The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions
... Benzodiazepines potentiate GABA-induced responses ...
... Benzodiazepines potentiate GABA-induced responses ...
Drugslides
... Existence of a drug can lead to discovery of a mechanism (e.g., opiates, salicylates, chlorpromazine). The majority of psychoactive drugs affect synaptic transmission. Drugs can have synergystic (combinatorial) interactions with other drugs. (Some may be good, many are bad) Many drugs have side effe ...
... Existence of a drug can lead to discovery of a mechanism (e.g., opiates, salicylates, chlorpromazine). The majority of psychoactive drugs affect synaptic transmission. Drugs can have synergystic (combinatorial) interactions with other drugs. (Some may be good, many are bad) Many drugs have side effe ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... presynaptic neuron used to synthesize more neurotransmitter ex: acetylcholine (Ach) split by enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
... presynaptic neuron used to synthesize more neurotransmitter ex: acetylcholine (Ach) split by enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
Biomedical
... - triggers widespread firing of the neurons—convulsions - these convulsions produce many changes in the central and peripheral nervous system - early on patients might receive 100s of treatments, now a patient would receive 12 or less treatments - for serious depression…when drug therapy has not wor ...
... - triggers widespread firing of the neurons—convulsions - these convulsions produce many changes in the central and peripheral nervous system - early on patients might receive 100s of treatments, now a patient would receive 12 or less treatments - for serious depression…when drug therapy has not wor ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
Document
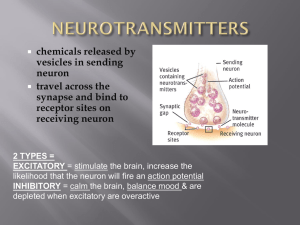
... receptors on the receiving neurons their effect may be either excitatory (making the cell more likely to fire) or inhibitory (making the cell less likely to fire). • Neurotransmitters that are not accepted by the receptor sites must be removed from the synapse in order for the next potential stimula ...
... receptors on the receiving neurons their effect may be either excitatory (making the cell more likely to fire) or inhibitory (making the cell less likely to fire). • Neurotransmitters that are not accepted by the receptor sites must be removed from the synapse in order for the next potential stimula ...
neurons
... nuts (ie walnuts, almonds), tofu, milk, eggs, certain cheeses, turkey, seafood, seeds ...
... nuts (ie walnuts, almonds), tofu, milk, eggs, certain cheeses, turkey, seafood, seeds ...
IMS-P21 Discovery of ASP5736, a Novel 5
... The 5-HT5A receptor is a G-protein-coupled seven-transmembrane receptor and expresses predominantly in neural tissues such as hippocampus, thalamus, amygdala and cerebral cortex with little expression in peripheral tissues. 5-HT5A KO mice were reported to show increased exploratory activity in respo ...
... The 5-HT5A receptor is a G-protein-coupled seven-transmembrane receptor and expresses predominantly in neural tissues such as hippocampus, thalamus, amygdala and cerebral cortex with little expression in peripheral tissues. 5-HT5A KO mice were reported to show increased exploratory activity in respo ...
`synapse`.
... Interaction of NT and protein receptor open post-synaptic membrane ion channel for Na+ After transmission the NT is either degraded by an enzyme or taken back into the pre-synaptic membrane by a transporter or reuptake pump ...
... Interaction of NT and protein receptor open post-synaptic membrane ion channel for Na+ After transmission the NT is either degraded by an enzyme or taken back into the pre-synaptic membrane by a transporter or reuptake pump ...
mechanisms for activation and inactivation of endorphins
... The concept that the population of receptor sites for the enkephalins and endorphins is heterogeneous, is based on the following experimental approaches. When the peptides are assayed in two pharmacological and two binding models, the rank order of activity differs in the four systems. The antagonis ...
... The concept that the population of receptor sites for the enkephalins and endorphins is heterogeneous, is based on the following experimental approaches. When the peptides are assayed in two pharmacological and two binding models, the rank order of activity differs in the four systems. The antagonis ...
