Study Guide – Unit 4: Genetics
... 13. Proteins are made on ___________________ in the cytoplasm of the cell. 14. State two differences between DNA and RNA. 15. List the two kinds of RNA and describe their job. 16. Circle the letter of the first step in protein synthesis. a. tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosome. b. the ribosome r ...
... 13. Proteins are made on ___________________ in the cytoplasm of the cell. 14. State two differences between DNA and RNA. 15. List the two kinds of RNA and describe their job. 16. Circle the letter of the first step in protein synthesis. a. tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosome. b. the ribosome r ...
Document
... found in living things. Which statement describes one characteristic of this molecule? (1) It is the template for the replication of genetic information. (2) Organic catalysts are made up of these molecules. (3) It is different in each cell of an organism. (4) Cell membranes contain many of these mo ...
... found in living things. Which statement describes one characteristic of this molecule? (1) It is the template for the replication of genetic information. (2) Organic catalysts are made up of these molecules. (3) It is different in each cell of an organism. (4) Cell membranes contain many of these mo ...
Problems 11
... change over time? Why or why not? If a wild-type repressor gene (I+) is contained on an F’ plasmid which is used to transfer DNA to an I– cell, there will be a delay in repression until there is enough time for the repressor to be transcribed and translated. So for instance, transfecting an I– P+ O+ ...
... change over time? Why or why not? If a wild-type repressor gene (I+) is contained on an F’ plasmid which is used to transfer DNA to an I– cell, there will be a delay in repression until there is enough time for the repressor to be transcribed and translated. So for instance, transfecting an I– P+ O+ ...
GENETICS REVIEWAPRIL26
... found in living things. Which statement describes one characteristic of this molecule? (1) It is the template for the replication of genetic information. (2) Organic catalysts are made up of these molecules. (3) It is different in each cell of an organism. (4) Cell membranes contain many of these mo ...
... found in living things. Which statement describes one characteristic of this molecule? (1) It is the template for the replication of genetic information. (2) Organic catalysts are made up of these molecules. (3) It is different in each cell of an organism. (4) Cell membranes contain many of these mo ...
EPIGENETICS Textbook
... – Found in 5’ promoter areas – NOT methylated on active and silent genes – EXCEPTIONS: • Silencing on X chromosome • When cells differentiate • Pathological processes, e.g., inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in some cancers ...
... – Found in 5’ promoter areas – NOT methylated on active and silent genes – EXCEPTIONS: • Silencing on X chromosome • When cells differentiate • Pathological processes, e.g., inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in some cancers ...
Genetics of Cancer
... production. Cells will pass the G1 S checkpoint even when chromosomal damage exists. ...
... production. Cells will pass the G1 S checkpoint even when chromosomal damage exists. ...
Document
... production. Cells will pass the G1 S checkpoint even when chromosomal damage exists. ...
... production. Cells will pass the G1 S checkpoint even when chromosomal damage exists. ...
Exam 1
... ___________________________ so that one face can interact with the water favorably while the other face forms favorable interactions with the core of the protein. 20. _____________________ is a nucleobase found in RNA but not DNA. 21. A _________________ is a compact, independently folded unit of a ...
... ___________________________ so that one face can interact with the water favorably while the other face forms favorable interactions with the core of the protein. 20. _____________________ is a nucleobase found in RNA but not DNA. 21. A _________________ is a compact, independently folded unit of a ...
Cornell Notes Template
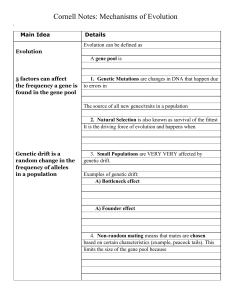
... 2. Natural Selection is also known as survival of the fittest It is the driving force of evolution and happens when ...
... 2. Natural Selection is also known as survival of the fittest It is the driving force of evolution and happens when ...
BRAF: from gene to cancer therapy
... Red boxes indicate a base change in the DNA sequence compared to the reference human genome sequenced. A mutation will be displayed as a base change occurring multiple times in the same location on both blue and yellow reads. A single red box on its own can indicate that the sequencing machine has m ...
... Red boxes indicate a base change in the DNA sequence compared to the reference human genome sequenced. A mutation will be displayed as a base change occurring multiple times in the same location on both blue and yellow reads. A single red box on its own can indicate that the sequencing machine has m ...
Key Idea 2 - Valhalla High School
... Organisms from all kingdoms possess a set of instructions (___genetic code_______) that determine their characteristics. These instructions are passed from __parents________ to offspring during reproduction. The inherited instructions that are passed from parent to offspring exist in the form of a c ...
... Organisms from all kingdoms possess a set of instructions (___genetic code_______) that determine their characteristics. These instructions are passed from __parents________ to offspring during reproduction. The inherited instructions that are passed from parent to offspring exist in the form of a c ...
