Heredity - El Camino College
... During ___________, tRNAs with anticodons complementary to the mRNA codons bring specific ______ _____ to the mRNA The linear sequence of the _____ codons determines the order of amino acids in the resulting polypeptide. ...
... During ___________, tRNAs with anticodons complementary to the mRNA codons bring specific ______ _____ to the mRNA The linear sequence of the _____ codons determines the order of amino acids in the resulting polypeptide. ...
Unit 6B Learning Targets
... Translation of the mRNA occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome. d. In prokaryotic organisms, transcription is coupled to translation of the message. Translation involves energy and many steps, including initiation, elongation, and termination. i. The mRNA interacts with the rRNA of the ribosome to ...
... Translation of the mRNA occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome. d. In prokaryotic organisms, transcription is coupled to translation of the message. Translation involves energy and many steps, including initiation, elongation, and termination. i. The mRNA interacts with the rRNA of the ribosome to ...
Unit 6 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS
... other organisms such as Fruit Flies, and then mammals (rats, mice). If mutations (such as cancer) develop, the government restricts its use. • Mutagens that lead to an increased chance of cancer are called _____________________. Examples of Mutations 1. DOWN' SYNDROME - A chromosomal translocation • ...
... other organisms such as Fruit Flies, and then mammals (rats, mice). If mutations (such as cancer) develop, the government restricts its use. • Mutagens that lead to an increased chance of cancer are called _____________________. Examples of Mutations 1. DOWN' SYNDROME - A chromosomal translocation • ...
Chapter 8
... Delete a small number of nucleotides at random positions along the gene. Insert either specific or random sequences into that position. This methods is described in Fig. 8.8. ...
... Delete a small number of nucleotides at random positions along the gene. Insert either specific or random sequences into that position. This methods is described in Fig. 8.8. ...
Folic acid
... • Inhibit the action of Topoisomerases including Type 2 (includes gyrase) and Topo..ase IV – Bacterial DNA is negatively supercoiled; these enzymes introduce or remove supercoiling and are required for relieving coiling stress during DNA replication. – Inhibition results in cell death due to release ...
... • Inhibit the action of Topoisomerases including Type 2 (includes gyrase) and Topo..ase IV – Bacterial DNA is negatively supercoiled; these enzymes introduce or remove supercoiling and are required for relieving coiling stress during DNA replication. – Inhibition results in cell death due to release ...
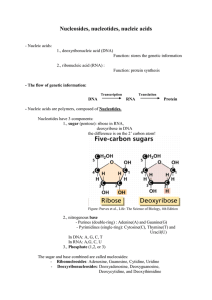
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... - Types and structure of RNA: - messenger RNA = mRNA: carries the information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regio ...
... - Types and structure of RNA: - messenger RNA = mRNA: carries the information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regio ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide D6
... 7. Each form of a gene is a(an) _____________. 8. When one flower crosses with another it is called _____________. 9. A structure made from DNA is called a(an) _____________________-. 10. The father of genetics is _________________. 11. The appearance of an individual is called their _______________ ...
... 7. Each form of a gene is a(an) _____________. 8. When one flower crosses with another it is called _____________. 9. A structure made from DNA is called a(an) _____________________-. 10. The father of genetics is _________________. 11. The appearance of an individual is called their _______________ ...
Name Period _____ Date ______ Mitosis Book Work! CHECK
... 5. For a cell to make proteins, enzymes must access its genes. When histones are modified with acetyl groups, their positive charge is neutralized, so they wrap DNA less tightly. How might this affect the rate of protein synthesis? ...
... 5. For a cell to make proteins, enzymes must access its genes. When histones are modified with acetyl groups, their positive charge is neutralized, so they wrap DNA less tightly. How might this affect the rate of protein synthesis? ...
Gene Expression
... consequences for the polypeptide specified by the mutated DNA. 10. Be able to relate gene expression to an organism’s phenotype. Terms N-base adenine (A) guanine (G) thymine (T) cytosine (C) uracil (U) pentose deoxyribose ribose phosphate nucleotide complementary bases DNA RNA ...
... consequences for the polypeptide specified by the mutated DNA. 10. Be able to relate gene expression to an organism’s phenotype. Terms N-base adenine (A) guanine (G) thymine (T) cytosine (C) uracil (U) pentose deoxyribose ribose phosphate nucleotide complementary bases DNA RNA ...
Genes for Speed or Endurance?
... Slow twitch fibres are more efficient in using oxygen to generate energy, while fast twitch fibres are less efficient in energy generation. Genetics The DNA molecule is the carrier of genetic information. Genes consist of the four types of DNA building bases called A, C, G, & T. The order of these b ...
