Prokaryotic Gene Expression Mechanisms RNA Types of RNA Other
... accessory proteins or subunits. ...
... accessory proteins or subunits. ...
Developmental Biology 8/e - Florida International University
... influenced by the gap genes and pair rule genes. - Expression of abdA and abdB genes is repressed by the gap gene proteins Hunchback and Kruppel. - The Antennapedia gene is activated by particular levels of ...
... influenced by the gap genes and pair rule genes. - Expression of abdA and abdB genes is repressed by the gap gene proteins Hunchback and Kruppel. - The Antennapedia gene is activated by particular levels of ...
Macromolecules Worksheet - High School Science Help
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
dna and its structure
... exposed, complementary nucleotides are added • Proteins help to unwind, copy, and rewind the DNA molecule ...
... exposed, complementary nucleotides are added • Proteins help to unwind, copy, and rewind the DNA molecule ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... Repressor proteins are normally produced and will bind to the operator preventing transcription for the lactase gene. If lactose if present, it will bind to the repressor protein which will change its shape and prevent it from binding on the ...
... Repressor proteins are normally produced and will bind to the operator preventing transcription for the lactase gene. If lactose if present, it will bind to the repressor protein which will change its shape and prevent it from binding on the ...
Release of Human Genome Project
... – Eukaryotes (organisms with single or multiple cells. their cells have nuclei. e.g., ...
... – Eukaryotes (organisms with single or multiple cells. their cells have nuclei. e.g., ...
Questions 33-38
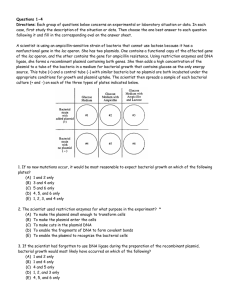
... of the lac operon, and the other contains the gene for ampicillin resistance. Using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase, she forms a recombinant plasmid containing both genes. She then adds a high concentration of the plasmid to a tube of the bacteria in a medium for bacterial growth that contains gl ...
... of the lac operon, and the other contains the gene for ampicillin resistance. Using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase, she forms a recombinant plasmid containing both genes. She then adds a high concentration of the plasmid to a tube of the bacteria in a medium for bacterial growth that contains gl ...
Natural Polymers - Wikispaces
... Nature uses natural polymers to make life possible, as all living things are made from these polymers. In many ways, these natural polymers are more important than other polymers. ...
... Nature uses natural polymers to make life possible, as all living things are made from these polymers. In many ways, these natural polymers are more important than other polymers. ...
Child Psychology, Second Canadian Edition
... • Mutations (genetic variations) can be adaptive or maladaptive • Dominant disorders – Huntington’s chorea: a fatal syndrome in which the nervous system degenerates in adulthood (age 30-40) ...
... • Mutations (genetic variations) can be adaptive or maladaptive • Dominant disorders – Huntington’s chorea: a fatal syndrome in which the nervous system degenerates in adulthood (age 30-40) ...
Holiday time test notes
... Before DNA can be replicated, the complimentary strands must be separated by an enzyme called helicase. To prevent the strands from pairing up again in the wake of helicase, single stranded binding proteins are attached. DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. The enzyme(s) that make new R/DNA polymers are ...
... Before DNA can be replicated, the complimentary strands must be separated by an enzyme called helicase. To prevent the strands from pairing up again in the wake of helicase, single stranded binding proteins are attached. DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. The enzyme(s) that make new R/DNA polymers are ...
1 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. • c
... segments within and between DNA molecules) increase variation. • Sexual reproduction in eukaryotes involving gamete formation, including crossing-‐over during meiosis and the random assortment of chromosomes during ...
... segments within and between DNA molecules) increase variation. • Sexual reproduction in eukaryotes involving gamete formation, including crossing-‐over during meiosis and the random assortment of chromosomes during ...
Reading Packet 5- Molecular Genetics Part 1 Chapter 16
... 4. Use the diagram below to note the flow of genetic information in a eukaryotic cell. Define each term that appears in the boxes. ...
... 4. Use the diagram below to note the flow of genetic information in a eukaryotic cell. Define each term that appears in the boxes. ...
Document
... the amino acid chain grows. – The mRNA is read codon by codon and the protein is built up one amino acid at a time in the correct sequence. ...
... the amino acid chain grows. – The mRNA is read codon by codon and the protein is built up one amino acid at a time in the correct sequence. ...
DNA Profiles
... Families of children with Canavan disease, a rare and fatal disorder, started a foundation to obtain tissue samples and funding for research The research hospital patented the gene and charged participating families for the test After a lawsuit, the hospital was allowed to continue to license ...
... Families of children with Canavan disease, a rare and fatal disorder, started a foundation to obtain tissue samples and funding for research The research hospital patented the gene and charged participating families for the test After a lawsuit, the hospital was allowed to continue to license ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... CENTRAL DOGMA: DNA RNA protein DNA directs the production of proteins by first being transcribed into an mRNA molecule whose sequence is dependent on the sequence of DNA. The mRNA is then “read” or translated by ribosomes in the cytoplasm in order to produce a polypeptide. 23. How does RNA diffe ...
... CENTRAL DOGMA: DNA RNA protein DNA directs the production of proteins by first being transcribed into an mRNA molecule whose sequence is dependent on the sequence of DNA. The mRNA is then “read” or translated by ribosomes in the cytoplasm in order to produce a polypeptide. 23. How does RNA diffe ...
Traditional and Modern Breeding Methods
... • Disease resistance • Hybrid production • Nutrient use efficiency • Carbon sequestration • Oil, starch and amino acids • Nutrient quality Achieving all these goals will require not only traditional breeder skills, but will be accelerated by the use of novel molecular techniques and biotechnology ...
... • Disease resistance • Hybrid production • Nutrient use efficiency • Carbon sequestration • Oil, starch and amino acids • Nutrient quality Achieving all these goals will require not only traditional breeder skills, but will be accelerated by the use of novel molecular techniques and biotechnology ...
Macromolecules Notes
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
DNA and protein synthesis
... cells are one such exception.) In prokaryotic cells there may be just one DNA molecule. In eukaryotic cells there are usually several. For example, humans have 46 DNA molecules in their cells (when they are not dividing), because each of our 46 chromosomes contains one DNA molecule. The DNA molecule ...
... cells are one such exception.) In prokaryotic cells there may be just one DNA molecule. In eukaryotic cells there are usually several. For example, humans have 46 DNA molecules in their cells (when they are not dividing), because each of our 46 chromosomes contains one DNA molecule. The DNA molecule ...
NetworkAnalysis_2012
... * Screened deletion libraries for >700 conditions * Found ‘phenotype’ for nearly all yeast genes * Characterized which genes could be functionally profiled by which assays (e.g. phenotype, gene expression, etc) ...
... * Screened deletion libraries for >700 conditions * Found ‘phenotype’ for nearly all yeast genes * Characterized which genes could be functionally profiled by which assays (e.g. phenotype, gene expression, etc) ...
DNA and the Genome
... There are far more possible codons than amino acids. There are 64 (4 3 ) possible combinations of the four bases but only 20 amino acids occurring in nature. This has led to more than one codon coding for an amino acid. There are three codons that do not code for amino acids: UGA, UAA and UAG. The o ...
... There are far more possible codons than amino acids. There are 64 (4 3 ) possible combinations of the four bases but only 20 amino acids occurring in nature. This has led to more than one codon coding for an amino acid. There are three codons that do not code for amino acids: UGA, UAA and UAG. The o ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.