Basics of Molecular Biology
... of bonds. (See [4, Figure 1.4].) There is an asymmetric orientation to this backbone imposed by its chemical structure: one end is called the N-terminus and the other end the C-terminus. This orientation imposes directionality on the amino acid sequence. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
... of bonds. (See [4, Figure 1.4].) There is an asymmetric orientation to this backbone imposed by its chemical structure: one end is called the N-terminus and the other end the C-terminus. This orientation imposes directionality on the amino acid sequence. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
2 Review of Stoichiometry and Genetics
... Transcription is the process by which genetic information is transmitted in the nucleus when mRNA forms on the surface of unwound DNA. The mRNA codes match up to the codes of the DNA and enough are copied so that the information of one gene is “copied”. Translation is the process that assembles the ...
... Transcription is the process by which genetic information is transmitted in the nucleus when mRNA forms on the surface of unwound DNA. The mRNA codes match up to the codes of the DNA and enough are copied so that the information of one gene is “copied”. Translation is the process that assembles the ...
The genetic code is a degenerate, non-overlapping set of
... are shorter, circular DNA molecules that may only contain one or a few genes and often carry traits such asantibiotic resistance. Transcription in prokaryotes (as in eukaryotes) requires the DNA double helix to partially unwind in the region of RNA synthesis. The region of unwinding is called a tran ...
... are shorter, circular DNA molecules that may only contain one or a few genes and often carry traits such asantibiotic resistance. Transcription in prokaryotes (as in eukaryotes) requires the DNA double helix to partially unwind in the region of RNA synthesis. The region of unwinding is called a tran ...
File
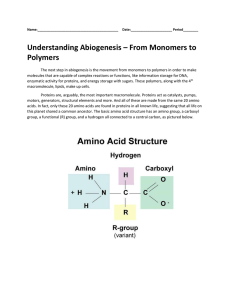
... Polymers The next step in abiogenesis is the movement from monomers to polymers in order to make molecules that are capable of complex reactions or functions, like information storage for DNA, enzymatic activity for proteins, and energy storage with sugars. These polymers, along with the 4th macromo ...
... Polymers The next step in abiogenesis is the movement from monomers to polymers in order to make molecules that are capable of complex reactions or functions, like information storage for DNA, enzymatic activity for proteins, and energy storage with sugars. These polymers, along with the 4th macromo ...
Summary of IPA in OS metastasis - Connective Tissue Oncology
... Vancouver General Hospital C.Beauchamp ...
... Vancouver General Hospital C.Beauchamp ...
Positive Gene Regulation
... Effects of mutations. Increased cell division, possibly leading to cancer, can result if the cell cycle is overstimulated, as in (a), or not inhibited when it normally would be, as in (b). ...
... Effects of mutations. Increased cell division, possibly leading to cancer, can result if the cell cycle is overstimulated, as in (a), or not inhibited when it normally would be, as in (b). ...
HUMAN GENETICS ARCHITECTURE LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... chromosome)—they are called "dominant" because a single copy—inherited from either parent—is enough to cause this trait to appear. This often means that one of the parents must also have the same trait, unless it has arisen due to a new mutation. Examples of autosomal dominant traits and disorders a ...
... chromosome)—they are called "dominant" because a single copy—inherited from either parent—is enough to cause this trait to appear. This often means that one of the parents must also have the same trait, unless it has arisen due to a new mutation. Examples of autosomal dominant traits and disorders a ...
Introduction continued
... Produces nearly data that have errors (so algorithms are to be extended to handle errors. Virus and bacteria (organisms most used in genetic research) Virus consists of a protein cap (capsid) with DNA (or RNA) inside - cells starts producing-coded proteins which promotes viral DNA replication (new c ...
... Produces nearly data that have errors (so algorithms are to be extended to handle errors. Virus and bacteria (organisms most used in genetic research) Virus consists of a protein cap (capsid) with DNA (or RNA) inside - cells starts producing-coded proteins which promotes viral DNA replication (new c ...
... repeats, which are sequences that are repeated multiple times on the same chromosome. The number of tandem repeats differs from one individual to another, causing the length of the PCR product to differ. For example one chromosome could look like this, with three tandem repeat (see above), while a c ...
CA DNA Test Development - Arabian Horse Association
... CA/CA (affected), it is possible that, in some cases, horses could have the affected genotype and show no clinical signs. If the MUTYH gene is not fully functioning, this could explain the variable expression. The physical differences between CA/CA (affected) horses could be due to varying levels of ...
... CA/CA (affected), it is possible that, in some cases, horses could have the affected genotype and show no clinical signs. If the MUTYH gene is not fully functioning, this could explain the variable expression. The physical differences between CA/CA (affected) horses could be due to varying levels of ...
Section: Sexual Reproduction
... Makes up “genes” – parts of the DNA strands that code for a specific protein ...
