DNA Replication: Seeing Double
... the Leading and Lagging strands two complete strands of DNA separate from one another. ...
... the Leading and Lagging strands two complete strands of DNA separate from one another. ...
BIO105 Learning objectives for test 3 Topic: The Cell cycle and
... - In their own words, briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. - Distinguish between transcription and translation. - Describe where transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes; explain why it is significant that in eukaryotes, transcription and translatio ...
... - In their own words, briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. - Distinguish between transcription and translation. - Describe where transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes; explain why it is significant that in eukaryotes, transcription and translatio ...
Alyson Zwickera, Tess Robartsa, Purvi Trivedia, Rattina
... Glycosylation is the cellular process of enzymatic addition of sugars to protein, forming complex glycoproteins that are vital for cellular function. In the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), during the N-glycosylation process (see Figure 1), ALG9 also known as α1,2mannosyltransferase facilitates the addit ...
... Glycosylation is the cellular process of enzymatic addition of sugars to protein, forming complex glycoproteins that are vital for cellular function. In the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), during the N-glycosylation process (see Figure 1), ALG9 also known as α1,2mannosyltransferase facilitates the addit ...
THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... colorblind male and a female with normal vision have a son who is colorblind. What are the parents’ ...
... colorblind male and a female with normal vision have a son who is colorblind. What are the parents’ ...
human genetic potential and chiropractic
... Mutations that occur only in an egg or sperm cell, or those that occur just after fertilization, are called new (de novo) mutations. De novo mutations may explain genetic disorders in which an affected child has a mutation in every cell, but has no family history of the disorder. Acquired (or somati ...
... Mutations that occur only in an egg or sperm cell, or those that occur just after fertilization, are called new (de novo) mutations. De novo mutations may explain genetic disorders in which an affected child has a mutation in every cell, but has no family history of the disorder. Acquired (or somati ...
Lecture 2
... be identified was the per gene of Drosophila. Mammals have 3 per genes (per1, per2 and per3) that are closely related to the single per gene of Drosophila, and the mammalian per genes are also involved in circadian clock function. This is particularly surprising because the clocks of flies and mamma ...
... be identified was the per gene of Drosophila. Mammals have 3 per genes (per1, per2 and per3) that are closely related to the single per gene of Drosophila, and the mammalian per genes are also involved in circadian clock function. This is particularly surprising because the clocks of flies and mamma ...
File
... Chloramphenical: binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome and inhibits protein synthesis. Kanamycin and neomycin: are deoxystreptamine aminoglycosides that bind to ribosomal components and inhibit protein synthesis. ...
... Chloramphenical: binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome and inhibits protein synthesis. Kanamycin and neomycin: are deoxystreptamine aminoglycosides that bind to ribosomal components and inhibit protein synthesis. ...
Human Genetic Potential
... Mutations that occur only in an egg or sperm cell, or those that occur just after fertilization, are called new (de novo) mutations. De novo mutations may explain genetic disorders in which an affected child has a mutation in every cell, but has no family history of the disorder. Acquired (or somati ...
... Mutations that occur only in an egg or sperm cell, or those that occur just after fertilization, are called new (de novo) mutations. De novo mutations may explain genetic disorders in which an affected child has a mutation in every cell, but has no family history of the disorder. Acquired (or somati ...
Proteins: Primary Structure
... the term quaternary structure Describe the properties and functions of fibrous proteins ...
... the term quaternary structure Describe the properties and functions of fibrous proteins ...
File - Follett Science
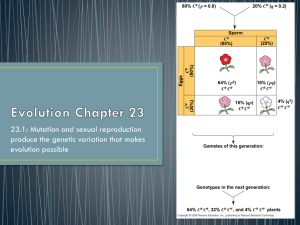
... • Sexual reproduction can shuffle existing alleles into new combinations • Sexual reproduction results in the recombination of alleles and is more important than mutation in producing the genetic differences • 3 mechanisms for shuffling of alleles: 1. Crossing over during prophase I of meiosis 2. I ...
... • Sexual reproduction can shuffle existing alleles into new combinations • Sexual reproduction results in the recombination of alleles and is more important than mutation in producing the genetic differences • 3 mechanisms for shuffling of alleles: 1. Crossing over during prophase I of meiosis 2. I ...
Exam 3 Key
... 31. Which statement describes the base pairing in nucleic acids? a. purine bases always pair with other purine bases b. purine bases only pair with pyrimidine bases * c. adenine cannot pair with either uracil of thymine d. hydrogen bonding can only occur between pyrimidines bases e. guanine pairs wi ...
... 31. Which statement describes the base pairing in nucleic acids? a. purine bases always pair with other purine bases b. purine bases only pair with pyrimidine bases * c. adenine cannot pair with either uracil of thymine d. hydrogen bonding can only occur between pyrimidines bases e. guanine pairs wi ...
