CELLular biology
... Significant breakthrough in the manipulation of plant and animal cells occurred when scientists learned how to move pieces of DNA within and between organisms. The key was the discovery of enzymes that cut DNA into fragments containing one or more genes. These DNA pieces could be separated from each ...
... Significant breakthrough in the manipulation of plant and animal cells occurred when scientists learned how to move pieces of DNA within and between organisms. The key was the discovery of enzymes that cut DNA into fragments containing one or more genes. These DNA pieces could be separated from each ...
Slide 1
... Telomeres are specialized DNA sequences that cap the ends of linear chromosomes and provide protection against gene erosion at cell divisions, chromosomal non-homologous end-joinings and nuclease attacks. ...
... Telomeres are specialized DNA sequences that cap the ends of linear chromosomes and provide protection against gene erosion at cell divisions, chromosomal non-homologous end-joinings and nuclease attacks. ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Populations
... change can form a new allele. Mutations in reproductive cells can be passed on to offspring. This increases the genetic variation in the gene pool. Because there are many genes in each individual and many individuals in a population, new mutations form frequently in gene pools. • Recombination New a ...
... change can form a new allele. Mutations in reproductive cells can be passed on to offspring. This increases the genetic variation in the gene pool. Because there are many genes in each individual and many individuals in a population, new mutations form frequently in gene pools. • Recombination New a ...
Meiosis and the Alternation of Generations
... favorable. If the environment changed sufficiently rapidly, these changes in the environment can make sex advantageous for the individual. Such rapid changes in environment are caused by the co-evolution between hosts and parasites Imagine, for example that there is one gene in parasites with two al ...
... favorable. If the environment changed sufficiently rapidly, these changes in the environment can make sex advantageous for the individual. Such rapid changes in environment are caused by the co-evolution between hosts and parasites Imagine, for example that there is one gene in parasites with two al ...
What can affect the effective population size? Genetic bottlenecks
... isochore repeating patterns in DNA which are found in warm-blooded critters, not ectotherms G & C are heavy, A & T are light Molecular evolution can be decoupled from morphological evolution Humans & chimps are genetically similar but morphologically distinct Neutral theory of molecular evolution Mo ...
... isochore repeating patterns in DNA which are found in warm-blooded critters, not ectotherms G & C are heavy, A & T are light Molecular evolution can be decoupled from morphological evolution Humans & chimps are genetically similar but morphologically distinct Neutral theory of molecular evolution Mo ...
Chapter 6: An Introduction to Proteins
... Hemoglobin (Hb) is an allosteric enzyme whose binding of oxygen can be increased by positive homotropic effects or decreased by negative heterotropic effectors. Draw a plot of fraction bound (Y) vs. [O2] for Hb as it might be found in the blood, then draw a curve for HB + a negative effector. Name o ...
... Hemoglobin (Hb) is an allosteric enzyme whose binding of oxygen can be increased by positive homotropic effects or decreased by negative heterotropic effectors. Draw a plot of fraction bound (Y) vs. [O2] for Hb as it might be found in the blood, then draw a curve for HB + a negative effector. Name o ...
Is it on or off? The Use of Microarrays in Functional Genomics
... Another exciting development in this field of personalized molecular medicine is using protein microarrays, based on the understanding that the dysfunction of protein interactions is the most direct, underlying cause of diseases as they oversee all biological processes and cellular fates. The intera ...
... Another exciting development in this field of personalized molecular medicine is using protein microarrays, based on the understanding that the dysfunction of protein interactions is the most direct, underlying cause of diseases as they oversee all biological processes and cellular fates. The intera ...
Chap2 DNA RNA and Protein
... methyltransferase [1]. A high CpG content is found in regions known as CpG islands (a stretch of DNA 1-2 kb that has clusters of CpG doublets). CpG islands surround the promoters of constitutively expressed genes where they are unmethylated. Methylation of a CpG island prevents activation of a prom ...
... methyltransferase [1]. A high CpG content is found in regions known as CpG islands (a stretch of DNA 1-2 kb that has clusters of CpG doublets). CpG islands surround the promoters of constitutively expressed genes where they are unmethylated. Methylation of a CpG island prevents activation of a prom ...
Pressure - People Server at UNCW
... Top: Na-K ATPase activity decreases at low T and at high P. Middle: DPH Anisotropy (polarization) increases with increased P or decreased T (more ordered membrane). ...
... Top: Na-K ATPase activity decreases at low T and at high P. Middle: DPH Anisotropy (polarization) increases with increased P or decreased T (more ordered membrane). ...
Human Genetics - Green Local Schools
... Blood functions principally as a vehicle with transports gases, metabolic waste products and hormones throughout the body. As blood passes through the lungs, oxygen molecules attach to the hemoglobin. As blood passes through the body’s tissues in capillary beds, the hemoglobin releases the oxygen. C ...
... Blood functions principally as a vehicle with transports gases, metabolic waste products and hormones throughout the body. As blood passes through the lungs, oxygen molecules attach to the hemoglobin. As blood passes through the body’s tissues in capillary beds, the hemoglobin releases the oxygen. C ...
