CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... The impulse reaches axonal terminal of presynaptic neuron causing depolarization of axonal terminal/synaptic knob. Ca2+ channels open and calcium ions rush into axonal terminal causing synaptic vesicles (filled with neurotransmitter/NT) to release NT via exocytosis into the synaptic cleft. NT diffus ...
... The impulse reaches axonal terminal of presynaptic neuron causing depolarization of axonal terminal/synaptic knob. Ca2+ channels open and calcium ions rush into axonal terminal causing synaptic vesicles (filled with neurotransmitter/NT) to release NT via exocytosis into the synaptic cleft. NT diffus ...
PDF
... (CCQ, MS, GD), Division of Neuroscience (GD), Program in Developmental Biology (GD), The Cain Foundation Laboratories (CCQ, GD), Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas; Program in Neuroscience (CCQ), Universite degli Studi di Brescie, Brescie, Italy; Department of Molecular Neurobiology (KM), In ...
... (CCQ, MS, GD), Division of Neuroscience (GD), Program in Developmental Biology (GD), The Cain Foundation Laboratories (CCQ, GD), Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas; Program in Neuroscience (CCQ), Universite degli Studi di Brescie, Brescie, Italy; Department of Molecular Neurobiology (KM), In ...
L6Development
... • Normal healthy adults (even in the absence of disease) show age-related differences in performance on many cognitive tasks – Working memory – Episodic memory – Prospective memory – Executive functions ...
... • Normal healthy adults (even in the absence of disease) show age-related differences in performance on many cognitive tasks – Working memory – Episodic memory – Prospective memory – Executive functions ...
Nervous from Cyber
... branchlets called telodendria which end in a small bulbous end called the synaptic knob. Synaptic knobs relay messages to other cells via neurotransmitters. Between the synaptic knobs are gaps called synapses. In the body cells usually carry a negative charge. Nervous cells are able to alter their c ...
... branchlets called telodendria which end in a small bulbous end called the synaptic knob. Synaptic knobs relay messages to other cells via neurotransmitters. Between the synaptic knobs are gaps called synapses. In the body cells usually carry a negative charge. Nervous cells are able to alter their c ...
Pathways - Orange Coast College
... Control highly variable and complex voluntary motor patterns. Occupy the highest level of processing and motor control. Motor commands may be conducted to specific motor neurons directly. May be conveyed indirectly by altering the activity of a reflex control center. ...
... Control highly variable and complex voluntary motor patterns. Occupy the highest level of processing and motor control. Motor commands may be conducted to specific motor neurons directly. May be conveyed indirectly by altering the activity of a reflex control center. ...
32. Sensory organs. organ of smell and taste
... The organs of taste & smell Taste (the tongue): • It is mainly composed of muscles • It is covered with a mucous membrane • Small nodules of tissue (papillae) cover the upper surface of the tongue • Between the papillae are the taste buds, which provide the sense of taste. ...
... The organs of taste & smell Taste (the tongue): • It is mainly composed of muscles • It is covered with a mucous membrane • Small nodules of tissue (papillae) cover the upper surface of the tongue • Between the papillae are the taste buds, which provide the sense of taste. ...
Neurulation and Ectoderm
... • Fine outgrowth, receptors During 1st year after birth, enough dendrites form to make 100,000 connections for each cortical neuron • Average cortical neuron connects to 10,000 other neural cells Axons • Long extension of cell body, carry impulse away from cell body • Forms as outgrowth of cell • El ...
... • Fine outgrowth, receptors During 1st year after birth, enough dendrites form to make 100,000 connections for each cortical neuron • Average cortical neuron connects to 10,000 other neural cells Axons • Long extension of cell body, carry impulse away from cell body • Forms as outgrowth of cell • El ...
5. Electrical Signals
... enclosed in the spine and connected to the brain, with which it forms the central nervous system) • Central nervous system (CNS): system of the body that includes the brain and spinal cord. • Sensory nerve cells: (nerves that receive sensory stimuli, such as how something feels and if it is painful) ...
... enclosed in the spine and connected to the brain, with which it forms the central nervous system) • Central nervous system (CNS): system of the body that includes the brain and spinal cord. • Sensory nerve cells: (nerves that receive sensory stimuli, such as how something feels and if it is painful) ...
Somatosensory system.
... those of peripheral neurons, but the RFs are larger than those of dorsal root ganglion cells and are commonly concentric, with a central excitatory area and a surrounding inhibitory area ...
... those of peripheral neurons, but the RFs are larger than those of dorsal root ganglion cells and are commonly concentric, with a central excitatory area and a surrounding inhibitory area ...
The Nervous System - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... connect the CNS to organs and other structures such as the heart, stomach, intestines, glands, blood vessels, and bladder (among others) “involuntary” nervous system. ...
... connect the CNS to organs and other structures such as the heart, stomach, intestines, glands, blood vessels, and bladder (among others) “involuntary” nervous system. ...
