Transition Metals - wellswaysciences
... • In each of these the mechanism is a surface reaction where reactant molecules are adsorbed onto the catalyst surface using the available partially filled d orbitals to form weak temporary bonds with the metal. • This weakens the original bonds between the reactant molecules. New bonds form between ...
... • In each of these the mechanism is a surface reaction where reactant molecules are adsorbed onto the catalyst surface using the available partially filled d orbitals to form weak temporary bonds with the metal. • This weakens the original bonds between the reactant molecules. New bonds form between ...
Reactions of Organometallic Complexes with Nucleophiles
... DGM Rules (these rules must be followed in order) Rule 1 – Even before Odd: Nucleophilic attack occurs preferentially at even polyenes ...
... DGM Rules (these rules must be followed in order) Rule 1 – Even before Odd: Nucleophilic attack occurs preferentially at even polyenes ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... COMPOUNDS. AS A RESULT, THE HAVE HIGHER BOILING POINTS THAN ALKANES WITH SIMILAR MOLECULAR WEIGHTS. HOWEVER, BECAUSE THEY DON’T HYDROGEN BOND WITH EACH OTHER, THEY HAVE LOWER BOILING POINTS THAT ALCOHOLS. • IN A SERIES OF COMPOUNDS OF SIMILAR MOLECULAR WEIGHTS, THEIR BOILING POINTS ARE AS ...
... COMPOUNDS. AS A RESULT, THE HAVE HIGHER BOILING POINTS THAN ALKANES WITH SIMILAR MOLECULAR WEIGHTS. HOWEVER, BECAUSE THEY DON’T HYDROGEN BOND WITH EACH OTHER, THEY HAVE LOWER BOILING POINTS THAT ALCOHOLS. • IN A SERIES OF COMPOUNDS OF SIMILAR MOLECULAR WEIGHTS, THEIR BOILING POINTS ARE AS ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with ...
... The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with ...
... The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... Most of the carbocation reacts to give the 1,2 product because of the smaller Ea leading to the 1,2 product. This is true at all temperatures. At higher temperatures the reverse reactions occur leading from the 1,2 or 1,4 product to the carbocation. Note that the 1,2 product is more easily converte ...
... Most of the carbocation reacts to give the 1,2 product because of the smaller Ea leading to the 1,2 product. This is true at all temperatures. At higher temperatures the reverse reactions occur leading from the 1,2 or 1,4 product to the carbocation. Note that the 1,2 product is more easily converte ...
Studies of stability constant on ternary chelates of bivalent
... present in its structure, which can bind to metal ions present in human body.[4] Metal complexes of drugs are found to be more potent than parent drugs.[5] Chemistry of drugs attracts many researchers because of its applications in medicinal chemistry. Interesting results have been reported earlier ...
... present in its structure, which can bind to metal ions present in human body.[4] Metal complexes of drugs are found to be more potent than parent drugs.[5] Chemistry of drugs attracts many researchers because of its applications in medicinal chemistry. Interesting results have been reported earlier ...
Answers to For Review Questions from the Textbook
... different. The tetrahedrally oriented ligands point differently in relationship to the d-orbitals than do the octahedrally oriented ligands. Plus, we have more ligands in an octahedral complex. See Figure 21.27 for the tetrahedral crystal field diagram. Notice that the orbitals are reverse of that i ...
... different. The tetrahedrally oriented ligands point differently in relationship to the d-orbitals than do the octahedrally oriented ligands. Plus, we have more ligands in an octahedral complex. See Figure 21.27 for the tetrahedral crystal field diagram. Notice that the orbitals are reverse of that i ...
Pptrajendraco 3d Elements - GCG-42
... [Co(NH3)5Cl]Br(aq) + AgNO3(aq) [Co(NH3)5Cl]NO3(aq) + AgBr(s) [Co(NH3)5Br]Cl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) [Co(NH3)5Br]NO3(aq) + AgCl(aq) ...
... [Co(NH3)5Cl]Br(aq) + AgNO3(aq) [Co(NH3)5Cl]NO3(aq) + AgBr(s) [Co(NH3)5Br]Cl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) [Co(NH3)5Br]NO3(aq) + AgCl(aq) ...
Ch 12- Transition Metales and coordination compound
... molecular compounds. It is important to recognize common molecules, to remember that they are neutral, and to know the charges on both monoatomic and polyatomic ions. The sum of charges on the metal ion and the ligands must equal the net charge on the complex. ...
