LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 The Central Nervous
... (1) Peduncles. The peduncles is a stemlike connecting part. The cerebellum is connected to the brainstem with three pairs of peduncles. (2) General shape and construction. A cross section of the cerebellum reveals that the outer cortex is composed of gray matter (cell bodies of neurons), with many f ...
... (1) Peduncles. The peduncles is a stemlike connecting part. The cerebellum is connected to the brainstem with three pairs of peduncles. (2) General shape and construction. A cross section of the cerebellum reveals that the outer cortex is composed of gray matter (cell bodies of neurons), with many f ...
Prescribing in the Elderly - Benton Franklin County Medical Society
... ↓ hepatic mass ↓ first-pass metabolism ↓ activation of prodrug ↑ bioavailability ...
... ↓ hepatic mass ↓ first-pass metabolism ↓ activation of prodrug ↑ bioavailability ...
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder What Happens in the Brain?
... are not. Instead we are billions of these things. So the signals have to ‘jump’ the gap between neurons.) The signaling process, not to put too fine a point on it, is sensitive, you see. Those neurons have to be well tuned before they can talk properly. Drugs, disease, moods, genetics all can affect ...
... are not. Instead we are billions of these things. So the signals have to ‘jump’ the gap between neurons.) The signaling process, not to put too fine a point on it, is sensitive, you see. Those neurons have to be well tuned before they can talk properly. Drugs, disease, moods, genetics all can affect ...
PharmII Block I Handouts
... A. Sucralfate (Carafate ®) is aluminum sucrose sulfate. B. It is thought to polymerize and bind selectively to necrotic tissue, thereby creating a barrier between the gastric contents and the gastric mucosa. C. Sucralfate is very effective for treating duodenal ulcers, and also suppresses H. Pylori ...
... A. Sucralfate (Carafate ®) is aluminum sucrose sulfate. B. It is thought to polymerize and bind selectively to necrotic tissue, thereby creating a barrier between the gastric contents and the gastric mucosa. C. Sucralfate is very effective for treating duodenal ulcers, and also suppresses H. Pylori ...
1 CREATIVE DEMONSTRATIVE EVIDENCE: “ADDING THE MIDAS
... any acceleration and deceleration in a traumatic event. The physician can explain that the skull is rigid but the brain has the consistency of Jell-O. With the aid of a model it is much easier to explain how any rapid changes in the direction of the movement of the skull and brain can cause the str ...
... any acceleration and deceleration in a traumatic event. The physician can explain that the skull is rigid but the brain has the consistency of Jell-O. With the aid of a model it is much easier to explain how any rapid changes in the direction of the movement of the skull and brain can cause the str ...
Pfenninger: Erectile dysfunction common
... severe ED. For those taking zero to two drugs, it was a 16 percent; for three to five drugs, 20 percent; six to nine drugs, 26 percent; and 10 or more drugs, 31 percent. After adjusting for all their other medical problems, men taking ten medications were twice as likely to have ED than men taking o ...
... severe ED. For those taking zero to two drugs, it was a 16 percent; for three to five drugs, 20 percent; six to nine drugs, 26 percent; and 10 or more drugs, 31 percent. After adjusting for all their other medical problems, men taking ten medications were twice as likely to have ED than men taking o ...
Darwin VII after - Ohio University
... Notice that the "Retina" is picking up the visual markings on the blocks. Like the real retina, it only picks up colors and "pixel" locations. A brain-based robot, with video cameras for eyes, a microphone for ears, a grasper hand, and the ability to detect "tastes" from the electrical conductiviey ...
... Notice that the "Retina" is picking up the visual markings on the blocks. Like the real retina, it only picks up colors and "pixel" locations. A brain-based robot, with video cameras for eyes, a microphone for ears, a grasper hand, and the ability to detect "tastes" from the electrical conductiviey ...
