Document
... ASOs are a bit like a cross between DNA and mRNA. They are chemically similar to DNA, but are made of a single strand like mRNA. Just like other gene silencing drugs, they are designed to stick to the HD mRNA and tell the cell to destroy it, so preventing the abnormal huntingtin protein from ever be ...
... ASOs are a bit like a cross between DNA and mRNA. They are chemically similar to DNA, but are made of a single strand like mRNA. Just like other gene silencing drugs, they are designed to stick to the HD mRNA and tell the cell to destroy it, so preventing the abnormal huntingtin protein from ever be ...
Cystic Fibrosis
... worldwide, more than 850 mutant alleles have been reported to the CF Genetic Analysis Consortium. These mutations affect CFTR through a variety of molecular mechanisms which can produce little or no functional CFTR at the apical membrane. ...
... worldwide, more than 850 mutant alleles have been reported to the CF Genetic Analysis Consortium. These mutations affect CFTR through a variety of molecular mechanisms which can produce little or no functional CFTR at the apical membrane. ...
05 Evolutionary Mechanisms
... change an existing one into another, thereby changing the frequency of both alleles. Gene duplications are the main source of new genetic material, as extra copies they are free to mutate with less likelihood of causing harm. Mutations occur as 1 in 10000 in a small genome (bacteria) to about 1 or m ...
... change an existing one into another, thereby changing the frequency of both alleles. Gene duplications are the main source of new genetic material, as extra copies they are free to mutate with less likelihood of causing harm. Mutations occur as 1 in 10000 in a small genome (bacteria) to about 1 or m ...
ciliate genomics consortium - Tetrahymena Genome Database
... and visualize their tagged proteins by either direct fluorescence microscopy (GFP, YFP, CFP tags) or by immunofluorescence/immunoblotting (2xHA & FLAG-HIS). These activities can also be carried out by students in cell biology class laboratories. III. KNOCKOUT CONSTRUCTION (KOC) – A 13-lab series of ...
... and visualize their tagged proteins by either direct fluorescence microscopy (GFP, YFP, CFP tags) or by immunofluorescence/immunoblotting (2xHA & FLAG-HIS). These activities can also be carried out by students in cell biology class laboratories. III. KNOCKOUT CONSTRUCTION (KOC) – A 13-lab series of ...
Biomolecules Worksheet
... 5). All enzymes and proteins are chains of specific amino acids, but in order for them to perform their specific tasks, they must also have the correct 3D shape. a) There are a number of structural levels in a protein, describe what is meant by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. ...
... 5). All enzymes and proteins are chains of specific amino acids, but in order for them to perform their specific tasks, they must also have the correct 3D shape. a) There are a number of structural levels in a protein, describe what is meant by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. ...
Chapter 1: Overview of Genetics
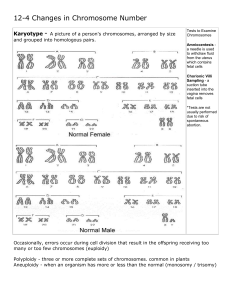
... 3. Genetic variation is due to changes in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA. These variations may be caused by: a. gene mutations at the nucleotide level b. major structural changes in a chromosome c. variation in the total number of chromosomes in an organism Traits Are Governed by Genes and by th ...
... 3. Genetic variation is due to changes in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA. These variations may be caused by: a. gene mutations at the nucleotide level b. major structural changes in a chromosome c. variation in the total number of chromosomes in an organism Traits Are Governed by Genes and by th ...
Microsoft Word 97
... The Actions of Mitosis and Cytokinesis ............................................................. Mitosis and Asexual Reproduction .................................................................... Meiosis ...
... The Actions of Mitosis and Cytokinesis ............................................................. Mitosis and Asexual Reproduction .................................................................... Meiosis ...
DNA Typing
... identifying breaks in chromosomes which cause the disease, etc.) Once the gene has been localized to a region of a chromosome, is to “walk” along the chromosome. The walk starts at a sequence known to be nearby, and continues until the gene of interest is ...
... identifying breaks in chromosomes which cause the disease, etc.) Once the gene has been localized to a region of a chromosome, is to “walk” along the chromosome. The walk starts at a sequence known to be nearby, and continues until the gene of interest is ...
Practice Exam 1 Answers
... B. preferentially binds to deoxyhemoglobin and stabilizes it. C. is present in fetal red blood cells. D. None of the above E. All of the above 7. The configuration of most α-carbon atoms of amino acids linked in a peptide bond is A. cis B. circular C. parallel D. trans E. perpendicular 8. If a parti ...
... B. preferentially binds to deoxyhemoglobin and stabilizes it. C. is present in fetal red blood cells. D. None of the above E. All of the above 7. The configuration of most α-carbon atoms of amino acids linked in a peptide bond is A. cis B. circular C. parallel D. trans E. perpendicular 8. If a parti ...
Genetics Part 2B 2015
... • Promote recombination, disrupt genes or control elements, & carry genes to new locations • May be harmful or lethal, but can also have small beneficial effects • Provides raw material for natural selection ...
... • Promote recombination, disrupt genes or control elements, & carry genes to new locations • May be harmful or lethal, but can also have small beneficial effects • Provides raw material for natural selection ...