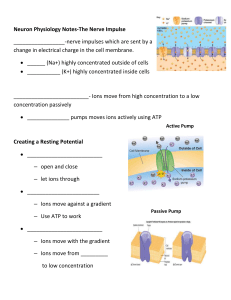
Neuron Physiology Notes
... by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters the neuron to change the potential to (-55mv) which causes “trigger zone” to allow even more sodium into the neuron. ...
... by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters the neuron to change the potential to (-55mv) which causes “trigger zone” to allow even more sodium into the neuron. ...
This Week at Elida - Elida Local Schools
... and controlling impulses is influenced by the sorts of experiences young people have, including their experiences in the classroom. Given the well-documented finding that practicing something will strengthen the brain circuits that control that behavior, it's important that, as educators, we provide ...
... and controlling impulses is influenced by the sorts of experiences young people have, including their experiences in the classroom. Given the well-documented finding that practicing something will strengthen the brain circuits that control that behavior, it's important that, as educators, we provide ...
Company Core Data Sheets (CCDS)
... Hyperprolactinaemia may be physiological (pregnancy, lactation) as well as be due to other causes among others tumours in hypothalamus or pituitary gland and a number of drugs. Therefore it is important that the specific cause to a hyperprolactinaemia is explained as far as possible and that causal ...
... Hyperprolactinaemia may be physiological (pregnancy, lactation) as well as be due to other causes among others tumours in hypothalamus or pituitary gland and a number of drugs. Therefore it is important that the specific cause to a hyperprolactinaemia is explained as far as possible and that causal ...
Mapping Neural Diversity: A Molecular Analysis of
... does that mean and what are the implications? BT: When working with our bioinformaticians, I wanted to be able to examine the gene expression signatures we obtained for our cell types, and then ask how well they matched any of those types for every cell. That examination, which uses a repetitive mac ...
... does that mean and what are the implications? BT: When working with our bioinformaticians, I wanted to be able to examine the gene expression signatures we obtained for our cell types, and then ask how well they matched any of those types for every cell. That examination, which uses a repetitive mac ...
ii. neuro-embryology
... Making Neuronal Connections: o Sometimes a neuron will reel out its axon as it grows. o At other times, a neuron will use physical or chemical (chemotaxis) cues to grow toward a target. Synaptic Plasticity: Modifications to neuronal connections made after development is complete. o They can be m ...
... Making Neuronal Connections: o Sometimes a neuron will reel out its axon as it grows. o At other times, a neuron will use physical or chemical (chemotaxis) cues to grow toward a target. Synaptic Plasticity: Modifications to neuronal connections made after development is complete. o They can be m ...
EpiTan in Collaboration to Develop Sustained Release Form of
... it has the added benefit that it does not affect normal healthy tissue.” Mr. Clark said, “Our plans with the new antibody project are to proceed through latter stage pre-clinical development, commencing the first tests on humans in 18 months.” Monoclonal antibodies can be genetically reengineered (h ...
... it has the added benefit that it does not affect normal healthy tissue.” Mr. Clark said, “Our plans with the new antibody project are to proceed through latter stage pre-clinical development, commencing the first tests on humans in 18 months.” Monoclonal antibodies can be genetically reengineered (h ...
Major lobes - Ohio University
... of elements from a large set of possibilities – usually realized in a descriptive way with the help of systems of rules and symbols. Models postulating central processes: like in a computer, working memory with a central monitor, having influence over many areas. Here: emergent processes, the result ...
... of elements from a large set of possibilities – usually realized in a descriptive way with the help of systems of rules and symbols. Models postulating central processes: like in a computer, working memory with a central monitor, having influence over many areas. Here: emergent processes, the result ...
ALTERATIONS IN NEUROLOGIC FUNCTION
... may produce a diminished or altered state of consciousness can also result in the disturbance of behavioral or emotional functioning may be either temporary or permanent and cause partial or total functional disability or psychosocial maladjustment ...
... may produce a diminished or altered state of consciousness can also result in the disturbance of behavioral or emotional functioning may be either temporary or permanent and cause partial or total functional disability or psychosocial maladjustment ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... • Phantom: occurs in people who have appendage amputated or structure removed such as a tooth. Gate control theory of pain-- in uninjured limb, pressure and touch sensation inhibits pain (thus the success of massage in pain relief). These sensations are lost with amputations and thus their inhibitor ...
... • Phantom: occurs in people who have appendage amputated or structure removed such as a tooth. Gate control theory of pain-- in uninjured limb, pressure and touch sensation inhibits pain (thus the success of massage in pain relief). These sensations are lost with amputations and thus their inhibitor ...
Powerpoint Presentation Toxicology Lecture
... explain how toxic potential of a drug can be quantified using a variety of methods ...
... explain how toxic potential of a drug can be quantified using a variety of methods ...
McCulloch-Pitts Neuron
... The activation of a McCulloch Pitts neuron is binary. Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the path is positive else its inhibitory. All excitatory connections to a neuron have the same weights. Each neuron has a fixed threshold: f(n) = ...
... The activation of a McCulloch Pitts neuron is binary. Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the path is positive else its inhibitory. All excitatory connections to a neuron have the same weights. Each neuron has a fixed threshold: f(n) = ...