... The reactivity series eg potassium, sodium, lithium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, iron and copper can be established by looking at the reactivity with acid and water Hydrogen and carbon are often included in the reactivity series. A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from a compound ...
Slide 1 - Alfred State College intranet site
... Carbonyl and Carboxyl Compounds III. Interesting Carbonyl Compounds Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
... Carbonyl and Carboxyl Compounds III. Interesting Carbonyl Compounds Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
Specific borane electron counting I - The School of Life Sciences at
... it is normally a Lewis base ligand (L) that provides the pair of electrons for the MrL bond in the vast majority of complexes, with there being relatively few well-defined complexes where the ligand is a Lewis acid (Z). In principle, one would expect that trivalent BX3 derivatives should be capable ...
... it is normally a Lewis base ligand (L) that provides the pair of electrons for the MrL bond in the vast majority of complexes, with there being relatively few well-defined complexes where the ligand is a Lewis acid (Z). In principle, one would expect that trivalent BX3 derivatives should be capable ...
Ch. 3. KINETIC VS. EQUILIBRIUM MODELING
... 4-4. Geometry of Common Inorganic Ligands All depends on the radius ratio (p.89) Plan triangular triangle (NO3-, CO3-, BO3-) ...
... 4-4. Geometry of Common Inorganic Ligands All depends on the radius ratio (p.89) Plan triangular triangle (NO3-, CO3-, BO3-) ...
Crystal Field Theory
... with metal ions in the center of the cube. The ligands occupy the four alternate corners of the cube leaving the rest four corners empty. The two ‘e’ orbitals point to the center of the face of the cube while the three ‘t2’ orbitals point to the center of the edges of the cube. Therefore, the angle ...
... with metal ions in the center of the cube. The ligands occupy the four alternate corners of the cube leaving the rest four corners empty. The two ‘e’ orbitals point to the center of the face of the cube while the three ‘t2’ orbitals point to the center of the edges of the cube. Therefore, the angle ...
Unidentate, Bidentate and Multidentate Ligands
... In the examples we've already looked at, each ligand only forms one bond with the central metal ion to give the complex ion. Such a ligand is said to be unidentate. That means literally that it only has one tooth! It only has one pair of electrons that it can use to bond to the metal - any other lon ...
... In the examples we've already looked at, each ligand only forms one bond with the central metal ion to give the complex ion. Such a ligand is said to be unidentate. That means literally that it only has one tooth! It only has one pair of electrons that it can use to bond to the metal - any other lon ...
Practice Questions for Chapters 1-8 CHEM 4000A
... A few of you also mentioned : Dess Martin oxidations (contain an iodine atom in a high oxidation state) or TPAP/NMO (catalytic tetrapropylammonium perruthenate = Pr4N+ RuO4- in the presence of stoichiometric N-methylmorpholine oxide) in your assignments. Which of your two examples is greener? Ex ...
... A few of you also mentioned : Dess Martin oxidations (contain an iodine atom in a high oxidation state) or TPAP/NMO (catalytic tetrapropylammonium perruthenate = Pr4N+ RuO4- in the presence of stoichiometric N-methylmorpholine oxide) in your assignments. Which of your two examples is greener? Ex ...
Metal carbonyl

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel carbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometalic complexes.Metal carbonyls are toxic by skin contact, inhalation or ingestion, in part because of their ability to carbonylate hemoglobin to give carboxyhemoglobin, which prevents the binding of O2.