The Drug development process
... • Furthermore, not all patients respond positively to a specific drug (e.g. IFN-β is of clinical benefit to only one in three multiple sclerosis patients. • The range and severity of adverse effects induced by a drug can also vary significantly within a patient population base, genetic variation amo ...
... • Furthermore, not all patients respond positively to a specific drug (e.g. IFN-β is of clinical benefit to only one in three multiple sclerosis patients. • The range and severity of adverse effects induced by a drug can also vary significantly within a patient population base, genetic variation amo ...
From Neurons to Brain: Adaptive Self
... structure of a brain. The alternative extreme explanation, of total randomness, could not be correct as well. After all, we know that while on the micro level (up to about 1mm) the structure appears to be random, on the macro level (above 1cm) the brain’s structure is quite deterministic. In additio ...
... structure of a brain. The alternative extreme explanation, of total randomness, could not be correct as well. After all, we know that while on the micro level (up to about 1mm) the structure appears to be random, on the macro level (above 1cm) the brain’s structure is quite deterministic. In additio ...
Test bank module 3 4 5 6 11 12
... A) a cell that serves as the basic building block of the nervous system. B) a layer of fatty tissue that encases the fibers of many neurons. C) an antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites. D) the extension of a neuron that carries messages away from the cell body. 8. The longe ...
... A) a cell that serves as the basic building block of the nervous system. B) a layer of fatty tissue that encases the fibers of many neurons. C) an antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites. D) the extension of a neuron that carries messages away from the cell body. 8. The longe ...
cns – antiepileptic drugs
... movement, falls to the floor, temporary loss of consciousness, which he regains immediately. The type of seizure demonstrated by this patient and that the nurse documents is: a. atonic seizure b. myoclonic seizure c. complex partial seizure with automatisms d. generalized seizure ...
... movement, falls to the floor, temporary loss of consciousness, which he regains immediately. The type of seizure demonstrated by this patient and that the nurse documents is: a. atonic seizure b. myoclonic seizure c. complex partial seizure with automatisms d. generalized seizure ...
Temporal Cortex
... area TE of inferior temporal cortex by manipulating visual stimuli. The color codes are used to correlate activation spots (left panel) and the stimuli evoked the activation patterns (Right panel). (Adapted from Tsunoda, Yamane, Nishizaki, and Tanifuji Nature Neuroscience 2001). ...
... area TE of inferior temporal cortex by manipulating visual stimuli. The color codes are used to correlate activation spots (left panel) and the stimuli evoked the activation patterns (Right panel). (Adapted from Tsunoda, Yamane, Nishizaki, and Tanifuji Nature Neuroscience 2001). ...
Neuron Function
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
Evolution of the Nervous System
... Conduction of a nerve impulse is an all-ornothing event Intensity of signal is determined by how many impulses are generated within a given time span ...
... Conduction of a nerve impulse is an all-ornothing event Intensity of signal is determined by how many impulses are generated within a given time span ...
Drugs and Treatments (1)
... • Effective on scaled fish, but can cause problems with scaleless fish (catfish). • Can produce kidney necrosis, destruction of hematopoietic tissue, increased liver fat and inhibition of digestive enzymes. ...
... • Effective on scaled fish, but can cause problems with scaleless fish (catfish). • Can produce kidney necrosis, destruction of hematopoietic tissue, increased liver fat and inhibition of digestive enzymes. ...
Evolution of the Nervous System
... Conduction of a nerve impulse is an all-ornothing event Intensity of signal is determined by how many impulses are generated within a given time span ...
... Conduction of a nerve impulse is an all-ornothing event Intensity of signal is determined by how many impulses are generated within a given time span ...
Script - Making Neuroscience Fun
... Your nervous system is connected to every part of your body. It is what makes your body work. Your brain helps you to do all of the behaviors that you do. The brains most important job is helping to keep you alive – as an animal and as part of a species. There is so much to know about the nervous sy ...
