Human Genetic Disorders
... have a baby girl. What information about the parents would you want to know? How would this help determine whether the baby will have hemophilia? ...
... have a baby girl. What information about the parents would you want to know? How would this help determine whether the baby will have hemophilia? ...
Biochemistry - Circle of Docs
... 4. Beta 1,4 bonds are found in a. Lactose 5. How many ATP’s are produced anaerobically a. 2 6. Which is a pyrimidine a. KING TUCK 7. Which is a secondary structure a. Sequence of amino acids b. Alpha helix c. Myoglobin d. Hemoglobin 8. Which carries the most cholesterol a. HDL b. LDL c. VLDL d. Chyl ...
... 4. Beta 1,4 bonds are found in a. Lactose 5. How many ATP’s are produced anaerobically a. 2 6. Which is a pyrimidine a. KING TUCK 7. Which is a secondary structure a. Sequence of amino acids b. Alpha helix c. Myoglobin d. Hemoglobin 8. Which carries the most cholesterol a. HDL b. LDL c. VLDL d. Chyl ...
Chapter 12 College Prep Biology
... Homozygous b/c the other terms involve contrasting alleles for a trait. A homozygous individual possesses two identical alleles for a trait. Red blood cells, phenylalanine, oxygen deprivation, hemoglobin. Phenylalanine b/c the other terms all relate to sickle cell anemia. Phenylalanine is the amin ...
... Homozygous b/c the other terms involve contrasting alleles for a trait. A homozygous individual possesses two identical alleles for a trait. Red blood cells, phenylalanine, oxygen deprivation, hemoglobin. Phenylalanine b/c the other terms all relate to sickle cell anemia. Phenylalanine is the amin ...
DNA: The Genetic Material
... sex-cell mutation. Answer: A mutagen in a body cell becomes part of the of the genetic sequence in that cell and in future daughter cells. The cell may die or simply not perform its normal function. These mutations are not passed on to the next generation. When mutations occur in sex cells, they wil ...
... sex-cell mutation. Answer: A mutagen in a body cell becomes part of the of the genetic sequence in that cell and in future daughter cells. The cell may die or simply not perform its normal function. These mutations are not passed on to the next generation. When mutations occur in sex cells, they wil ...
amino-terminal
... How to calculate the number of amino acids in a protein • We can calculate the approximate number of amino • acid residues in a simple protein containing no other chemical constituents by dividing its molecular weight by 110. • Although the average molecular weight of the 20 common amino acids is a ...
... How to calculate the number of amino acids in a protein • We can calculate the approximate number of amino • acid residues in a simple protein containing no other chemical constituents by dividing its molecular weight by 110. • Although the average molecular weight of the 20 common amino acids is a ...
ch 10 Human GeneticsTest Qustions Study Guide
... Write these answers on a separate paper. 1. Y/N Can a pedigree be used on each of the following to a. Determine whether an allele is dominant or recessive. b. Show how a trait is passed from one generation to the next. c. Determine whether a trait is inherited. 2. In a pedigree, a circle represent a ...
... Write these answers on a separate paper. 1. Y/N Can a pedigree be used on each of the following to a. Determine whether an allele is dominant or recessive. b. Show how a trait is passed from one generation to the next. c. Determine whether a trait is inherited. 2. In a pedigree, a circle represent a ...
metabolism of amino acids
... 2) Taking a protein rich diet- aa intake exceeds the body’s need for prot- degraded 3) During starvation or in uncontrolled DM – when carb cannot be utilized, proteins are used as fuel ...
... 2) Taking a protein rich diet- aa intake exceeds the body’s need for prot- degraded 3) During starvation or in uncontrolled DM – when carb cannot be utilized, proteins are used as fuel ...
Studying DNA replication to find smarter cancer drugs
... when conditions are appropriate. For example, a G1 checkpoint blocks entry into S phase if DNA is damaged, while an intra-S checkpoint blocks the initiation of new replication forks if existing forks have stalled (Figure 4). The combined activity of CDKs and Geminin ensure that once the cell has ent ...
... when conditions are appropriate. For example, a G1 checkpoint blocks entry into S phase if DNA is damaged, while an intra-S checkpoint blocks the initiation of new replication forks if existing forks have stalled (Figure 4). The combined activity of CDKs and Geminin ensure that once the cell has ent ...
Gene Section SH3GL2 (SH3-domain GRB2-like 2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Rat germinal centre kinse-like kinase (rGLK), a serine/threonine cytosolic kinase, interacted with SH3GL2. rGLK modulated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity by phosphorylation and binds to the SH3 domain of SH3GL2 through a C-terminal proline rich domain. Coexpression of rGLK and full length SH3 ...
... Rat germinal centre kinse-like kinase (rGLK), a serine/threonine cytosolic kinase, interacted with SH3GL2. rGLK modulated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity by phosphorylation and binds to the SH3 domain of SH3GL2 through a C-terminal proline rich domain. Coexpression of rGLK and full length SH3 ...
DNA replication and PCR ppt
... The bases face inward and pair in a highly specific fashion with bases in the other chain A only with T, G only with C Because of this pairing – each strand is complementary to the other 5’ ACGTC 3’ 3’ TGCAG 5’ Thus DNA is double stranded ...
... The bases face inward and pair in a highly specific fashion with bases in the other chain A only with T, G only with C Because of this pairing – each strand is complementary to the other 5’ ACGTC 3’ 3’ TGCAG 5’ Thus DNA is double stranded ...
slides
... 4) Very short exons: some exons are only 3 bp long in Arabidopsis genes and probably even 1 bp for the coding part of exons at either end of the coding sequence, meaning that start or stop codons can be interrupted by an intron. Such small exons are easily missed by all content sensors, especially i ...
