Chapter 5 notes cont.
... which contain long hydrocarbon chains. • Some fats are solid at room temperature. Other fats called oils are liquids at room temperature. • In addition to storing energy for later use, fatty tissues cushion your organs and provide your body with insulation. ...
... which contain long hydrocarbon chains. • Some fats are solid at room temperature. Other fats called oils are liquids at room temperature. • In addition to storing energy for later use, fatty tissues cushion your organs and provide your body with insulation. ...
Old exam 2 from 2002
... was responsible for inheritance, used radiolabeled sulfur and phosphorus that tagged either protein or nucleic acid in separate experiments. They used a virus of E. coli called a: ...
... was responsible for inheritance, used radiolabeled sulfur and phosphorus that tagged either protein or nucleic acid in separate experiments. They used a virus of E. coli called a: ...
Carbon compounds - Sonoma Valley High School
... polymer of amino acids. • 20 different types of amino acids are found in nature. • Proteins are for structure, hormones, and enzymes. • Composed of elements N,O,C,H. ...
... polymer of amino acids. • 20 different types of amino acids are found in nature. • Proteins are for structure, hormones, and enzymes. • Composed of elements N,O,C,H. ...
Carcinomas with DNA Mismatch Repair Deficiency
... The DNA mismatch repair proteins are ubiquitously expressed in normal human tissues, particularly proliferating tissues, and nuclear expression in crypt epithelium and lymphocytes serves as an internal positive control for stain quality. In the setting of HNPCC, most hereditary and second-hit tumor ...
... The DNA mismatch repair proteins are ubiquitously expressed in normal human tissues, particularly proliferating tissues, and nuclear expression in crypt epithelium and lymphocytes serves as an internal positive control for stain quality. In the setting of HNPCC, most hereditary and second-hit tumor ...
Chapter 3
... 14. Identify and describe the steps that result in DNA replication Know why it is called semi-conservative replication Role of DNA polymerase and helicase 15. Describe the events that take place in transcription 16. Describe the events that take place in translation – protein synthesis 17. Know ...
... 14. Identify and describe the steps that result in DNA replication Know why it is called semi-conservative replication Role of DNA polymerase and helicase 15. Describe the events that take place in transcription 16. Describe the events that take place in translation – protein synthesis 17. Know ...
Protein Nomenclature
... • Novel acid-base properties • varied structure and chemical functionality • Chirality ...
... • Novel acid-base properties • varied structure and chemical functionality • Chirality ...
Word file - UC Davis
... no mutants, there were no mutations, and so the mean number of mutations m that occurs during the growth of a culture can be calculated from p0, the proportion of cultures with no mutants: m = -log ( p0 ) . Let us consider a bacterium B that is sensitive to a bacteriophage T, unless it carries a mut ...
... no mutants, there were no mutations, and so the mean number of mutations m that occurs during the growth of a culture can be calculated from p0, the proportion of cultures with no mutants: m = -log ( p0 ) . Let us consider a bacterium B that is sensitive to a bacteriophage T, unless it carries a mut ...
Molecular Biology and DNA
... Occassionally, a base is out of order and the protein cannot form right. • This creates a mutation • Bases can be added or deleted to create mutations • Added bases bump the chain up one base, deleted bases shift the chain back one base • Enzyme checkers make sure deletions happen very infrequently ...
... Occassionally, a base is out of order and the protein cannot form right. • This creates a mutation • Bases can be added or deleted to create mutations • Added bases bump the chain up one base, deleted bases shift the chain back one base • Enzyme checkers make sure deletions happen very infrequently ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA - Northwestern High School
... 10.3 Chromosomes and DNA replication • Prokaryotes – DNA in cytoplasm • Eukaryotes – DNA in nucleus – DNA extremely long!!! • Human DNA actual size is 3 meters long • Chromosome 13 has a DNA segment 3.2 cm long ...
... 10.3 Chromosomes and DNA replication • Prokaryotes – DNA in cytoplasm • Eukaryotes – DNA in nucleus – DNA extremely long!!! • Human DNA actual size is 3 meters long • Chromosome 13 has a DNA segment 3.2 cm long ...
Slides 4 - UF CISE - University of Florida
... PAM Matrices (1) • Starts with a multiple sequence alignment of very similar (>85% identity) proteins. ...
... PAM Matrices (1) • Starts with a multiple sequence alignment of very similar (>85% identity) proteins. ...
Chromosome variation
... 1.Quick review of conjugation: F-, F+, Hfr 2. Transformation: a different process of recombination, can be used to map genes 3. Bacteriophages are viruses that use bacteria as hosts; they can mediate bacterial DNA transfer - transduction 4. Extrachromosomal inheritance: Phenotype of maternal parent ...