... molecular compounds. It is important to recognize common molecules, to remember that they are neutral, and to know the charges on both monoatomic and polyatomic ions. The sum of charges on the metal ion and the ligands must equal the net charge on the complex. ...
Crystal field theory (II) Octahedral complexes and Jahn
... Square planar complexes for d8 configurations: Jahn‐Teller distortion leads to tetragonal distortion of the octahedron. The extreme of tetragonal distortion is the loss of the axial ligands, and the formation of a square‐planar complex. As there is no ligand on one z‐axis the d orbitals split fur ...
... Square planar complexes for d8 configurations: Jahn‐Teller distortion leads to tetragonal distortion of the octahedron. The extreme of tetragonal distortion is the loss of the axial ligands, and the formation of a square‐planar complex. As there is no ligand on one z‐axis the d orbitals split fur ...
Outer-sphere Ligand to Ligand Charge Transfer of Metal Complexes
... tical composition [Ni(tim)][M(mnt)2] precipitated. The black colour is caused essentially by a very broad and intense long-wavelength band: M = Ni, A,,. ...
... tical composition [Ni(tim)][M(mnt)2] precipitated. The black colour is caused essentially by a very broad and intense long-wavelength band: M = Ni, A,,. ...
Complex forming reactions and complexometry Complex forming
... coordination number (mono-, di-, tri-, etc.), and then comes the name of the ligand (an –o tag is also appended to it if the ligand itself has charge), plus the name of the metal ion with its valence state indicated. Examples: [Ag(NH3)2]+ [Ni(H2O)6]2+ ...
... coordination number (mono-, di-, tri-, etc.), and then comes the name of the ligand (an –o tag is also appended to it if the ligand itself has charge), plus the name of the metal ion with its valence state indicated. Examples: [Ag(NH3)2]+ [Ni(H2O)6]2+ ...
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY ESSENTIALS
... Associative mechanisms for metals in octahedral fields are difficult stereochemically (due to ligand crowding); therefore, they are rare for all but the largest metal ion centers. The associative mechanism is well known and preferred for fourcoordinate square-planar complexes. Pure dissociative mech ...
... Associative mechanisms for metals in octahedral fields are difficult stereochemically (due to ligand crowding); therefore, they are rare for all but the largest metal ion centers. The associative mechanism is well known and preferred for fourcoordinate square-planar complexes. Pure dissociative mech ...
Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing a Pyridyl-Supported Pyrazolyl
... Na2CO3, or Et3N did not produce the desired Ru(II) complexes of type 2. Unexpectedly, compound 1 reacted with 1.0 equiv of RuCl3 · 3H2O and carbon monoxide in ethylene glycol at 190 °C formed complex 2 in 40% isolated yield under the optimized conditions13 (Scheme 1). When the n-heptyl group in the ...
... Na2CO3, or Et3N did not produce the desired Ru(II) complexes of type 2. Unexpectedly, compound 1 reacted with 1.0 equiv of RuCl3 · 3H2O and carbon monoxide in ethylene glycol at 190 °C formed complex 2 in 40% isolated yield under the optimized conditions13 (Scheme 1). When the n-heptyl group in the ...
Worked Examples: Chapter 8
... The three complex ions [Mn(CN)6]5-, [Mn(CN)6]4-, and [Mn(CN)6]3have all been synthesized and are all low-spin octahedral complexes. For each complex ion, determine the oxidation number of Mn, the configuration of the d-electrons (how many t2g and how many eg), and the number of unpaired electrons. ...
... The three complex ions [Mn(CN)6]5-, [Mn(CN)6]4-, and [Mn(CN)6]3have all been synthesized and are all low-spin octahedral complexes. For each complex ion, determine the oxidation number of Mn, the configuration of the d-electrons (how many t2g and how many eg), and the number of unpaired electrons. ...
Assignment 5 (key)
... environments – two COs are in axial positions, and three CO’s occupy equatorial positions. CO axial equatorial OC ...
... environments – two COs are in axial positions, and three CO’s occupy equatorial positions. CO axial equatorial OC ...
52142_present
... phenolic-OH group did not form H-bonding in ligands L2 and L3 where it is observed after 3400 cm-1. Furthers, the existence of two bands at 3278 cm-1 (L1) and 3227 cm-1 (L4) may be attributed to ν(OH)enolic in H-bond bonding with azomethine group. The lower shift for these two bands than the normal ...