... 4) Very short exons: some exons are only 3 bp long in Arabidopsis genes and probably even 1 bp for the coding part of exons at either end of the coding sequence, meaning that start or stop codons can be interrupted by an intron. Such small exons are easily missed by all content sensors, especially i ...
Bio research bio and fromatics lab - BLI-Research-Synbio
... codon is formed in a DNA sequence the ribosome comes along and attaches to the codon and helps create proteins. A gene is made up of many nucleotides which make up the sequence of DNA. 7. What could happen to an organism if it inherited a gene that coded for a defective protein? Why? The organism wo ...
... codon is formed in a DNA sequence the ribosome comes along and attaches to the codon and helps create proteins. A gene is made up of many nucleotides which make up the sequence of DNA. 7. What could happen to an organism if it inherited a gene that coded for a defective protein? Why? The organism wo ...
The many faces of hypoglycaemia in the paediatric population
... • Urinary organic acid and acylcarnitine analysis (e.g. shortchain L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCHAD) deficiency) ...
... • Urinary organic acid and acylcarnitine analysis (e.g. shortchain L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCHAD) deficiency) ...
Ch. 14 The Human Genome-Sec. 1 Human Heredity
... are carriers for sickle cell disease. Children who receive a recessive gene from each parent can become blind. Arms and legs can become paralyzed or even die. Strokes and heart attacks are common. Treatments are available to decrease the complications of this disease but there is no cure. Many Afric ...
... are carriers for sickle cell disease. Children who receive a recessive gene from each parent can become blind. Arms and legs can become paralyzed or even die. Strokes and heart attacks are common. Treatments are available to decrease the complications of this disease but there is no cure. Many Afric ...
Lecture 32 POWERPOINT here
... from mother and one from father. If a genetic trait is dominant, a person only needs to inherit one copy of the gene for the trait to be expressed. • Recessive - refers to an allele that causes a phenotype (visible or detectable characteristic) that is only seen in a homozygous genotype (an organism ...
... from mother and one from father. If a genetic trait is dominant, a person only needs to inherit one copy of the gene for the trait to be expressed. • Recessive - refers to an allele that causes a phenotype (visible or detectable characteristic) that is only seen in a homozygous genotype (an organism ...
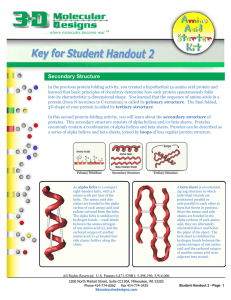
Secondary Structure - 3D Molecular Designs
... Folding a Toober Model of the Zinc Finger In this activity, you will fold a model of the first of three zinc fingers of the Zif268 protein. Zinc finger proteins regulate the transcription of DNA into mRNA – by binding to DNA and attracting RNA polymerase. A zinc finger protein contains two cysteine ...
... Folding a Toober Model of the Zinc Finger In this activity, you will fold a model of the first of three zinc fingers of the Zif268 protein. Zinc finger proteins regulate the transcription of DNA into mRNA – by binding to DNA and attracting RNA polymerase. A zinc finger protein contains two cysteine ...
Automatic Annotation of Gene Lists from Literature Analysis
... 1) For a gene i, if the term count xi is significantly higher than expected by chance (determined by λ0 and di), then the term may be related to the gene i; 2) If there are many genes related to the term, then this term is enriched in the given gene list. ...
... 1) For a gene i, if the term count xi is significantly higher than expected by chance (determined by λ0 and di), then the term may be related to the gene i; 2) If there are many genes related to the term, then this term is enriched in the given gene list. ...
Introduction - OpenWetWare
... a hole in the membrane, or a specific pore protein embedded in the membrane.) Some species of bacteria are naturally competent, but the strain of E. coli we use in the lab must be artificially made competent before we can transform it. There are two types of competent cells, electrocompetent and che ...
... a hole in the membrane, or a specific pore protein embedded in the membrane.) Some species of bacteria are naturally competent, but the strain of E. coli we use in the lab must be artificially made competent before we can transform it. There are two types of competent cells, electrocompetent and che ...
Medical Genetics 1
... Ethnic associations with AR disease • In particular populations, recessive allele frequency may have increased by selection in heterozygotes, or by genetic drift • -Thalassaemia: Cypriots, Greeks, Italians, Chinese, African-Americans • Sickle Cell Disease: Arabs, West Indians • Tay-Sachs Disease: ...
... Ethnic associations with AR disease • In particular populations, recessive allele frequency may have increased by selection in heterozygotes, or by genetic drift • -Thalassaemia: Cypriots, Greeks, Italians, Chinese, African-Americans • Sickle Cell Disease: Arabs, West Indians • Tay-Sachs Disease: ...
Predicting TF affinities to Promoters of tissue specific genes
... The RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a multi protein complex that consists of the actual enzyme and several associated basal TFs which are required for proper binding to core promoters and subsequently for initiating transcription (Hahn 2004, Butler et al., 2002). Several sequence motifs found in ty ...
... The RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a multi protein complex that consists of the actual enzyme and several associated basal TFs which are required for proper binding to core promoters and subsequently for initiating transcription (Hahn 2004, Butler et al., 2002). Several sequence motifs found in ty ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.













![Biochemistry_and_Digestion_2010[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008289894_1-a2dae968af20e40d29d6bcd9c3fab727-300x300.png)