... 1.Quick review of conjugation: F-, F+, Hfr 2. Transformation: a different process of recombination, can be used to map genes 3. Bacteriophages are viruses that use bacteria as hosts; they can mediate bacterial DNA transfer - transduction 4. Extrachromosomal inheritance: Phenotype of maternal parent ...
Proteins
... Scientists conjectured that proteins came from DNA; but how did DNA code for proteins? If one nucleotide codes for one amino acid, then there’d be 41 amino acids However, there are 20 amino acids, so at least 3 bases codes for one amino acid, since 42 = 16 and 43 = 64 ...
... Scientists conjectured that proteins came from DNA; but how did DNA code for proteins? If one nucleotide codes for one amino acid, then there’d be 41 amino acids However, there are 20 amino acids, so at least 3 bases codes for one amino acid, since 42 = 16 and 43 = 64 ...
2008 Spring Biological database Homework 1
... Is the secondary structure of this protein known? If so, how many “helical fold”are there in its 3D protein structure? How did you determine the exact amino acid number of each helical region? Yes, the secondary structure of erythropoietin is known. There are four helical folds in its 3D protein str ...
... Is the secondary structure of this protein known? If so, how many “helical fold”are there in its 3D protein structure? How did you determine the exact amino acid number of each helical region? Yes, the secondary structure of erythropoietin is known. There are four helical folds in its 3D protein str ...
Eukaryotic transcriptional control
... both homodimers or heterodimers with other members of the same class. (b) In the hypothetical example shown, transcription factors A, B, and C can each interact with each other, permitting the three factors to bind to six different DNA sequences (sites 1–6) and creating six combinations of activatio ...
... both homodimers or heterodimers with other members of the same class. (b) In the hypothetical example shown, transcription factors A, B, and C can each interact with each other, permitting the three factors to bind to six different DNA sequences (sites 1–6) and creating six combinations of activatio ...
Blank Jeopardy - Hazlet Township Public Schools
... A mutation is a change in the order of the bases in an organism’s DNA. A mutagen is an outside element that causes damage to DNA such as ultraviolet radiation ...
... A mutation is a change in the order of the bases in an organism’s DNA. A mutagen is an outside element that causes damage to DNA such as ultraviolet radiation ...
Homework1_23
... Finally, determine the number of sites in the gene at which allelic variants, or mutations, are known to occur. These mutations are often the result of a single base substitution, also known as Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, or SNP. Mutations can also be caused by deletion or insertion of one or mo ...
... Finally, determine the number of sites in the gene at which allelic variants, or mutations, are known to occur. These mutations are often the result of a single base substitution, also known as Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, or SNP. Mutations can also be caused by deletion or insertion of one or mo ...
dna ppt
... • Mutagen- any substance that causes a mutation to occur – Examples: chemicals, radiation, high temps ...
... • Mutagen- any substance that causes a mutation to occur – Examples: chemicals, radiation, high temps ...
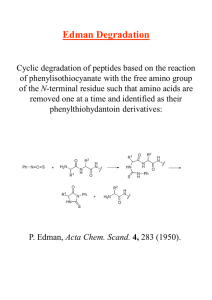
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... that body color AND wing size must be linked – look at the expected v/s observed ratios in the ...
... that body color AND wing size must be linked – look at the expected v/s observed ratios in the ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
... phenotype is heritable and transmitted to daughter cells. 5. Only an inherited cancer susceptibility can pass to future generations. 6. Cancer cells divide continuously and indefinitely; they are heritable, transplantable, dedifferentiated, and lack contact inhibition 7. Loss of specialization 8. An ...
... phenotype is heritable and transmitted to daughter cells. 5. Only an inherited cancer susceptibility can pass to future generations. 6. Cancer cells divide continuously and indefinitely; they are heritable, transplantable, dedifferentiated, and lack contact inhibition 7. Loss of specialization 8. An ...
Dr Ishtiaq genetic code
... for the same amino acid. For example, in serine codon UCA, if A is changed to U giving the codon UCU, it still code for serine. See table. ii- Missense mutation: the codon containing the changed base may code for a different amino acid. For example, if the serine codon UCA is changed to be CCA ( U i ...
... for the same amino acid. For example, in serine codon UCA, if A is changed to U giving the codon UCU, it still code for serine. See table. ii- Missense mutation: the codon containing the changed base may code for a different amino acid. For example, if the serine codon UCA is changed to be CCA ( U i ...
02421-11.1 Gene Transfer
... composed of large molecules that are capable of being put together in an almost unlimited number of ways. B. DNA - make up chromosomes. Chromosomes are contributed by each parent and determine how the animal will be structured. C. RNA - ribonucleic acids - a messenger substance which transfers messa ...
... composed of large molecules that are capable of being put together in an almost unlimited number of ways. B. DNA - make up chromosomes. Chromosomes are contributed by each parent and determine how the animal will be structured. C. RNA - ribonucleic acids - a messenger substance which transfers messa ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.