... phenolic-OH group did not form H-bonding in ligands L2 and L3 where it is observed after 3400 cm-1. Furthers, the existence of two bands at 3278 cm-1 (L1) and 3227 cm-1 (L4) may be attributed to ν(OH)enolic in H-bond bonding with azomethine group. The lower shift for these two bands than the normal ...
Pi-Acid handout - U of L Class Index
... Unlike CO, metal coordination can either raise or lower n(CN) (2000-2200 cm-1) because the HOMO of CNR is much more antibonding than that of CO. ...
... Unlike CO, metal coordination can either raise or lower n(CN) (2000-2200 cm-1) because the HOMO of CNR is much more antibonding than that of CO. ...
No Slide Title
... • Primary amines and carbonyls form Imines (also called Schiff base) – examples include, hydrazones, phenylhydrazones, 2,4dinitrophenylhydrazones, semicarbazones, tosylhydrazones, oximes ...
... • Primary amines and carbonyls form Imines (also called Schiff base) – examples include, hydrazones, phenylhydrazones, 2,4dinitrophenylhydrazones, semicarbazones, tosylhydrazones, oximes ...
22-2 Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... • Ethanol and CO2 are produced by yeast when they ferment sugars, such as those in grapes and bread dough. • To name alcohols, use a number or numbers, if needed to designate the location of the –OH groups and then say the rootword for the number of carbons followed by –ol. ...
... • Ethanol and CO2 are produced by yeast when they ferment sugars, such as those in grapes and bread dough. • To name alcohols, use a number or numbers, if needed to designate the location of the –OH groups and then say the rootword for the number of carbons followed by –ol. ...
Carbonyl Compounds
... Esters do not have any free OH groups and therefore they are unable to form hydrogen bonds, either with other ester molecules or with water. This means that: the boiling points of esters are lower than the boiling points of carboxylic acids of similar Mr esters are almost insoluble in water Este ...
... Esters do not have any free OH groups and therefore they are unable to form hydrogen bonds, either with other ester molecules or with water. This means that: the boiling points of esters are lower than the boiling points of carboxylic acids of similar Mr esters are almost insoluble in water Este ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... • Common names for ketones give the names of the two alkyl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon followed by the word ketone. • Ketones are named systematically by replacing the final -e of the alkane name with -one. The numbering of the chain begins at the end nearest the carbonyl group. The locati ...
... • Common names for ketones give the names of the two alkyl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon followed by the word ketone. • Ketones are named systematically by replacing the final -e of the alkane name with -one. The numbering of the chain begins at the end nearest the carbonyl group. The locati ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-ISSN: 2278-5736.
... The IR spectral data of the ligand and the complexes are given in table-3. Comparison of the IR spectrum of the free ligand and the complexes reveals that C=N stretching has shifted from 1590cm-1 to 1612cm-1. The upward shift in the C=N stretching frequency indicates the formation of coordinate cova ...
... The IR spectral data of the ligand and the complexes are given in table-3. Comparison of the IR spectrum of the free ligand and the complexes reveals that C=N stretching has shifted from 1590cm-1 to 1612cm-1. The upward shift in the C=N stretching frequency indicates the formation of coordinate cova ...
decanuclear mixed-valence manganese(ii, iii) isobutyrate cluster
... (SMM). Application of flexible bulky organic ligands can lead to formation of coordination clusters with highnuclearity [1]. This type of complexes containing mixed-valence ions could exhibit magnetic properties. The new neutral beetle-like decanuclear manganese compound [Mn10O2(O2CCH(CH3)2)18((HO2C ...
... (SMM). Application of flexible bulky organic ligands can lead to formation of coordination clusters with highnuclearity [1]. This type of complexes containing mixed-valence ions could exhibit magnetic properties. The new neutral beetle-like decanuclear manganese compound [Mn10O2(O2CCH(CH3)2)18((HO2C ...
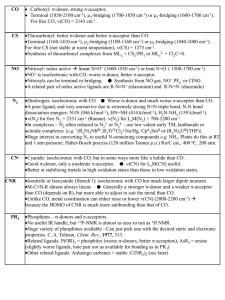
Metal carbonyl

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel carbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometalic complexes.Metal carbonyls are toxic by skin contact, inhalation or ingestion, in part because of their ability to carbonylate hemoglobin to give carboxyhemoglobin, which prevents the binding of O2.