Chapter 3 Neurons powerpoints
... Action potentials do not vary in intensity, either within the same neuron at different times or across different neurons Information is conveyed by the number and frequency of action potentials The information conveyed by an action potential depends on the pathway it is a part of. The image of ...
... Action potentials do not vary in intensity, either within the same neuron at different times or across different neurons Information is conveyed by the number and frequency of action potentials The information conveyed by an action potential depends on the pathway it is a part of. The image of ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
Abstract
... even consciousness are thought to be realized through complex interactions of streams of millisecond-order electrical spikes (known as action potentials) generated by billions of neurons. How can one investigate such a complicated organ? As action potentials are electric signals mediated by flows of ...
... even consciousness are thought to be realized through complex interactions of streams of millisecond-order electrical spikes (known as action potentials) generated by billions of neurons. How can one investigate such a complicated organ? As action potentials are electric signals mediated by flows of ...
Neurotox I
... Cl. tetani produces 70,000 KDa protein called tetanospasmin Blocks inhibitory synaptic input on spinal motor neurons, resulting in spastic paralysis. moved through nerve cells via retrograde axonal transport until it binds, or is fixed, to gangliosides in the brain stem or cord. Ricin also retrograd ...
... Cl. tetani produces 70,000 KDa protein called tetanospasmin Blocks inhibitory synaptic input on spinal motor neurons, resulting in spastic paralysis. moved through nerve cells via retrograde axonal transport until it binds, or is fixed, to gangliosides in the brain stem or cord. Ricin also retrograd ...
Nervous System - Crossword Labs
... membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All neural tissue outside CNS 20. cytoplasm of axon 21. Cell that receives message 22. carries action potential to target 24. Cells with highly branched processes; contact neuroglia directly 25. Ne ...
... membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All neural tissue outside CNS 20. cytoplasm of axon 21. Cell that receives message 22. carries action potential to target 24. Cells with highly branched processes; contact neuroglia directly 25. Ne ...
Chemical transmission and drug action in the central nervous
... such as hallucinations and delusions, and usually allow the patient to function more effectively and appropriately. patients vary a great deal in the amount of drug needed to reduce symptoms without producing troublesome side effects. ...
... such as hallucinations and delusions, and usually allow the patient to function more effectively and appropriately. patients vary a great deal in the amount of drug needed to reduce symptoms without producing troublesome side effects. ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... 2. Humanistic psychologists focused attention on the importance of people's: a) potential for healthy growth. b) unconscious thought processes. c) childhood memories. d) genetic predispositions. 3. Cognitive neuroscience studies relationships between: a) childhood memories and psychological disorder ...
... 2. Humanistic psychologists focused attention on the importance of people's: a) potential for healthy growth. b) unconscious thought processes. c) childhood memories. d) genetic predispositions. 3. Cognitive neuroscience studies relationships between: a) childhood memories and psychological disorder ...
Psychoactive Drugs
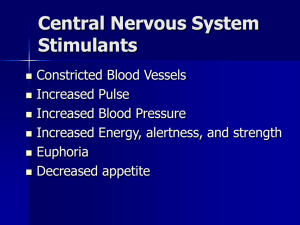
... increase the release, and decrease the removal, of norepinephrine and dopamine at synapses, resulting in increased receptor activity. Amphetamines stimulate the brain and sympathetic nervous system, raising heart rate and blood pressure and constricting blood vessels. In some extreme cases, abuse of ...
... increase the release, and decrease the removal, of norepinephrine and dopamine at synapses, resulting in increased receptor activity. Amphetamines stimulate the brain and sympathetic nervous system, raising heart rate and blood pressure and constricting blood vessels. In some extreme cases, abuse of ...
Understanding the Basics of Pharmacology
... diminishes by one half Loading dose: larger dose given rapidly to reach therapeutic level quickly ...
... diminishes by one half Loading dose: larger dose given rapidly to reach therapeutic level quickly ...
Chapter 5 Quantitative and Thought Questions 5.1 Patient A`s drug
... of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Therefore, the drug must be acting at a point beyond this kinase (e.g., at the level of the phosphorylated protein mediating this response). 5.4 Not in most cells, because there are other physiological mechanisms by which signals impinging on the cell can increase c ...
... of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Therefore, the drug must be acting at a point beyond this kinase (e.g., at the level of the phosphorylated protein mediating this response). 5.4 Not in most cells, because there are other physiological mechanisms by which signals impinging on the cell can increase c ...
WHY STUDY ADDICTION IN AP PSYCHOLOGY?
... previously brought them pleasure. Now, they need to take drugs just to try and bring their dopamine function back up to normal. And, they must take larger amounts of the drug than they first did to create the dopamine high—an ...
... previously brought them pleasure. Now, they need to take drugs just to try and bring their dopamine function back up to normal. And, they must take larger amounts of the drug than they first did to create the dopamine high—an ...
SNARE molecules at the trans-Golgi network and endosome and their roles in neuronal growth and axonal transport.
... Polarized membrane traffic to different domains of the neuron is well documented, and is required for both establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. Some soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins, which are key components of the eukaryotic membr ...
... Polarized membrane traffic to different domains of the neuron is well documented, and is required for both establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. Some soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins, which are key components of the eukaryotic membr ...
Nervous Systems
... Voltage-gated Na+ channel = CLOSED Nerve impulse: stimulus causes a change in membrane potential Action potential: neuron membrane depolarizes All-or-nothing response ...
... Voltage-gated Na+ channel = CLOSED Nerve impulse: stimulus causes a change in membrane potential Action potential: neuron membrane depolarizes All-or-nothing response ...
Neurotransmitters
... Serotonin (excitatory and inhibitory) o Serotonin has been found to be intimately involved in emotion and mood. o Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, problems with anger control, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. o Too little also leads to an increased appetite for ...
... Serotonin (excitatory and inhibitory) o Serotonin has been found to be intimately involved in emotion and mood. o Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, problems with anger control, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. o Too little also leads to an increased appetite for ...
Week Three Slides
... Acts on cell body in VTA to increase number of action potentials Also binds to receptors on axon terminals in nucleus accumbens to release more dopamine with each action potential ...
... Acts on cell body in VTA to increase number of action potentials Also binds to receptors on axon terminals in nucleus accumbens to release more dopamine with each action potential ...
Serotonin (5-HT) - Addiction Science Network
... Mimics 5HT at 5HT1A autoreceptors on raphe cell bodies, slows firing rate of serotonergic neurons Current theories focus on glutamate release in thalamocortical terminals, causing dissociation between sensory relay and cortical output ...
... Mimics 5HT at 5HT1A autoreceptors on raphe cell bodies, slows firing rate of serotonergic neurons Current theories focus on glutamate release in thalamocortical terminals, causing dissociation between sensory relay and cortical output ...
Fiche UE 5BN08 Ouverture en Neurosciences
... psychoactive drugs, that have behavioral consequences. Drugs tolerance, sensitization and dependency will be analyzed in light of the most recent molecular and cellular data, particularly on the functional plasticity mechanisms that are associated in the CNS to these phenomena. ...
... psychoactive drugs, that have behavioral consequences. Drugs tolerance, sensitization and dependency will be analyzed in light of the most recent molecular and cellular data, particularly on the functional plasticity mechanisms that are associated in the CNS to these phenomena. ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Drug use triggers changes in brain chemistry producing changes in behavior (physically, mentally, emotionally) ...
... 1. Drug use triggers changes in brain chemistry producing changes in behavior (physically, mentally, emotionally) ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...