Bacterial species
... DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation in eukaryotes. Methylation refers to 1. altering RNA polymerase activity by methylation of RNA polymerase 2. altering translational activity especially of highly methylated tRNAs. 3. alteration of DNA polymerase activity by addition of ...
... DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation in eukaryotes. Methylation refers to 1. altering RNA polymerase activity by methylation of RNA polymerase 2. altering translational activity especially of highly methylated tRNAs. 3. alteration of DNA polymerase activity by addition of ...
Study Guide for Test
... “To do” list and tips for studying: Form a small study group and discuss all of the following. Understand all terms above and be able to put them into context. Pick three words (at random) and be able to form one sentence, incorporating all ideas together. Review all journal entries, notes, and ...
... “To do” list and tips for studying: Form a small study group and discuss all of the following. Understand all terms above and be able to put them into context. Pick three words (at random) and be able to form one sentence, incorporating all ideas together. Review all journal entries, notes, and ...
rsc prize and award lecture
... MRC LABORATORY OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY WEDNESDAY 12TH JANUARY 2011 BERRILL LECTURE THEATRE, THE OPEN UNIVERSITY ...
... MRC LABORATORY OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY WEDNESDAY 12TH JANUARY 2011 BERRILL LECTURE THEATRE, THE OPEN UNIVERSITY ...
Gene Section CBFb (subunit b of core binding factor)
... CBF binds to a core motif of the DNA (herein the name); CBFb by itself does not contain any known DNA binding motif or any transcriptional activation domain; CBFa binds to DNA; CBFb increases CBFa's affinity to DNA by 5 to 10 fold; CBF is a transcription factor which regulates the expression of myel ...
... CBF binds to a core motif of the DNA (herein the name); CBFb by itself does not contain any known DNA binding motif or any transcriptional activation domain; CBFa binds to DNA; CBFb increases CBFa's affinity to DNA by 5 to 10 fold; CBF is a transcription factor which regulates the expression of myel ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
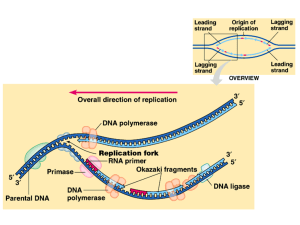
... • Enzymes unwind the double helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
... • Enzymes unwind the double helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
zChap00_Front_140901
... excerpts derived from this work. Non-commercial. You may not use this work for commercial purposes. Share Alike. If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same or similar licence to this one. For any reuse or distribution, you must m ...
... excerpts derived from this work. Non-commercial. You may not use this work for commercial purposes. Share Alike. If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same or similar licence to this one. For any reuse or distribution, you must m ...
Genetics Module B, Anchor 2 Basic Mendelian Genetics: 1. Different
... Frameshift mutations alter more codons, and thus have a more severe effect on the function of the protein. If substitution mutations result in a stop codon they are also severe. 5. List and describe the types of chromosome mutations. Deletion – gene deleted Duplication – extra copy of gene included ...
... Frameshift mutations alter more codons, and thus have a more severe effect on the function of the protein. If substitution mutations result in a stop codon they are also severe. 5. List and describe the types of chromosome mutations. Deletion – gene deleted Duplication – extra copy of gene included ...
DNA and Evolution
... are always limited, which implies that some individuals die without reproducing. Survival is affected by how well an individual is adapted to the environment. Or, how well the individual’s genes match the needs and challenges imposed by the environment it lives in. – adaptations are specific traits ...
... are always limited, which implies that some individuals die without reproducing. Survival is affected by how well an individual is adapted to the environment. Or, how well the individual’s genes match the needs and challenges imposed by the environment it lives in. – adaptations are specific traits ...
Document
... and a clone derived from that library hybridized to the 2 kb, 6 kb, and 9 kb restriction fragments only. When sequenced, this cDNA clone was 720 nucleotides in length and therefore incomplete. The amino terminal sequence of the protein encoding this gene was known, however, and a synthetic oligonucl ...
... and a clone derived from that library hybridized to the 2 kb, 6 kb, and 9 kb restriction fragments only. When sequenced, this cDNA clone was 720 nucleotides in length and therefore incomplete. The amino terminal sequence of the protein encoding this gene was known, however, and a synthetic oligonucl ...
Molecular Evolution - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... Consider molecular evolutionary changes at two levels •Changes in DNA; -Point mutation; mutations of single genes; small alterations in sequence or number of nucleotides -Chromsomal mutations; alterations that are more extensive than point mutations; four types – deletions duplications, inversions, ...
... Consider molecular evolutionary changes at two levels •Changes in DNA; -Point mutation; mutations of single genes; small alterations in sequence or number of nucleotides -Chromsomal mutations; alterations that are more extensive than point mutations; four types – deletions duplications, inversions, ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.