DNA
... – the density of the studied particles should lie within the density range of the gradient. • The necessary density gradients are typically formed with sucrose ...
... – the density of the studied particles should lie within the density range of the gradient. • The necessary density gradients are typically formed with sucrose ...
Images
... Ionic Bonds • Atoms give up or take on electrons in order to achieve complete outer shell ...
... Ionic Bonds • Atoms give up or take on electrons in order to achieve complete outer shell ...
Section A: Eukaryotic Chromatin Structure
... amount of DNA relative to their condensed length. • Each human chromosome averages about 2 x 108 nucleotide pairs. • If extended, each DNA molecule would be about 6 cm long, thousands of times longer than the cell diameter. • This chromosome and 45 other human chromosomes fit into the nucleus. • Thi ...
... amount of DNA relative to their condensed length. • Each human chromosome averages about 2 x 108 nucleotide pairs. • If extended, each DNA molecule would be about 6 cm long, thousands of times longer than the cell diameter. • This chromosome and 45 other human chromosomes fit into the nucleus. • Thi ...
Nerve activates contraction
... amount of DNA relative to their condensed length. • Each human chromosome averages about 2 x 108 nucleotide pairs. • If extended, each DNA molecule would be about 6 cm long, thousands of times longer than the cell diameter. ...
... amount of DNA relative to their condensed length. • Each human chromosome averages about 2 x 108 nucleotide pairs. • If extended, each DNA molecule would be about 6 cm long, thousands of times longer than the cell diameter. ...
Your assignment is to label each scenario, as either Lamarck`s
... What Happened to the Dinosaurs? In “Sex, Drugs, Disasters, and the Extinction of the Dinosaurs,” Stephen Jay Gould puts forth three explanations from scientists to explain the demise of the dinosaurs: sex, drugs, and disaster. Your Assignment is to read the following explanations as to the demise o ...
... What Happened to the Dinosaurs? In “Sex, Drugs, Disasters, and the Extinction of the Dinosaurs,” Stephen Jay Gould puts forth three explanations from scientists to explain the demise of the dinosaurs: sex, drugs, and disaster. Your Assignment is to read the following explanations as to the demise o ...
Microbiology Babylon university 2nd stage pharmacy collage
... Restriction & Other Constraints on Gene Transfer Restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases) provide bacteria with a mechanism to distinguish between their own DNA and DNA from other biologic sources. These enzymes hydrolyze DNA at restriction sites determined by specific DNA sequences ranging f ...
... Restriction & Other Constraints on Gene Transfer Restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases) provide bacteria with a mechanism to distinguish between their own DNA and DNA from other biologic sources. These enzymes hydrolyze DNA at restriction sites determined by specific DNA sequences ranging f ...
DNA - NRF IR Repository
... up into different regions called genes. Products that the genes code for, which most often are proteins, are used to build features and initiate or regulate certain processes in the cell or tissue. So the genes determine how organisms are made, what they look like and all the processes that sustain ...
... up into different regions called genes. Products that the genes code for, which most often are proteins, are used to build features and initiate or regulate certain processes in the cell or tissue. So the genes determine how organisms are made, what they look like and all the processes that sustain ...
Fact Sheet 55|HUNTINGTON DISEASE In summary Huntington
... the huntingtin protein also becomes longer and this appears to interfere with its function, therefore a copy of the HTT gene with an expanded CAG repeat length can be considered faulty. The number of CAG repeats can increase when the HTT gene is passed from a parent to a child, this is known as anti ...
... the huntingtin protein also becomes longer and this appears to interfere with its function, therefore a copy of the HTT gene with an expanded CAG repeat length can be considered faulty. The number of CAG repeats can increase when the HTT gene is passed from a parent to a child, this is known as anti ...
Chapter 3
... A. shape and function arise from the primary structure B. Fibrous proteins have polypeptide chains organized as strands or sheets; they contribute to the shape, internal organization, and movement of cells. ...
... A. shape and function arise from the primary structure B. Fibrous proteins have polypeptide chains organized as strands or sheets; they contribute to the shape, internal organization, and movement of cells. ...
DNA 101 intro
... • One of two or more forms of a gene at a given position on a chromosome. They are caused by a difference in the sequence of DNA. • A gene which controls eye colour in humans may have two alternative forms – an allele that can produce blue eyes (b), and an allele that produces brown eyes (B). In a p ...
... • One of two or more forms of a gene at a given position on a chromosome. They are caused by a difference in the sequence of DNA. • A gene which controls eye colour in humans may have two alternative forms – an allele that can produce blue eyes (b), and an allele that produces brown eyes (B). In a p ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.