In the 150 years since Darwin wrote On the Origin of Species our
... this technique of treatment, for example, the genetic disorder gyrate atrophy affects the eye and eventually leads to blindness. The retina is damaged by an enzyme defect that causes a build up of the amino acid ornithine. This defect is caused by 35 different mutations in a single gene and so findi ...
... this technique of treatment, for example, the genetic disorder gyrate atrophy affects the eye and eventually leads to blindness. The retina is damaged by an enzyme defect that causes a build up of the amino acid ornithine. This defect is caused by 35 different mutations in a single gene and so findi ...
Gene Structure: Searching Genbank and Interpreting
... normal amounts of hemoglobin, then an imbalance occurs. This imbalance is called "thalassemia”. If the beta portion failed, then it would be beta-thalassesmia. The condition is an inherited one, and therefore genetic. In this case, the thallesemia is caused by a mutation that leads to an incorrect s ...
... normal amounts of hemoglobin, then an imbalance occurs. This imbalance is called "thalassemia”. If the beta portion failed, then it would be beta-thalassesmia. The condition is an inherited one, and therefore genetic. In this case, the thallesemia is caused by a mutation that leads to an incorrect s ...
Cell wk 8
... 1. A hypothetical membrane interface exists between a cell and a capillary. The following values for partial pressures (mm mercury, Hg) of gases A and B are measured: p p Gas A (cell) 50, (capillary), 65. p p Gas B (cell) 50, (capillary) 35. Predict the direction of diffusion for each gas. 2. Atmosp ...
... 1. A hypothetical membrane interface exists between a cell and a capillary. The following values for partial pressures (mm mercury, Hg) of gases A and B are measured: p p Gas A (cell) 50, (capillary), 65. p p Gas B (cell) 50, (capillary) 35. Predict the direction of diffusion for each gas. 2. Atmosp ...
Recently genetic tests for DNA markers for marbling and tenderness
... polymorphism or SNP (referred to as “snip”) where alleles differ from each other by the sequence of only a single nucleotide base pair. SNP genetic tests focus on detecting precise single nucleotide base pair differences among the three billion nucleotide base pairs that make up the bovine genome. G ...
... polymorphism or SNP (referred to as “snip”) where alleles differ from each other by the sequence of only a single nucleotide base pair. SNP genetic tests focus on detecting precise single nucleotide base pair differences among the three billion nucleotide base pairs that make up the bovine genome. G ...
Chapter 12 Powerpoint
... peptide chain. Once incorporated into the peptide chain, the amino acids are known as amino acid residues. ...
... peptide chain. Once incorporated into the peptide chain, the amino acids are known as amino acid residues. ...
Test Info Sheet
... deletion/duplication testing (ExonArrayDx) of the appropriate gene at no additional charge. Mutations found in the first person of a family to be tested are confirmed by repeat analysis using sequencing, restriction fragment analysis, or another appropriate method. Testing for the BCKDHA, BCKDHB and ...
... deletion/duplication testing (ExonArrayDx) of the appropriate gene at no additional charge. Mutations found in the first person of a family to be tested are confirmed by repeat analysis using sequencing, restriction fragment analysis, or another appropriate method. Testing for the BCKDHA, BCKDHB and ...
CS691K Bioinformatics Kulp Lecture Notes #0 Molecular
... • In both processes, DNA is copied by breaking doublestrand (dsDNA) into single-strands (ssDNA) at origins of replication and synthesizing a complementary copy from the template. – 50 bp/sec * 15K origins = ~1 hr to replicate human genome ...
... • In both processes, DNA is copied by breaking doublestrand (dsDNA) into single-strands (ssDNA) at origins of replication and synthesizing a complementary copy from the template. – 50 bp/sec * 15K origins = ~1 hr to replicate human genome ...
Document
... •Mutation refers to a change in a base-pair (e.g. G-C bp to A-T bp is a mutation) •Problems arise when DNA damage is converted to mutation ...
... •Mutation refers to a change in a base-pair (e.g. G-C bp to A-T bp is a mutation) •Problems arise when DNA damage is converted to mutation ...
CHIMERISM. Principles and practise.
... Hemoglobin H-Constant Spring disease is a more severe form of this hemolytic disorder. Most severe form is a thalassemia major, in which fetus produces no a globins, which is generally incompatible with life. ...
... Hemoglobin H-Constant Spring disease is a more severe form of this hemolytic disorder. Most severe form is a thalassemia major, in which fetus produces no a globins, which is generally incompatible with life. ...
Genetic Transformation computer exercise v02 r01
... database of all publicly available DNA sequences and their protein translations, for the foreign gene used in the Genetic Transformation Lab. Sequences in GenBank are contributed by individual labs and sequencing facilities all over the world. As of April 2008, there were more than 76 million indivi ...
... database of all publicly available DNA sequences and their protein translations, for the foreign gene used in the Genetic Transformation Lab. Sequences in GenBank are contributed by individual labs and sequencing facilities all over the world. As of April 2008, there were more than 76 million indivi ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Results from 2 or more polypeptide chains forming 1 macromolecule Collagen – fibrous protein made of 3 polypeptides coiled like a rope Hemoglobin – globular protein made of four polypeptides (2 alpha & 2 beta chains) Sickle-Cell Disease o Inherited blood disorder o Single amino acid change i ...