... Slow twitch fibres are more efficient in using oxygen to generate energy, while fast twitch fibres are less efficient in energy generation. Genetics The DNA molecule is the carrier of genetic information. Genes consist of the four types of DNA building bases called A, C, G, & T. The order of these b ...
File
... takes the information encoded in DNA and encodes it into mRNA, which heads out of the cell’s nucleus and into the cytoplasm. During translation, the mRNA works with a ribosome and tRNA to synthesize proteins. Transcription The first step in transcription is the partial unwinding of the DNA molecule ...
... takes the information encoded in DNA and encodes it into mRNA, which heads out of the cell’s nucleus and into the cytoplasm. During translation, the mRNA works with a ribosome and tRNA to synthesize proteins. Transcription The first step in transcription is the partial unwinding of the DNA molecule ...
Basic Cancer Genetics
... Examples of carcinogens that could could mutagenesis o Obviously we get the connection with smoking and lung cancer, although 10% of lung cancers are in people who never smoked. The truth is that the vast majority of cancers are NOT caused by specific mutagenic chemicals that enter the body. Mos ...
... Examples of carcinogens that could could mutagenesis o Obviously we get the connection with smoking and lung cancer, although 10% of lung cancers are in people who never smoked. The truth is that the vast majority of cancers are NOT caused by specific mutagenic chemicals that enter the body. Mos ...
Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary name describe
... name and describe the functions of the four groups of organic compounds found in living things. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, & Nucleic Acids) describe how polymers are built from monomers (dehydration synthesis) and ...
... name and describe the functions of the four groups of organic compounds found in living things. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, & Nucleic Acids) describe how polymers are built from monomers (dehydration synthesis) and ...
The Genetic Science Glossary - Canadian Council of Churches
... Deoxyribonucleic acid. The molecule that encodes genetic information. DNA is a double stranded molecule held together by hoods between base pairs of nucleotides. There are four bases in DNA: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). Generally, A only bonds to T and C to G. DNA Analogy: ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid. The molecule that encodes genetic information. DNA is a double stranded molecule held together by hoods between base pairs of nucleotides. There are four bases in DNA: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). Generally, A only bonds to T and C to G. DNA Analogy: ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet - Answers
... - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide is deleted)? Deletion, insertion. - Do all mutations result in a faulty protein? Why or why not? No, because if you make mRNA that codes for same amino acids, you will end up with the same protein. This happens because some codons code fo ...
... - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide is deleted)? Deletion, insertion. - Do all mutations result in a faulty protein? Why or why not? No, because if you make mRNA that codes for same amino acids, you will end up with the same protein. This happens because some codons code fo ...
Comparative Genomics 2015 File
... The cladogram diagram below shows the relationship of selected animals based on their shared anatomical features. For example: out of seven key traits, all of these animals have a dorsal nerve cord, but only humans, monkeys and kangaroos have mammary glands. ...
... The cladogram diagram below shows the relationship of selected animals based on their shared anatomical features. For example: out of seven key traits, all of these animals have a dorsal nerve cord, but only humans, monkeys and kangaroos have mammary glands. ...
Microbiology Study Guide – Exam #2
... is NOT what you should study but rather is a guide to help organize your studying of the material listed. Your actual studying should involve the textbook, Powerpoint slides, your notes and other supplemental material such as Mastering Microbiology. Keep in mind that you will not be tested on materi ...
... is NOT what you should study but rather is a guide to help organize your studying of the material listed. Your actual studying should involve the textbook, Powerpoint slides, your notes and other supplemental material such as Mastering Microbiology. Keep in mind that you will not be tested on materi ...
BiochemLecture03
... gene is 110 kb long made up of 65 introns. • Titin has 175 introns. • With these large complex genes it is difficult to identify all of the exons and introns. ...
... gene is 110 kb long made up of 65 introns. • Titin has 175 introns. • With these large complex genes it is difficult to identify all of the exons and introns. ...
Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3)
... denaturing at extremes of pH and high temperatures denaturing as an irreversible change inhibiting enzyme function denaturing changing the shape of the active site ...
... denaturing at extremes of pH and high temperatures denaturing as an irreversible change inhibiting enzyme function denaturing changing the shape of the active site ...
Protein Synthesis - BLI-Research-SynBio-2016-session-2
... •Now we have mature mRNA transcribed from the cell’s DNA. It is leaving the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Once in the cytoplasm, it finds a ribosome so that translation can begin. We know how mRNA is made, but how do we “read” the code? ...
... •Now we have mature mRNA transcribed from the cell’s DNA. It is leaving the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Once in the cytoplasm, it finds a ribosome so that translation can begin. We know how mRNA is made, but how do we “read” the code? ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.