... Makes up “genes” – parts of the DNA strands that code for a specific protein ...
Wks #11. Answers
... the message, which prevents digestion of the mRNA by 5’nuclease enzymes of the nucleus. In addition, a mature mRNA would have a poly-A tail at the 3’-end of the molecule. Poly-A polymerase would add between 20 and 200 adenines to the 3’ end to protect the mRNA from enzymatic digestion by nucleases. ...
... the message, which prevents digestion of the mRNA by 5’nuclease enzymes of the nucleus. In addition, a mature mRNA would have a poly-A tail at the 3’-end of the molecule. Poly-A polymerase would add between 20 and 200 adenines to the 3’ end to protect the mRNA from enzymatic digestion by nucleases. ...
Lecture 9. Treatments
... urea through a series of enzymatic reactions termed the urea cycle. Elevated ammonia can therefore be detected in patients with urea cycle disorders, as well as other conditions involving liver failure. Enzyme testing is performed for a wide range of metabolic disorders to confirm a diagnosis suspec ...
... urea through a series of enzymatic reactions termed the urea cycle. Elevated ammonia can therefore be detected in patients with urea cycle disorders, as well as other conditions involving liver failure. Enzyme testing is performed for a wide range of metabolic disorders to confirm a diagnosis suspec ...
File - The Building Blocks For Learning
... Standard: All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain the instructions that code for the formation of proteins, which carry out most of the work of cells. Background Information: Your cells come in all shapes and sizes. Different type ...
... Standard: All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain the instructions that code for the formation of proteins, which carry out most of the work of cells. Background Information: Your cells come in all shapes and sizes. Different type ...
Slide 1
... polymer is unique for each gene. • Genes are normally hundreds to thousands of nucleotides long. • The linear order الترتيب التتابعيof bases in a gene specifies يُحددthe order of amino acids ( ترتيب األحماض األمينيةthe monomers of a protein). ...
... polymer is unique for each gene. • Genes are normally hundreds to thousands of nucleotides long. • The linear order الترتيب التتابعيof bases in a gene specifies يُحددthe order of amino acids ( ترتيب األحماض األمينيةthe monomers of a protein). ...
Sources of Variation
... This can be advantageous because no information is lost and new genes are gained. ...
... This can be advantageous because no information is lost and new genes are gained. ...
Goals of pharmacogenomics
... Measurement of the expression of thousands of genes in hundreds of cancer specimens has begun to reveal novel molecularly defined subclasses of tumor; some of these classes appear to predict clinical behavior, while others may define tumor types that are ripe for directed development of therapeutics ...
... Measurement of the expression of thousands of genes in hundreds of cancer specimens has begun to reveal novel molecularly defined subclasses of tumor; some of these classes appear to predict clinical behavior, while others may define tumor types that are ripe for directed development of therapeutics ...
Name
... Completion Complete each statement on the line provided. 16. A(n) is all of the genes that are present in a particular population. 17. The passing of genes from one organism to another organism that is not its offspring is called ...
... Completion Complete each statement on the line provided. 16. A(n) is all of the genes that are present in a particular population. 17. The passing of genes from one organism to another organism that is not its offspring is called ...
Evidence of Evolution
... of rock. Younger fossils are found in superficial layers of rock. • Carbon dating can be used to determine the age of a fossil. ...
... of rock. Younger fossils are found in superficial layers of rock. • Carbon dating can be used to determine the age of a fossil. ...
Editorial Darwin, Evolution and the Origin of Species
... adapt to their environments via minute physical adjustments. Biologists have since found evidence that dramatic adaptations can also occur, for instance in the form of major morphological changes. These adaptations appear to be the cause of changes in structure from apes to man and various human rac ...
... adapt to their environments via minute physical adjustments. Biologists have since found evidence that dramatic adaptations can also occur, for instance in the form of major morphological changes. These adaptations appear to be the cause of changes in structure from apes to man and various human rac ...
Style D 36 by 54 - Bourns College of Engineering
... Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins provides a way to manipulate the structures of proteins, monitor protein function and create proteins with novel properties. In previous studies, by creating orthogonal tRNA- synthetase pairs with specificity to unnatural ...
... Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins provides a way to manipulate the structures of proteins, monitor protein function and create proteins with novel properties. In previous studies, by creating orthogonal tRNA- synthetase pairs with specificity to unnatural ...
Sample Exam 3 answer key
... ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ________________ Given that cystic fibrosis is a recessive mutation, will the fetus be affected? Explain. Both parents are heterozygous – contain 4 EcoR1 fragments (one of which (4 kb) is common between the wild type and mutant gene). The fetus has this common fragment and one ot ...
... ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ________________ Given that cystic fibrosis is a recessive mutation, will the fetus be affected? Explain. Both parents are heterozygous – contain 4 EcoR1 fragments (one of which (4 kb) is common between the wild type and mutant gene). The fetus has this common fragment and one ot ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.