... Your nervous system is connected to every part of your body. It is what makes your body work. Your brain helps you to do all of the behaviors that you do. The brains most important job is helping to keep you alive – as an animal and as part of a species. There is so much to know about the nervous sy ...
Substance Related Disorders
... • In the substance use disorder chapter the biggest change from the dependence and abuse diagnosis is the move to Mild, Moderate, and Severe. To determine the severity of the disorder, a criteria 1-11 has been established. • The presence of 2-3 symptoms out of the 11 is defined as Mild. • The presen ...
... • In the substance use disorder chapter the biggest change from the dependence and abuse diagnosis is the move to Mild, Moderate, and Severe. To determine the severity of the disorder, a criteria 1-11 has been established. • The presence of 2-3 symptoms out of the 11 is defined as Mild. • The presen ...
Course Outline Template Word Document
... Upon completion of this course with 75% proficiency, the student will be able to: 1. Describe general pharmacological principles including the history and development of drugs, pharmokinetics, pharmodynamics, and routes of administration. 2. The student will identify bronchodilator medications; list ...
... Upon completion of this course with 75% proficiency, the student will be able to: 1. Describe general pharmacological principles including the history and development of drugs, pharmokinetics, pharmodynamics, and routes of administration. 2. The student will identify bronchodilator medications; list ...
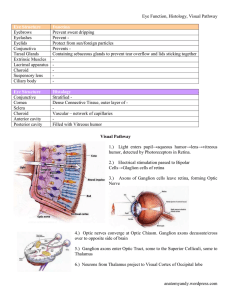
Eye Structure - WordPress.com
... Prevent Protect from sun/foreign particles Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
... Prevent Protect from sun/foreign particles Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
Program booklet - Munich Center for NeuroSciences
... members like p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) have been shown to undergo a regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) process. RIP is an elegant way for cells to transduce signals or simply to quickly remove proteins from the cell surface. It is a tightly regulated mechanism fundamental for key bio ...
... members like p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) have been shown to undergo a regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) process. RIP is an elegant way for cells to transduce signals or simply to quickly remove proteins from the cell surface. It is a tightly regulated mechanism fundamental for key bio ...
Document
... Problems of Muscle Activation • Muscle activation muscle force is nonlinear problem • Primary motor cortex drives motor activation – Depends on force, muscle length, limb geometry, orientation of limb relative to external forces, and inertia of moving segments ...
... Problems of Muscle Activation • Muscle activation muscle force is nonlinear problem • Primary motor cortex drives motor activation – Depends on force, muscle length, limb geometry, orientation of limb relative to external forces, and inertia of moving segments ...
Nervous System Diseases
... • Characterized by headache, neck stiffness, fever, confusion or altered mental state • Inability to tolerate light and loud noises • Life threatening! ...
... • Characterized by headache, neck stiffness, fever, confusion or altered mental state • Inability to tolerate light and loud noises • Life threatening! ...
Basic Anatomy and Terminology of the Head and Brain Scalp and
... The largest area of the brain is the cerebrum. It is the large, outer part of the brain, the part that you think of when you picture the brain. The cerebrum is divided into two halves or cerebral hemispheres. Each cerebral hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body. The surfaces of the cerebr ...
... The largest area of the brain is the cerebrum. It is the large, outer part of the brain, the part that you think of when you picture the brain. The cerebrum is divided into two halves or cerebral hemispheres. Each cerebral hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body. The surfaces of the cerebr ...
The Neuron - Austin Community College
... Dopamine - plays a role in motor coordination Norepinephrine - released in sympathetic synapses controlling smooth and cardiac muscle, and glands. Serotonin - involved in temperature regulation, sensory perception, and emotion, induces sleep. Neurtotransmitters must be removed from the synaptic clef ...
... Dopamine - plays a role in motor coordination Norepinephrine - released in sympathetic synapses controlling smooth and cardiac muscle, and glands. Serotonin - involved in temperature regulation, sensory perception, and emotion, induces sleep. Neurtotransmitters must be removed from the synaptic clef ...