... Results from 2 or more polypeptide chains forming 1 macromolecule Collagen – fibrous protein made of 3 polypeptides coiled like a rope Hemoglobin – globular protein made of four polypeptides (2 alpha & 2 beta chains) Sickle-Cell Disease o Inherited blood disorder o Single amino acid change i ...
Document
... production of proteins • New traits can be passed to offspring – May be helpful, bad or cause no change at all ...
... production of proteins • New traits can be passed to offspring – May be helpful, bad or cause no change at all ...
1: How is ribonucleic acid like DNA
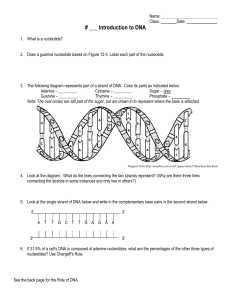
... Name ____________________________________Date ____________________ ...
... Name ____________________________________Date ____________________ ...
Gene Section GATA2 (GATA binding protein 2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... of erythroid differentiation depends of GATA2, but during maturation GATA2 expression decreases progressively at the benefit of GATA1. ...
... of erythroid differentiation depends of GATA2, but during maturation GATA2 expression decreases progressively at the benefit of GATA1. ...
Barbara McClintock
... She found 2 new dominant genetic loci that she names Dissociatior (Ds) and Activator (Ac) ...
... She found 2 new dominant genetic loci that she names Dissociatior (Ds) and Activator (Ac) ...
Cytosine – ______ Sugar
... Thymine – _________ Phosphate – Note: The oval circles are still part of the sugar, but are drawn in to represent where the base is attached. ...
... Thymine – _________ Phosphate – Note: The oval circles are still part of the sugar, but are drawn in to represent where the base is attached. ...
The Story of pRB
... clone gene. e.g. isolation of cdc mutants and the retinoblastoma story 2. reverse genetics: clone the gene then make a mutant to cause phenotype b. reverse genetics in mice is possible 1. ES cells are pluripotent cells that you can grow in culture 2. Homologous recombination is used to knock out a g ...
... clone gene. e.g. isolation of cdc mutants and the retinoblastoma story 2. reverse genetics: clone the gene then make a mutant to cause phenotype b. reverse genetics in mice is possible 1. ES cells are pluripotent cells that you can grow in culture 2. Homologous recombination is used to knock out a g ...
All life is based on the same genetic code
... inherited; some are not. Inherited mutations can affect the long-term survival of a whole population of organisms. ...
... inherited; some are not. Inherited mutations can affect the long-term survival of a whole population of organisms. ...
notes
... A gene is a sequence of DNA which encodes a polypeptide sequence A gene sequence is converted into a polypeptide sequence via the processes of transcription (making an mRNA transcript) and translation (polypeptide synthesis) Translation uses tRNA molecules and ribosomes to join amino acids into a ...
... A gene is a sequence of DNA which encodes a polypeptide sequence A gene sequence is converted into a polypeptide sequence via the processes of transcription (making an mRNA transcript) and translation (polypeptide synthesis) Translation uses tRNA molecules and ribosomes to join amino acids into a ...
From Gene to Protein
... refined to be one-gene-onepolypeptide hypothesis Crick – Central Dogma of Genetics • DNA RNA Protein ...
... refined to be one-gene-onepolypeptide hypothesis Crick – Central Dogma of Genetics • DNA RNA Protein ...
BIOL 241 Nucleic Acids and Gene Expression I. Genes (Overview) A
... B. Each amino acid (20) coded for by at least one codon See Figure 3.35 1. all but two amino acids can have more than one codon - usually differ in the third base 2. 3 codons are STOP codons 3. mRNA = series of codons translated into chains of amino acids C. Change in a single nucleotide (mRNA) can ...
... B. Each amino acid (20) coded for by at least one codon See Figure 3.35 1. all but two amino acids can have more than one codon - usually differ in the third base 2. 3 codons are STOP codons 3. mRNA = series of codons translated into chains of amino acids C. Change in a single nucleotide (mRNA) can ...
Answer Key Lab DNA Structure
... 7. What is the difference between transcription and translation? Transcription happens when information from the DNA template is transcribed onto messenger RNA. Translation happens when information from RNA is translated into proteins. ...
... 7. What is the difference between transcription and translation? Transcription happens when information from the DNA template is transcribed onto messenger RNA. Translation happens when information from RNA is translated into proteins. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Occurs during S phase of cell cycle. - Strands of double helix unzip allowing DNA polymerase to pair individual nucleotides with the template strands. Semi-Conservative Replication Occurs simultaneously in both directions, and begins at several points simultaneously. ...
... Occurs during S phase of cell cycle. - Strands of double helix unzip allowing DNA polymerase to pair individual nucleotides with the template strands. Semi-Conservative Replication Occurs simultaneously in both directions, and begins at several points simultaneously. ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... Translation- cellular process that converts the mRNA codons into amino acids to build proteins. First let’s practice reading the mRNA into amino acids and then I will outline the process of how it’s done step by step. Look at the sequence of mRNA below and the chart in Fig. ___ on page _____. ...
... Translation- cellular process that converts the mRNA codons into amino acids to build proteins. First let’s practice reading the mRNA into amino acids and then I will outline the process of how it’s done step by step. Look at the sequence of mRNA below and the chart in Fig. ___ on page _____. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.