Document
... number of chromosomes for that organism? A) 6 B) 12 C) 24 D) 24 pairs E) either 6 or 24, depending on the cell type 19) Haploid cells A) can result from meiosis. B) cannot be produced by mitosis. C) function as gametes or spores in sexually reproducing organisms. D) have one member of each pair of h ...
... number of chromosomes for that organism? A) 6 B) 12 C) 24 D) 24 pairs E) either 6 or 24, depending on the cell type 19) Haploid cells A) can result from meiosis. B) cannot be produced by mitosis. C) function as gametes or spores in sexually reproducing organisms. D) have one member of each pair of h ...
Chapter 9 – DNA-Based Information Technologies
... DNA • After a cloning vector and insert DNA have been joined in vitro, recombinant DNA is introduced into a host cell such as E. coli (transformation) • Only a small percentage of cells take up the DNA • Selection -cells are grown under conditions in which only transformed cells survive • Screening ...
... DNA • After a cloning vector and insert DNA have been joined in vitro, recombinant DNA is introduced into a host cell such as E. coli (transformation) • Only a small percentage of cells take up the DNA • Selection -cells are grown under conditions in which only transformed cells survive • Screening ...
1 Evolutionary Developmental Biology (Evo
... melanogaster, some Drosophila species have dark spots on their wings. The spots typically occur on males and are used for courting females. The development of the spots is controlled by expression of the yellow gene – a dark spot forms where yellow is expressed. Whether or not yellow is expressed in ...
... melanogaster, some Drosophila species have dark spots on their wings. The spots typically occur on males and are used for courting females. The development of the spots is controlled by expression of the yellow gene – a dark spot forms where yellow is expressed. Whether or not yellow is expressed in ...
Page 1 AP Biology TEST #5 - Chapters 11-14, 16
... B) regulator proteins; regulators C) repressor proteins; silencers D) Both a and b 48. DNA binding proteins A) have distinct three-dimensional structures that allow them to bind to the DNA. B) can be transcription factors. C) can help condense the DNA in the nucleus. D) All of the above 49. Chromati ...
... B) regulator proteins; regulators C) repressor proteins; silencers D) Both a and b 48. DNA binding proteins A) have distinct three-dimensional structures that allow them to bind to the DNA. B) can be transcription factors. C) can help condense the DNA in the nucleus. D) All of the above 49. Chromati ...
Biochemistry PPT - Effingham County Schools
... How do you build a cell? Start with water, add lots of small carboncontaining molecules and ……. ...
... How do you build a cell? Start with water, add lots of small carboncontaining molecules and ……. ...
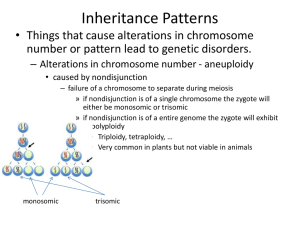
Inheritance Patterns - Santa Susana High School
... – non-homologous alterations • translocation – attachment of a deleted region from a non-homologous chromosome – reciprocal translocations occur when neighboring chromosomes cross over » gene number is conserved although gene dosing secondary to gene position may be affected – implicated in many ca ...
... – non-homologous alterations • translocation – attachment of a deleted region from a non-homologous chromosome – reciprocal translocations occur when neighboring chromosomes cross over » gene number is conserved although gene dosing secondary to gene position may be affected – implicated in many ca ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • GGU = • UAA = There are 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. So, different codons can code for the same amino acid. ...
... • GGU = • UAA = There are 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. So, different codons can code for the same amino acid. ...
Unit 7 packet pt 5
... Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with eight genes on it. Your job is to analyze the genes of its DNA and determine what tr ...
... Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with eight genes on it. Your job is to analyze the genes of its DNA and determine what tr ...
Everything you wanted to know about ENCODE
... Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter region together turn a gene on or off. These proteins are themselves regulated by their own promoters leading to a gene regulatory network with many of the same properties as a neural network. ...
... Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter region together turn a gene on or off. These proteins are themselves regulated by their own promoters leading to a gene regulatory network with many of the same properties as a neural network. ...
Biochemistry of Cells - Warren County Public Schools
... Side make proteins The process is called condensation or dehydration Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
... Side make proteins The process is called condensation or dehydration Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
Ch 14- 17 Unit Test - Akron Central Schools
... • During meiosis, a defect occurs in a cell that results in the failure of microtubules, spindle fibers, to bind at the kinetochores, a protein structure on chromatids where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. Which of the following is the most likely res ...
... • During meiosis, a defect occurs in a cell that results in the failure of microtubules, spindle fibers, to bind at the kinetochores, a protein structure on chromatids where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. Which of the following is the most likely res ...
Biology_Ch._14
... 3. different chromosomes have the same number of genes. 4. different chromosomes contain the same number of DNA bases. ...
... 3. different chromosomes have the same number of genes. 4. different chromosomes contain the same number of DNA bases. ...
Genetics 314 – Spring, 2005
... 3. You want to express the DNA sequence in bacteria. Your friend says you need to add additional sequences to get expression. What sequences do you need to add and what are they needed for to allow expression of the DNA sequence in bacteria? ...
... 3. You want to express the DNA sequence in bacteria. Your friend says you need to add additional sequences to get expression. What sequences do you need to add and what are they needed for to allow expression of the DNA sequence in bacteria? ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.