Document
... serotonin, acetylcholine, nitric oxide, and endorphins? Starting from an arriving action potential explain what happens at the synapse. Your answer should include the following terms (calcium, vesicle, neurotransmitter, exocytosis, diffusion, receptor, activation, inactivation, reuptake, transporter ...
... serotonin, acetylcholine, nitric oxide, and endorphins? Starting from an arriving action potential explain what happens at the synapse. Your answer should include the following terms (calcium, vesicle, neurotransmitter, exocytosis, diffusion, receptor, activation, inactivation, reuptake, transporter ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
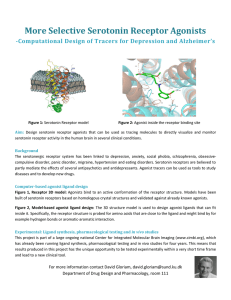
More Selective Serotonin Receptor Agonists
... Aim: Design serotonin receptor agonists that can be used as tracing molecules to directly visualize and monitor serotonin receptor activity in the human brain in several clinical conditions. Background The serotonergic receptor system has been linked to depression, anxiety, social phobia, schizophre ...
... Aim: Design serotonin receptor agonists that can be used as tracing molecules to directly visualize and monitor serotonin receptor activity in the human brain in several clinical conditions. Background The serotonergic receptor system has been linked to depression, anxiety, social phobia, schizophre ...
Synaptic Transmission
... Alzheimer’s Disease • Deterioration of memory, reasoning, and language skills • Low levels of Ach found in those with Alzheimer’s disease ...
... Alzheimer’s Disease • Deterioration of memory, reasoning, and language skills • Low levels of Ach found in those with Alzheimer’s disease ...
Synaptic Transmission - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... Alzheimer’s Disease • Deterioration of memory, reasoning, and language skills • Low levels of Ach found in those with Alzheimer’s disease ...
... Alzheimer’s Disease • Deterioration of memory, reasoning, and language skills • Low levels of Ach found in those with Alzheimer’s disease ...
Module 9: Synaptic Transmission
... neurons in the substantia nigra • Symptoms include – difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements – tremors at rest – stooped posture – rigidity – poor balance ...
... neurons in the substantia nigra • Symptoms include – difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements – tremors at rest – stooped posture – rigidity – poor balance ...
Psychoactive drugs • Drugs which affect mental processes • May be
... • A 4th way in which psychoactive drugs can affect brain functioning: involves disruption of the mechanisms by which neurotransmitters are deactivated • Neurotransmitters normally have only limited period of time to bind to receptors • Shortly after being released • will either be broken down by en ...
... • A 4th way in which psychoactive drugs can affect brain functioning: involves disruption of the mechanisms by which neurotransmitters are deactivated • Neurotransmitters normally have only limited period of time to bind to receptors • Shortly after being released • will either be broken down by en ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
Cellular and Molecul..
... transduce intracellular signals by coupling to GTP-binding proteins • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
... transduce intracellular signals by coupling to GTP-binding proteins • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
Types of neurons - Brigham Young University
... Some Drugs work on receptors Some drugs are shaped like neurotransmitters Antagonists : fit the receptor but poorly and block the NT e.g. beta blockers ...
... Some Drugs work on receptors Some drugs are shaped like neurotransmitters Antagonists : fit the receptor but poorly and block the NT e.g. beta blockers ...
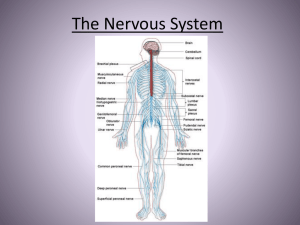
The Nervous System
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
Limbic system
... Hormones: chemical messengers released into the blood by glands Endocrine system: relating to hormones, their functions, and sources Neurons: specialized nerve cells that make up the nervous system and release transmitters ...
... Hormones: chemical messengers released into the blood by glands Endocrine system: relating to hormones, their functions, and sources Neurons: specialized nerve cells that make up the nervous system and release transmitters ...