Teacher notes and student sheets
... Cystic Fibrosis is one of the commonest inherited diseases in the UK. It is caused by mutations in the CTFR gene. These mutated alleles are recessive. (a) Before the faulty gene was identified affected families had no way of preventing the birth of children with the disease, except by not having chi ...
... Cystic Fibrosis is one of the commonest inherited diseases in the UK. It is caused by mutations in the CTFR gene. These mutated alleles are recessive. (a) Before the faulty gene was identified affected families had no way of preventing the birth of children with the disease, except by not having chi ...
anti-codon
... Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs ...
... Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs ...
Protein Synthesis
... DNA “message” from the nucleus to the rest of the cell ii. tRNA – transfer RNA – brings or “transfers” amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes to assemble proteins iii.rRNA – ribosomal RNA – helps ...
... DNA “message” from the nucleus to the rest of the cell ii. tRNA – transfer RNA – brings or “transfers” amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes to assemble proteins iii.rRNA – ribosomal RNA – helps ...
Genetics Pre/Post Test
... 12. Which of the following best describes the chromosomes of eukaryotic cells? a. More-complex eukaryotes have more chromosomes than simpler eukaryotes do b. Different kinds of eukaryotes have different numbers of chromosomes. c. The chromosomes in a pair contain very different genetic information. ...
... 12. Which of the following best describes the chromosomes of eukaryotic cells? a. More-complex eukaryotes have more chromosomes than simpler eukaryotes do b. Different kinds of eukaryotes have different numbers of chromosomes. c. The chromosomes in a pair contain very different genetic information. ...
Trans-activation and DNA-binding properties of
... above background while the full length Sox-18 protein activates only - 10-fold, suggesting that the additional DNA-binding domain suppresses /ra/w-activation. The activation domain of the related Sry protein was shown to be confined to a glutamine/histidinerichregion,just downstream of the HMG box ( ...
... above background while the full length Sox-18 protein activates only - 10-fold, suggesting that the additional DNA-binding domain suppresses /ra/w-activation. The activation domain of the related Sry protein was shown to be confined to a glutamine/histidinerichregion,just downstream of the HMG box ( ...
Chapter 17 Transcriptional Regulation In Eukaryotes
... -Diverse (다양한) regulatory factors are involved 1)activators & repressors: DNA binding proteins and help or hinder (방해하다) transcription initiation at specific genes in response to appropriate (적절한) signal 2)promoters: region at the gene where transcriptional machinery binds; regulatory binding sites ...
... -Diverse (다양한) regulatory factors are involved 1)activators & repressors: DNA binding proteins and help or hinder (방해하다) transcription initiation at specific genes in response to appropriate (적절한) signal 2)promoters: region at the gene where transcriptional machinery binds; regulatory binding sites ...
Topic 4: Genetics - wfs
... 5. The Human Genome Project sequenced the entire human genome and found there to be 25000 to 30000 genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 6. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability t ...
... 5. The Human Genome Project sequenced the entire human genome and found there to be 25000 to 30000 genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 6. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability t ...
(Simple) Physical Models of Protein Folding
... •Linear polymer chain composed of tens (peptides) to thousands (proteins) of monome •Monomers are 20 naturally occurring amino acids •Different proteins have different amino acid sequences •Structureless, extended unfolded state •Compact, ‘unique’ native folded state (with secondary and tertiary str ...
... •Linear polymer chain composed of tens (peptides) to thousands (proteins) of monome •Monomers are 20 naturally occurring amino acids •Different proteins have different amino acid sequences •Structureless, extended unfolded state •Compact, ‘unique’ native folded state (with secondary and tertiary str ...
Exam 2
... ____31. When a typical restriction enzyme cuts a DNA molecule, the cuts are staggered so that the DNA fragments have singlestranded ends. This is important in recombinant DNA work because _____. A. it allows a cell to recognize fragments produced by the enzyme B. the single-stranded ends serve as st ...
... ____31. When a typical restriction enzyme cuts a DNA molecule, the cuts are staggered so that the DNA fragments have singlestranded ends. This is important in recombinant DNA work because _____. A. it allows a cell to recognize fragments produced by the enzyme B. the single-stranded ends serve as st ...
Quarter 2 Final Exam Preliminary Study Guide
... Trait that can be in genes but be covered by dominant gene ...
... Trait that can be in genes but be covered by dominant gene ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... saturated fat intake should not exceed 10% of a person’s total fat intake because they may contribute to high blood cholesterol – a significant risk factor in heart disease and stroke. By contrast, certain oils such as the omega-3 rich fish oils seem to have a protective effect in heart disease. ...
... saturated fat intake should not exceed 10% of a person’s total fat intake because they may contribute to high blood cholesterol – a significant risk factor in heart disease and stroke. By contrast, certain oils such as the omega-3 rich fish oils seem to have a protective effect in heart disease. ...
2010 SEC Definition-style Questions
... (A nucleus having) Two sets of chromosomes (or two copies of each chromosome) ...
... (A nucleus having) Two sets of chromosomes (or two copies of each chromosome) ...
Adobe Acrobat Document
... single DNA strand and forms the complementary copy. How transcription works enzyme 1. DNA strand splits, with the help of an _____________ called DNA helicase _______________. *This exposes the active strand ...
... single DNA strand and forms the complementary copy. How transcription works enzyme 1. DNA strand splits, with the help of an _____________ called DNA helicase _______________. *This exposes the active strand ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.